金属离子代谢: 慢性肝病中医药防治新思路
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240732
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:郭新华、王佳慧负责课题设计,资料分析,撰写论文;段雪琳、彭岳、赵铁建参与查阅文献,整理数据,修改论文;郑洋、赵斌负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Metal ion metabolism: New ideas for the traditional Chinese medicine prevention and treatment of chronic liver disease
-
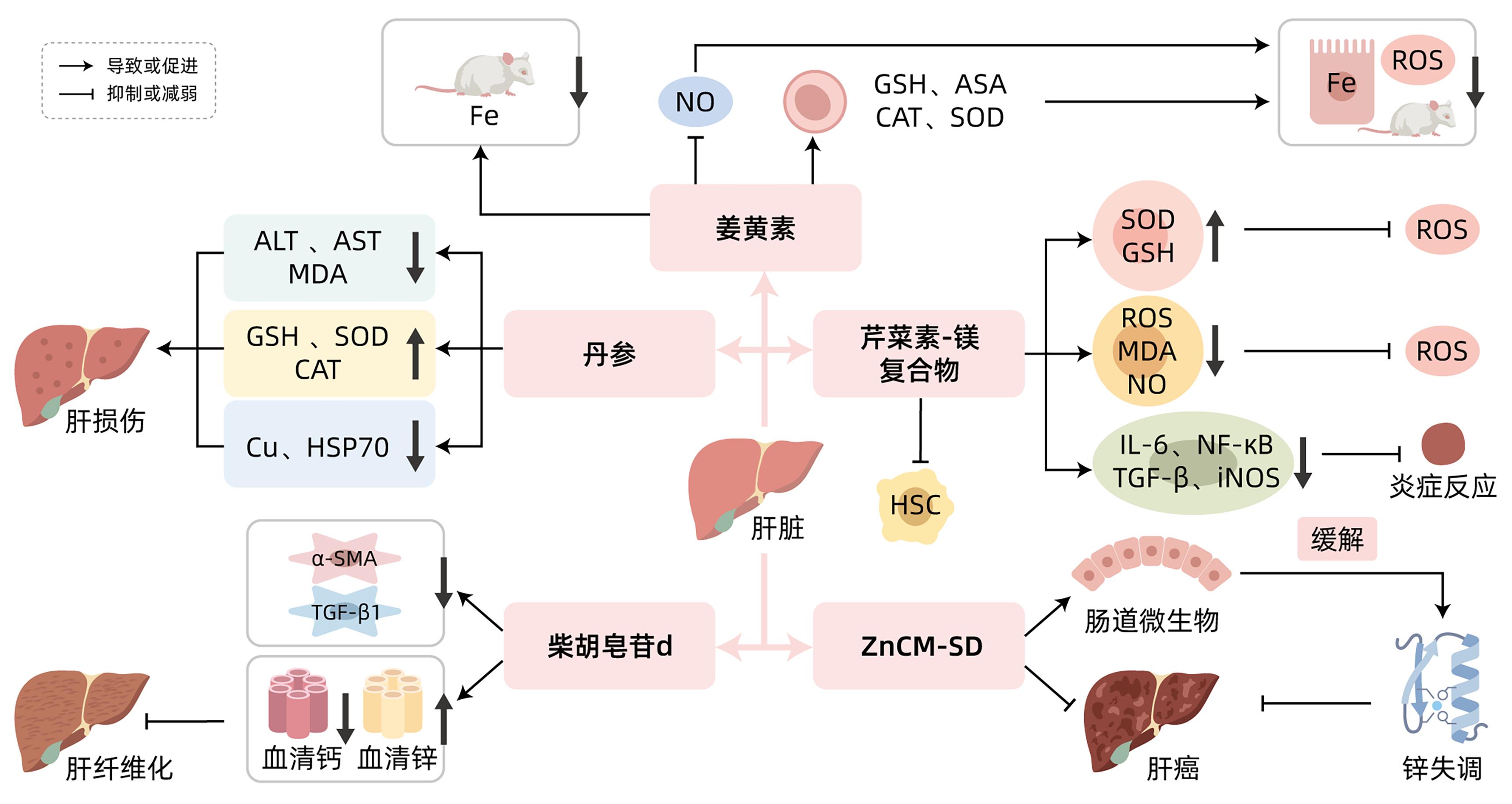
摘要: 慢性肝病具有较高的发病率,给社会和家庭带来沉重负担。研究发现金属离子代谢与慢性肝病密切相关,部分中草药可以通过调控金属离子代谢发挥防治慢性肝病的作用。目前用于治疗慢性肝病的合成药物疗效并不理想,因此多种中草药被用于慢性肝病的补充和替代疗法。本文介绍了金属离子代谢在慢性肝病中的作用和中草药及其活性成分对慢性肝病的调控作用,分析表明金属离子代谢有望为慢性肝病的研究提供新思路,为临床慢性肝病的治疗提供理论依据。对于金属离子代谢防治慢性肝病,未来还需要更多前瞻性临床研究数据,为慢性肝病患者提供有效、安全的治疗方案。Abstract: Chronic liver disease (CLD) tends to have a high incidence rate and impose a serious burden on society and families. Studies have shown that metal ion metabolism is closely associated with CLD, and some Chinese herbal medicines can play a role in the prevention and treatment of CLD by regulating metal ion metabolism. At present, the synthetic drugs currently used for the treatment of CLD fail to achieve a satisfactory effect, and therefore, a variety of Chinese herbal medicines are being used as supplementary and alternative therapies for CLD. This article introduces the role of metal ion metabolism in CLD and the regulatory effect of Chinese herbal medicines and their active components on CLD, and the analysis shows that metal ion metabolism is expected to provide new ideas for the research on CLD and a theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of CLD. For the role of metal ion metabolism in the treatment of CLD, more prospective clinical study data are needed in the future to provide effective and safe treatment regimens for patients with CLD.
-
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- Metal Ions /
- Drugs, Chinese Herbal
-
[1] RODRÍGUEZ MJ, SABAJ M, TOLOSA G, et al. Maresin-1 prevents liver fibrosis by targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 12): 3406. DOI: 10.3390/cells10123406. [2] WANG CY, BABITT JL. Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis[J]. Blood, 2019, 133( 1): 18- 29. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-06-815894. [3] LIU T, LIU YL, ZHANG FY, et al. Association of copper metabolism disorder with cell damage and liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 9): 2244- 2251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.032.柳涛, 刘雅丽, 张飞宇, 等. 铜代谢失调与细胞损伤及肝病的关系[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 9): 2244- 2251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.032. [4] HIMOTO T, MASAKI T. Associations between zinc deficiency and metabolic abnormalities in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10( 1): 88. DOI: 10.3390/nu10010088. [5] TIAN H, XIANG P, ZHOU WH, et al. Correlation between the physiological characteristics of magnesium and cirrhosis[J]. Hebei Med J, 2021, 43( 8): 1246- 1251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2021.08.029.田慧, 向平, 周卫华, 等. 镁离子的生理特点及与肝硬化的关系[J]. 河北医药, 2021, 43( 8): 1246- 1251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2021.08.029. [6] OLIVA-VILARNAU N, HANKEOVA S, VORRINK SU, et al. Calcium signaling in liver injury and regeneration[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2018, 5: 192. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00192. [7] SI MJ. Research progress on the correlation between abnormal iron metabolism and liver diseases[J]. Med Equip, 2022, 35( 2): 188- 191. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2376.2022.02.077.司茂杰. 铁代谢异常与肝脏疾病相关性的研究进展[J]. 医疗装备, 2022, 35( 2): 188- 191. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2376.2022.02.077. [8] ZHAO JY, LI YW, LI L. The role of iron and hepcidin in hepatic fibrosis[J]. Prog Physiol Sci, 2010, 41( 3): 183- 188.赵晋英, 李艳伟, 李琳. 铁和铁调素在肝纤维化中的作用[J]. 生理科学进展, 2010, 41( 3): 183- 188. [9] SIKORSKA K, BERNAT A, WROBLEWSKA A. Molecular pathogenesis and clinical consequences of iron overload in liver cirrhosis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2016, 15( 5): 461- 479. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(16)60135-2. [10] KEITH B, JOHNSON RS, SIMON MC. HIF1α and HIF2α: Sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011, 12( 1): 9- 22. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3183. [11] ZHANG LJ, DAI XZ, WANG L, et al. Iron overload accelerated lipid metabolism disorder and liver injury in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 961892. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.961892. [12] ZHANG LL, CHENG N, WANG X. Metabolic mechanism of copper and its toxic effect on liver[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2016, 21( 12): 762- 764. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2016.12.016.张亮亮, 程楠, 王训. 铜代谢机制及其对肝脏的毒性作用[J]. 胃肠病学, 2016, 21( 12): 762- 764. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2016.12.016. [13] LI YW, WAN XH, NING Q, et al. Excessive copper induces hepatocyte apoptosis and affects Bax and Bcl-2 expression in rat liver[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2008, 10( 1): 42- 46.李毓雯, 万小华, 宁琴, 等. 铜过量负荷导致肝细胞凋亡及其对Bax Bcl-2基因表达的影响[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2008, 10( 1): 42- 46. [14] YI B, CHEN Y, LIANG XH, et al. Serum copper and zinc levels of liver disease[J]. Bull Hunan Med Univ, 2002, 27( 3): 295- 296. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-7347.2002.03.037.易斌, 陈宇, 梁湘辉, 等. 肝病患者血清铜、锌含量研究[J]. 湖南医科大学学报, 2002, 27( 3): 295- 296. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-7347.2002.03.037. [15] GOU Y, ZHANG Y, QI JX, et al. Enhancing the copper(II) complexes cytotoxicity to cancer cells through bound to human serum albumin[J]. J Inorg Biochem, 2015, 144: 47- 55. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.12.012. [16] AIGNER E, STRASSER M, HAUFE H, et al. A role for low hepatic copper concentrations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2010, 105( 9): 1978- 1985. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.170. [17] GRÜNGREIFF K, REINHOLD D, WEDEMEYER H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2016, 15( 1): 7- 16. DOI: 10.5604/16652681.1184191. [18] LIUZZI JP, COUSINS RJ. Mammalian zinc transporters[J]. Annu Rev Nutr, 2004, 24: 151- 172. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.24.012003.132402. [19] KOHGO Y, IKUTA K, OHTAKE T, et al. Iron overload and cofactors with special reference to alcohol, hepatitis C virus infection and steatosis/insulin resistance[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2007, 13( 35): 4699- 4706. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4699. [20] GRÜNGREIFF K, GOTTSTEIN T, REINHOLD D, et al. Albumin substitution in decompensated liver cirrhosis: Don’t forget zinc[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13( 11): 4011. DOI: 10.3390/nu13114011. [21] WEAVER BP, ZHANG YX, HISCOX S, et al. Zip4(Slc39a4) expression is activated in hepatocellular carcinomas and functions to repress apoptosis, enhance cell cycle and increase migration[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5( 10): e13158. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013158. [22] LIN CC, HUANG JF, TSAI LY, et al. Selenium, iron, copper, and zinc levels and copper-to-zinc ratios in serum of patients at different stages of viral hepatic diseases[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2006, 109( 1): 15- 24. DOI: 10.1385/BTER:109:1:015. [23] KODAMA H, TANAKA M, NAITO Y, et al. Japan’s practical guidelines for zinc deficiency with a particular focus on taste disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, and liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 8): 2941. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082941. [24] ROMANI AM. Magnesium homeostasis and alcohol consumption[J]. Magnes Res, 2008, 21( 4): 197- 204. [25] KABE Y, ANDO K, HIRAO S, et al. Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: Distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2005, 7( 3-4): 395- 403. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.395. [26] LIU SJ, ZHANG HW, GU CY, et al. Associations between hepatitis B virus mutations and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2009, 101( 15): 1066- 1082. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djp180. [27] LI Z, ZHENG YM. Effects of magnesium ions on the growth and proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism[J]. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg, 2022, 25( 8): 608- 611, 617. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2022.08.004.李征, 郑亚民. 金属镁离子对肝癌细胞生长增殖的影响及作用机制分析[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2022, 25( 8): 608- 611, 617. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2022.08.004. [28] CUI JW, ZHANG J, CHENG WZ, et al. Clinical observation on the serum vitamin D level of the patients with chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2017, 27( 5): 269- 271, 275. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2017.05.004.崔剑巍, 张菁, 成伟忠, 等. 慢性HBV感染者血清维生素D水平的临床观察[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2017, 27( 5): 269- 271, 275. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2017.05.004. [29] XU XY, XIA SW, HUANG XJ, et al. Relationship between disease severity and serum calcium level in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Lab Diagn, 2019, 23( 11): 1929- 1931. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2019.11.016.徐晓义, 夏树伟, 黄小俊, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎患者病情严重程度与血清钙水平的关系[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2019, 23( 11): 1929- 1931. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2019.11.016. [30] BIVER E, CALMY A, RIZZOLI R. Bone health in HIV and hepatitis B or C infections[J]. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2017, 9( 1): 22- 34. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X16671927. [31] YIN LY, YIN J, CUI JF, et al. Association between serum calcium levels and the risk of liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2013, 34( 5): 457- 460. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2013.05.010.尹梁宇, 阴建, 崔剑峰, 等. 血清钙离子水平与肝硬化发病风险相关性研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2013, 34( 5): 457- 460. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2013.05.010. [32] ZHANG YG, ZHANG G. The relationship between cell calcium and hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chin J N Clin Med, 2019, 12( 6): 683- 687.张英耿, 张国. 细胞钙与肝纤维化的关系[J]. 中国临床新医学, 2019, 12( 6): 683- 687. [33] WU WJ, YANG MF, ZHU RM. Research progress on molecular biological mechanism of hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2009, 12( 4): 308- 311. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2009.04.028.吴文娟, 杨妙芳, 朱人敏. 肝星状细胞活化的分子生物学机制研究进展[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2009, 12( 4): 308- 311. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2009.04.028. [34] GUERRA MT, FLORENTINO RM, FRANCA A, et al. Expression of the type 3 InsP3 receptor is a final common event in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gut, 2019, 68( 9): 1676- 1687. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317811. [35] YU ZY, WANG KS, REN YX, et al. Mechanism of action of curcumin in treatment of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 4): 900- 904. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.04.044.俞泽元, 王科深, 任彦先, 等. 姜黄素抗胰腺癌的作用机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 4): 900- 904. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.04.044. [36] RAINEY NE, MOUSTAPHA A, SARIC A, et al. Iron chelation by curcumin suppresses both curcumin-induced autophagy and cell death together with iron overload neoplastic transformation[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2019, 5: 150. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-019-0234-y. [37] SWAMY AV, GULLIAYA S, THIPPESWAMY A, et al. Cardioprotective effect of curcumin against doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in albino rats[J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2012, 44( 1): 73- 77. DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.91871. [38] BADRIA FA, IBRAHIM AS, BADRIA AF, et al. Curcumin attenuates iron accumulation and oxidative stress in the liver and spleen of chronic iron-overloaded rats[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10( 7): e0134156. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134156. [39] UEDA S, MASUTANI H, NAKAMURA H, et al. Redox control of cell death[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2002, 4( 3): 405- 414. DOI: 10.1089/15230860260196209. [40] HUANG LL, SU J. Research progress on the mechanism of action and clinical application of Danshen[J]. Chin J Drug Abuse Prev Treat, 2023, 29( 6): 1002- 1006. DOI: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2023.06.022.黄丽丽, 苏静. 丹参的作用机制及临床应用研究进展[J]. 中国药物滥用防治杂志, 2023, 29( 6): 1002- 1006. DOI: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2023.06.022. [41] YANG CL, WU J, CHEN YK. Protective effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza on high-copper diet-induced liver injury in rats[J]. J Tradit Chin Vet Med, 2016, 35( 6): 13- 16. DOI: 10.13823/j.cnki.jtcvm.2016.06.003.杨成林, 邬静, 陈宇科. 丹参对铜诱导大鼠肝损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2016, 35( 6): 13- 16. DOI: 10.13823/j.cnki.jtcvm.2016.06.003. [42] FANG AP, CHEN PY, WANG XY, et al. Serum copper and zinc levels at diagnosis and hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144( 11): 2823- 2832. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31991. [43] ALEXANDER JL, WILSON ID, TEARE J, et al. Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 14( 6): 356- 365. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.20. [44] SHEN L, JI HF. Bidirectional interactions between dietary curcumin and gut microbiota[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2019, 59( 18): 2896- 2902. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1478388. [45] VINOD BS, ANTONY J, NAIR HH, et al. Mechanistic evaluation of the signaling events regulating curcumin-mediated chemosensitization of breast cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2013, 4( 2): e505. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.26. [46] WU RH, MEI XT, YE YB, et al. Zn(II)-curcumin solid dispersion impairs hepatocellular carcinoma growth and enhances chemotherapy by modulating gut microbiota-mediated zinc homeostasis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 150: 104454. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104454. [47] MENG ZQ. Study on the mechanism of apigenin alleviates liver injury induced by high fat diet through activating autophagy[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023.孟卓群. 芹菜素激活自噬缓解高脂饮食所致肝损伤的作用机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. [48] XU XR, LI M, CHEN WW, et al. Apigenin attenuates oxidative injury in ARPE-19 cells thorough activation of Nrf2 pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 4378461. DOI: 10.1155/2016/4378461. [49] PAN HY, WANG FG, ZHUANG RX, et al. Study on preparation of apigenin-magnesium complex[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2014, 32( 2): 337- 339. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2014.02.039.潘红英, 王福根, 庄让笑, 等. 芹菜素镁制备工艺的研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2014, 32( 2): 337- 339. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2014.02.039. [50] PAN XW, SHAO YD, WANG FG, et al. Protective effect of apigenin magnesium complex on H2O2-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in rat hepatic stellate cells[J]. Pharm Biol, 2020, 58( 1): 553- 560. DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1772840. [51] GUO JZ, WAN F, LI X, et al. Study of the influence about the lipoperoxidation and zine, calcium content on Saikosaponin-d against liver fibrosis in rats[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2009, 25( 3): 11- 14.郭景珍, 万方, 李忻, 等. 柴胡皂苷d对肝纤维化大鼠脂质过氧化与微量元素锌、钙的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2009, 25( 3): 11- 14. [52] ZHAO JL, MA LJ, QU M, et al. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine treatment on serum trace elements in rats with schistosomiasis hepatic fibrosis[J]. Shandong Med J, 2008, 48( 19): 38- 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2008.19.015.赵建玲, 麻丽娟, 屈明, 等. 中药治疗对血吸虫肝纤维化鼠血清微量元素的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2008, 48( 19): 38- 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2008.19.015. [53] HU Y, WANG XL, LI DG, et al. Experimental study on the effects of Ca2+ antagonists on rat model of cirrhosis with portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Dig, 1995, 15( 2): 89- 91.胡颖, 王秀玲, 李定国, 等. 钙拮抗剂对大鼠肝硬化模型门脉高压的实验研究[J]. 中华消化杂志, 1995, 15( 2): 89- 91. [54] LIAO Y, HE YH, LUO YW. Role of oxidative stress in acute liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 10): 2402- 2407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.039.廖月, 何毅怀, 罗亚文. 氧化应激在急性肝损伤中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 10): 2402- 2407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.039. [55] SEKI E, SCHWABE RF. Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 3): 1066- 1079. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27332. -



 PDF下载 ( 1157 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1157 KB)


 下载:
下载: