-
摘要: 胆汁淤积性肝病(CLD)是指各种病因引起的胆汁代谢异常、流出受阻、胆管损伤等肝脏疾病,主要病因包括:药物、毒物、免疫、遗传、梗阻、感染、肿瘤等。胆汁淤积是CLD共有的病理改变,而不同病因淤胆的部位、组织病理及超微结构等改变,具有相对特异性。依据病因,重点阐述自身免疫性胆管炎、遗传代谢性肝病、大胆管病变的病理学特征,引申鉴别其他CLD,以期提高对CLD病理学的认识,助力精准诊疗。Abstract: Cholestatic liver disease (CLD) is a group of liver diseases caused by various reasons, such as abnormal bile metabolism, blocked outflow, and bile duct injury, and the major causes of CLD include drugs, poisons, immunity, genetics, obstruction, infection, and tumor. Cholestasis is a common pathological change in CLD; however, the site, histopathology, and ultrastructure of cholestasis due to different etiologies are relatively specific. According to the etiology, this article elaborates on the pathological characteristics of CLD such as autoimmune cholangitis, inherited metabolic liver disease, and large bile duct disease and introduces the differential diagnosis of other types of CLD, in order to improve the understanding of CLD pathology and facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment.
-
Key words:
- Cholestasi /
- Biopsy /
- Pathology /
- Diagnosis
-
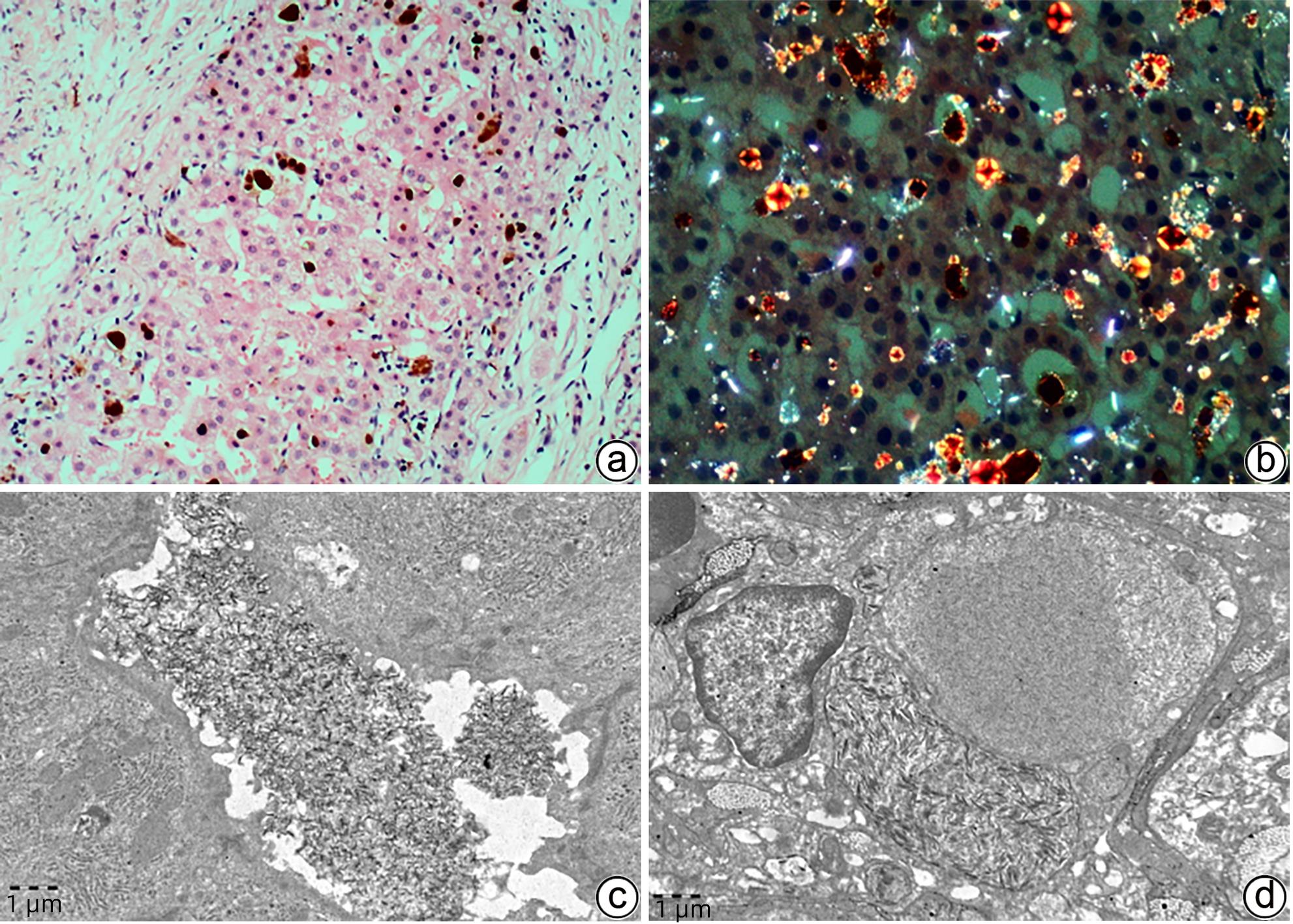
注: a,肝细胞及毛细胆管内两种颜色的淤胆颗粒及胆栓,一种“巧克力”色,另一种淡黄色(HE染色,×100);b,偏振光显微镜可见红色双折光中的“Maltese十字”或星状暗区(HE染色,偏振光,×200);c,毛细胆管内可见原卟啉结晶(箭头),呈丝状弧形排列,毛细胆管腔面微绒毛减少,紧密连接延长(TEM,×15 000);d,Kupffer细胞胞质溶酶体内充满丝状原卟啉结晶(箭头),窦周间隙可见胶原纤维束沉积(TEM,×15 000)。
图 6 EPP的组织病理学及超微结构特征
Figure 6. Histopathological and ultrastructural characteristics of EPP
-
[1] JOHNSON CA, GISSEN P, SERGI C. Molecular pathology and genetics of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes[J]. J Med Genet, 2003, 40( 5): 311- 319. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.40.5.311. [2] ESTRADAS J, PASCUAL-RAMOS V, MARTÍNEZ B, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis with giant-cell transformation[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2009, 8( 1): 68- 70. [3] SARCOGNATO S, SACCHI D, GRILLO F, et al. Autoimmune biliary diseases: Primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Pathologica, 2021, 113( 3): 170- 184. DOI: 10.32074/1591-951X-245. [4] ZEN Y, HUBSCHER SG, NAKANUMA Y. Bile duct diseases. BurtAD, FerrellLD, HübscherSG, eds. MacSween’s pathology of the liver[M]. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2018: 515. [5] TAKAHASHI T, MIURA T, NAKAMURA J, et al. Plasma cells and the chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis of primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55( 3): 846- 855. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24757. [6] CAREY EJ, ALI AH, LINDOR KD. Primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386: 1565- 1575. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00154-3. [7] KARLSEN TH, FOLSERAAS T, THORBURN D, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis-a comprehensive review[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67( 6): 1298- 1323. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.022. [8] HIRSCHFIELD GM, KARLSEN TH, LINDOR KD, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Lancet, 2013, 382( 9904): 1587- 1599. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60096-3. [9] PORTMANN B, ZEN Y. Inflammatory disease of the bile ducts-cholangiopathies: Liver biopsy challenge and clinicopathological correlation[J]. Histopathology, 2012, 60( 2): 236- 248. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.03853.x. [10] COLLING R, VERRILL C, FRYER E, et al. Bile duct basement membrane thickening in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Histopathology, 2016, 68( 6): 819- 824. DOI: 10.1111/his.12857. [11] FIEL MI, SIMA HR, AZARIAN A, et al. A morphometric study of the hepatic arterioles in end-stage primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Virchows Arch, 2015, 466( 2): 143- 149. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-014-1680-9. [12] CARRASCO-AVINO G, SCHIANO TD, WARD SC, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Detailed histologic assessment and integration using bioinformatics highlights arterial fibrointimal hyperplasia as a novel feature[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2015, 143( 4): 505- 513. DOI: 10.1309/AJCPVKFVIPRBXQR2. [13] NAKAZAWA T, NAITOH I, HAYASHI K, et al. Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis based on cholangiographic classification[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2012, 47( 1): 79- 87. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-011-0465-z. [14] ZHANG JP, HOU XT, YIN ZC, et al. Gilbert syndrome: Clinicopathological and genetic analyses of 29 cases[J]. Chin J Diagn Pathol, 2018, 25( 2): 85- 89. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2018.02.002.张继平, 侯晓涛, 尹自长, 等. Gilbert综合征29例临床病理及基因分析[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2018, 25( 2): 85- 89. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2018.02.002. [15] ATAOLLAHI M, DEHGHANI SM, ANBARDAR MH, et al. Liver histologic changes in children with type 1 of Crigler-Najjar syndrome[J]. Arkh Patol, 2021, 83( 5): 27- 30. DOI: 10.17116/patol20218305127. [16] FATA CR, GILLIS LA, PACHECO MC. Liver fibrosis associated with crigler-najjar syndrome in a compound heterozygote: A case report[J]. Pediatr Dev Pathol, 2017, 20( 6): 522- 525. DOI: 10.1177/1093526617697059. [17] WU ZB. Ultramicro-pathological diagnostics[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific& Technical Publishers, 2003.武忠弼. 超微病理诊断学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2003. [18] LI LT, WANG JS. Advances in the study of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. Infect Dis Inf, 2019, 32( 2): 162- 165. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2019.02.017.李丽婷, 王建设. 进行性家族性肝内胆汁淤积症研究进展[J]. 传染病信息, 2019, 32( 2): 162- 165. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2019.02.017. [19] WENG YH, XIONG QF, LIU DX, et al. Clinical and pathological features of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 154- 159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.024.翁宇航, 熊清芳, 刘杜先, 等. 进行性家族性肝内胆汁淤积症3型临床病理特征分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 1): 154- 159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.024. [20] QIU YL, GONG JY, FENG JY, et al. Defects in myosin VB are associated with a spectrum of previously undiagnosed low γ-glutamyltransferase cholestasis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65( 5): 1655- 1669. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29020. [21] GOMEZ-OSPINA N, POTTER CJ, XIAO R, et al. Mutations in the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 10713. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10713. [22] HALAWI A, IBRAHIM N, BITAR R. Triggers of benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and its pathophysiology: A review of literature[J]. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2021, 84( 3): 477- 486. DOI: 10.51821/84.3.013. [23] GUINDI M. Wilson disease[J]. Semin Diagn Pathol, 2019, 36( 6): 415- 422. DOI: 10.1053/j.semdp.2019.07.008. [24] FANNI D, GUIDO M, GEROSA C, et al. Liver changes in Wilson’s disease: The full spectrum. A report of 127 biopsies from 43 patients[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 25( 12): 4336- 4344. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202106_26142. [25] ZHAO XY, HE ZY, LIU LW, et al. Comparative study of pathological characteristics of 45 patients with primary and secondary hemochromatosis[J]. Infect Dis Inf, 2019, 32( 2): 127- 131. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2019.02.007.赵新颜, 何志颖, 刘立伟, 等. 45例原发性与继发性血色病临床病理特点对比研究[J]. 传染病信息, 2019, 32( 2): 127- 131. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2019.02.007. [26] MIYAMOTO R, JUN SD, OTA K, et al. Neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency with no hepatic steatosis: A case report[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2021, 21( 1): 237. DOI: 10.1186/s12887-021-02717-w. [27] ZHANG JP, CHENG YB, ZHOU XJ, et al. Neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency: A clinicopathological analysis of two cases[J]. Chin J Diagn Pathol, 2018, 25( 4): 261- 265. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2018.04.006.张继平, 程艳波, 周晓军, 等. Citrin缺陷导致的新生儿肝内胆汁淤积症2例临床病理观察[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2018, 25( 4): 261- 265. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2018.04.006. [28] FABRIS L, MILANI C, FIOROTTO R, et al. Dysregulation of the Scribble/YAP/β-catenin axis sustains the fibroinflammatory response in a PKHD1-/- mouse model of congenital hepatic fibrosis[J]. FASEB J, 2022, 36( 6): e22364. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202101924R. [29] SAXENA R. Practical hepatic pathology: A diagnostic approach[M]. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2018. [30] DESMET VJ. Congenital diseases of intrahepatic bile ducts: Variations on the theme“ductal plate malformation”[J]. Hepatology, 1992, 16( 4): 1069- 1083. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840160434. [31] CHEN IY, WHITNEY-MILLER CL, LIAO XY. Congenital hepatic fibrosis and its mimics: A clinicopathologic study of 19 cases at a single institution[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2021, 16( 1): 81. DOI: 10.1186/s13000-021-01142-y. [32] GILBERT MA, BAUER RC, RAJAGOPALAN R, et al. Alagille syndrome mutation update: Comprehensive overview of JAG1 and NOTCH2 mutation frequencies and insight into missense variant classification[J]. Hum Mutat, 2019, 40( 12): 2197- 2220. DOI: 10.1002/humu.23879. [33] WU LN, SUN LY, ZHU ZJ, et al. Clinical and histological characteristics of patients with Alagille syndrome[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2023, 28( 3): 351- 354, 363. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.03.018.武丽娜, 孙丽莹, 朱志军, 等. Alagille综合征的临床及病理特征分析[J]. 肝脏, 2023, 28( 3): 351- 354, 363. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.03.018. [34] CASANOVA-GONZÁLEZ MJ, TRAPERO-MARUGÁN M, JONES EA, et al. Liver disease and erythropoietic protoporphyria: A concise review[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16( 36): 4526- 4531. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4526. [35] ANSTEY AV, HIFT RJ. Liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria: Insights and implications for management[J]. Gut, 2007, 56( 7): 1009- 1018. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.097576. [36] MACDONALD DM, GERMAIN D, PERROT H. The histopathology and ultrastructure of liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria[J]. Br J Dermatol, 1981, 104( 1): 7- 17. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb01705.x. [37] VIJ M, RELA M. Biliary atresia: Pathology, etiology and pathogenesis[J]. Future Sci OA, 2020, 6( 5): FSO466. DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2019-0153. -



 PDF下载 ( 1969 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1969 KB)

 下载:
下载: