肝巨噬细胞调控肝癌癌前病变恶变的研究进展
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240527
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:闫瑞娟负责构思文章思路,设计文章结构并撰写文章;焦俊喆、黄玉、魏海梁负责研究文献,更新、补充相关内容;闫曙光负责设计并讨论文章构架;常占杰负责基础理论指导;郭英君负责修改文章,设计文章结构并参与部分文章撰写;李京涛负责审核文章思路并修改。
Research advances in liver macrophages regulating malignant transformation of hepatic precancerous lesions
-
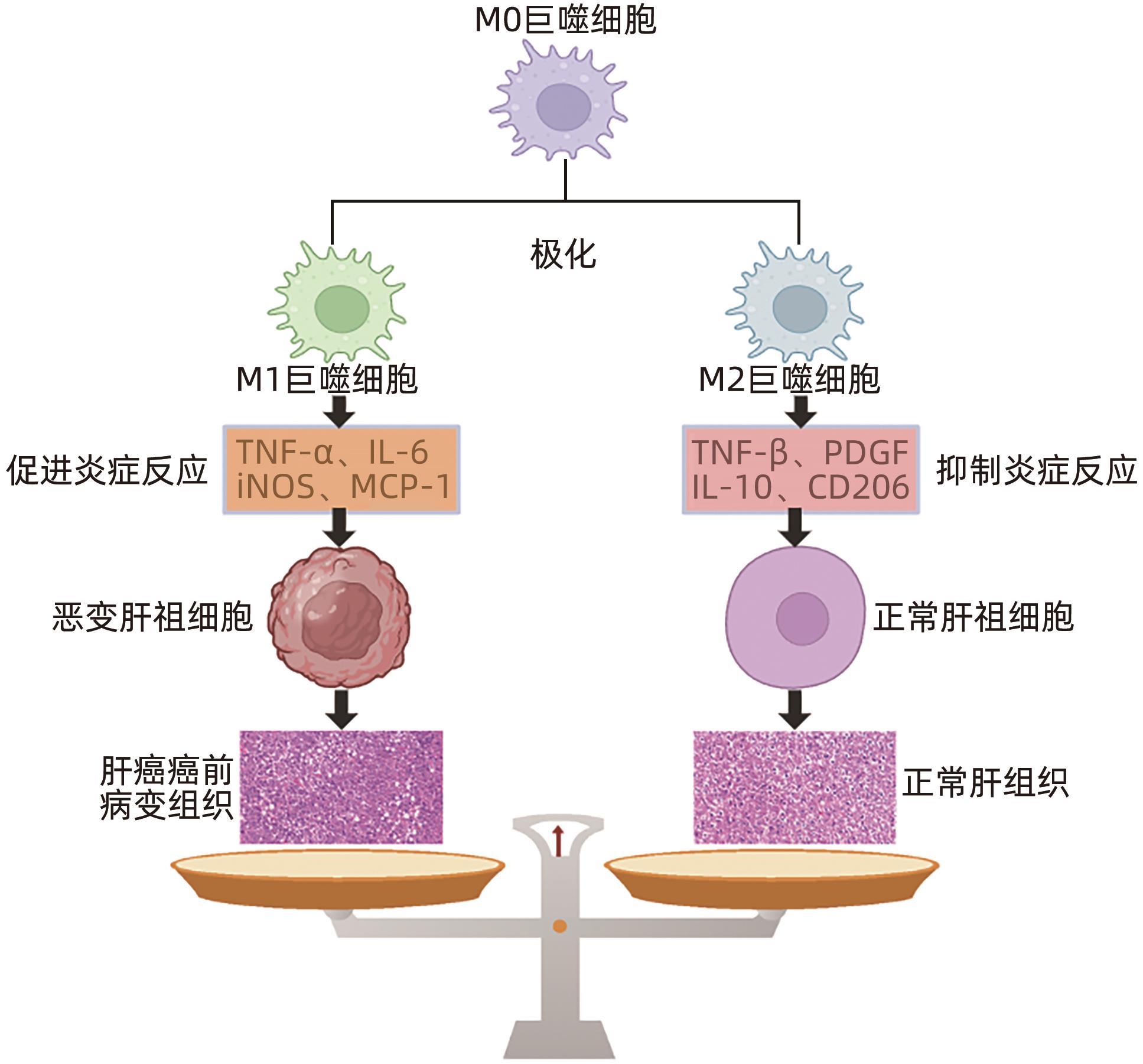
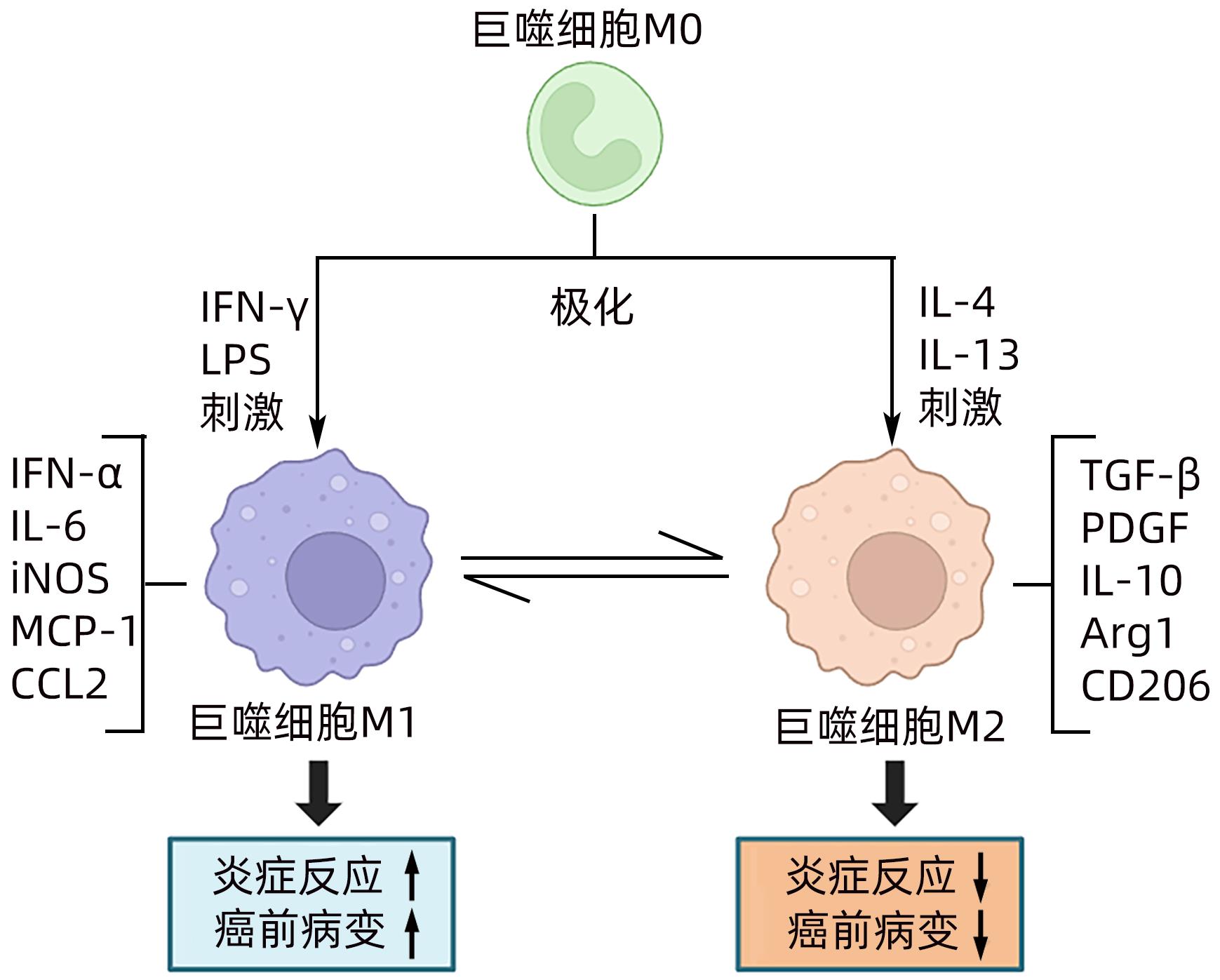
摘要: 肝巨噬细胞是肝脏中重要的免疫细胞,其通过极化为M1型和M2型,分别表达“促炎因子”和“抑炎因子”,进而发挥调控炎症损伤反应的作用。肝祖细胞恶变是肝癌癌前病变恶性进展的核心机制,其发生的关键因素是炎症损伤微环境的持续刺激,与M1/M2巨噬细胞极化密切相关。本综述主要围绕“巨噬细胞极化-慢性炎症-肝祖细胞恶变”关系进行探讨,为肝癌癌前病变的预防和治疗提供重要的理论依据。Abstract: Liver macrophages are important immune cells in the liver, and they express proinflammatory factors and anti-inflammatory factors through polarization into M1 type and M2 type, respectively, thereby playing a role in regulating inflammatory damage response. The malignant transformation of hepatic progenitor cells is the core mechanism of the malignant progression of hepatic precancerous lesions, and its key factor is the continuous stimulation of inflammatory microenvironment, which is closely associated with M1/M2 macrophage polarization. This review mainly focuses on the association between macrophage polarization, chronic inflammation, and malignant transformation of hepatic progenitor cells, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of hepatic precancerous lesions.
-
-
[1] VOGEL A, MEYER T, SAPISOCHIN G, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400( 10360): 1345- 1362. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4. [2] WANG C, VEGNA S, JIN HJ, et al. Inducing and exploiting vulnerabilities for the treatment of liver cancer[J]. Nature, 2019, 574( 7777): 268- 272. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1607-3. [3] RENZULLI M, BISELLI M, BROCCHI S, et al. New hallmark of hepatocellular carcinoma, early hepatocellular carcinoma and high-grade dysplastic nodules on Gd-EOB-DTPA MRI in patients with cirrhosis: A new diagnostic algorithm[J]. Gut, 2018, 67( 9): 1674- 1682. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315384. [4] JIAO JZ, LI JT, YAN SG, et al. Current research status of precancerous dysplastic nodules in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33( 5): 974- 978. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.05.039.焦俊喆, 李京涛, 闫曙光, 等. 肝细胞癌癌前异型增生结节的研究现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33( 5): 974- 978. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.05.039. [5] Professional Committee for Prevention and Control of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases of Chinese Preventive Medicine Association; Professional Committee for Hepatology, Chinese Research Hospital Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, et al. Guideline for stratified screening and surveillance of primary liver cancer(2020 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 2): 286- 295. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.009.中华预防医学会肝胆胰疾病预防与控制专业委员会, 中国研究型医院学会肝病专业委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会, 等. 原发性肝癌的分层筛查与监测指南(2020版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 2): 286- 295. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.009. [6] MARQUARDT JU, ANDERSEN JB, THORGEIRSSON SS. Functional and genetic deconstruction of the cellular origin in liver cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2015, 15( 11): 653- 667. DOI: 10.1038/nrc4017. [7] ZHU LQ, FINKELSTEIN D, GAO CL, et al. Multi-organ mapping of cancer risk[J]. Cell, 2016, 166( 5): 1132- 1146. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.045. [8] MIYAJIMA A, TANAKA M, ITOH T. Stem/progenitor cells in liver development, homeostasis, regeneration, and reprogramming[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 14( 5): 561- 574. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.04.010. [9] BRIA A, MARDA J, ZHOU JM, et al. Hepatic progenitor cell activation in liver repair[J]. Liver Res, 2017, 1( 2): 81- 87. DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.08.002. [10] WU CC, LIN CJ, KUO KK, et al. Correlation between cancer stem cells, inflammation and malignant transformation in a DEN-induced model of hepatic carcinogenesis[J]. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2022, 44( 7): 2879- 2886. DOI: 10.3390/cimb44070198. [11] PU WJ, ZHU H, ZHANG MJ, et al. Bipotent transitional liver progenitor cells contribute to liver regeneration[J]. Nat Genet, 2023, 55( 4): 651- 664. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01335-9. [12] LIU WT, GAO L, HOU XJ, et al. TWEAK signaling-induced ID1 expression drives malignant transformation of hepatic progenitor cells during hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Adv Sci, 2023, 10( 18): e2300350. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202300350. [13] NIO K, YAMASHITA T, KANEKO S. The evolving concept of liver cancer stem cells[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16( 1): 4. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-016-0572-9. [14] THAN NN, NEWSOME PN. Stem cells for liver regeneration[J]. QJM, 2014, 107( 6): 417- 421. DOI: 10.1093/qjmed/hcu013. [15] YAN ZJ, CHEN L, WANG HY. To be or not to be: The double-edged sword roles of liver progenitor cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2023, 1878( 3): 188870. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188870. [16] SIA D, VILLANUEVA A, FRIEDMAN SL, et al. Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects onPatient prognosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152( 4): 745- 761. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.048. [17] HAIDERI SS, MCKINNON AC, TAYLOR AH, et al. Injection of embryonic stem cell derived macrophages ameliorates fibrosis in a murine model of liver injury[J]. NPJ Regen Med, 2017, 2: 14. DOI: 10.1038/s41536-017-0017-0. [18] ZENG JX, JING YY, WU QL, et al. Autophagy is required for hepatic differentiation of hepatic progenitor cells via Wnt signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 6627506. DOI: 10.1155/2021/6627506. [19] NATI M, CHUNG KJ, CHAVAKIS T. The role of innate immune cells in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Innate Immun, 2022, 14( 1): 31- 41. DOI: 10.1159/000518407. [20] KHURANA A, NAVIK U, ALLAWADHI P, et al. Spotlight on liver macrophages for halting liver disease progression and injury[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2022, 26( 8): 707- 719. DOI: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2133699. [21] SOUCIE EL, WENG ZM, GEIRSDÓTTIR L, et al. Lineage-specific enhancers activate self-renewal genes in macrophages and embryonic stem cells[J]. Science, 2016, 351( 6274): aad5510. DOI: 10.1126/science.aad5510. [22] BLÉRIOT C, DUPUIS T, JOUVION G, et al. Liver-resident macrophage necroptosis orchestrates type 1 microbicidal inflammation and type-2-mediated tissue repair during bacterial infection[J]. Immunity, 2015, 42( 1): 145- 158. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.020. [23] VANNELLA KM, WYNN TA. Mechanisms of organ injury and repair by macrophages[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2017, 79: 593- 617. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034356. [24] LUO Y, XIAO JH. Inflammatory auxo-action in the stem cell division theory of cancer[J]. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e15444. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15444. [25] LI XF, CHEN C, XIANG DM, et al. Chronic inflammation-elicited liver progenitor cell conversion to liver cancer stem cell with clinical significance[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66( 6): 1934- 1951. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29372. [26] SICA A, INVERNIZZI P, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in liver homeostasis and pathology[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59( 5): 2034- 2042. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26754. [27] MURRAY PJ, ALLEN JE, BISWAS SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines[J]. Immunity, 2014, 41( 1): 14- 20. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008. [28] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233( 9): 6425- 6440. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.26429. [29] JIN K, LI T, SÁNCHEZ-DUFFHUES G, et al. Involvement of inflammation and its related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8( 13): 22145- 22165. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13530. [30] YANG L, ZHANG Y. Tumor-associated macrophages: From basic research to clinical application[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10( 1): 58. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0430-2. [31] MAO YL, WANG BK, XU X, et al. Glycyrrhizic acid promotes M1 macrophage polarization in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages associated with the activation of JNK and NF-κB[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2015, 2015: 372931. DOI: 10.1155/2015/372931. [32] TANG Y, KITISIN K, JOGUNOORI W, et al. Progenitor/stem cells give rise to liver cancer due to aberrant TGF-beta and IL-6 signaling[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008, 105( 7): 2445- 2450. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705395105. [33] HAN CY, YANG Y, SHENG YJ, et al. The mechanism of lncRNA-CRNDE in regulating tumour-associated macrophage M2 polarization and promoting tumour angiogenesis[J]. J Cellular Molecular Medi, 2021, 25( 9): 4235- 4247. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16477. [34] GUNASSEKARAN GR, POONGKAVITHAI VADEVOO SM, BAEK MC, et al. M1 macrophage exosomes engineered to foster M1 polarization and target the IL-4 receptor inhibit tumor growth by reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages into M1-like macrophages[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 278: 121137. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121137. [35] ORECCHIONI M, GHOSHEH Y, PRAMOD AB, et al. Macrophage polarization: Different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. classically and M2(LPS-) vs. alternatively activated macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1084. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084. [36] RINGELHAN M, PFISTER D, O’CONNOR T, et al. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Immunol, 2018, 19( 3): 222- 232. DOI: 10.1038/s41590-018-0044-z. [37] Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China(2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 2): 277- 292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007.中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会医政医管局. 原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 2): 277- 292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007. [38] CHEN JM, CHEN L, ZERN MA, et al. The diversity and plasticity of adult hepatic progenitor cells and their niche[J]. Liver Int, 2017, 37( 9): 1260- 1271. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13377. [39] HOU XJ, YE F, LI XY, et al. Immune response involved in liver damage and the activation of hepatic progenitor cells during liver tumorigenesis[J]. Cell Immunol, 2018, 326: 52- 59. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.08.004. [40] KAUR S, SIDDIQUI H, BHAT MH. Hepatic progenitor cells in action: Liver regeneration or fibrosis?[J]. Am J Pathol, 2015, 185( 9): 2342- 2350. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.06.004. [41] ALEKSANDROVA K, BOEING H, NÖTHLINGS U, et al. Inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers and risk of liver and biliary tract cancer[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 3): 858- 871. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27016. [42] YANG X, SHAO CC, DUAN LX, et al. Oncostatin M promotes hepatic progenitor cell activation and hepatocarcinogenesis via macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-Α[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 517: 46- 54. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.05.039. [43] LI L, CUI L, LIN P, et al. Kupffer-cell-derived IL-6 is repurposed for hepatocyte dedifferentiation via activating progenitor genes from injury-specific enhancers[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30( 3): 283- 299. e 9. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.01.009. [44] GALDIERO MR, BONAVITA E, BARAJON I, et al. Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in cancer[J]. Immunobiology, 2013, 218( 11): 1402- 1410. DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.06.003. [45] GOSWAMI KK, GHOSH T, GHOSH S, et al. Tumor promoting role of anti-tumor macrophages in tumor microenvironment[J]. Cell Immunol, 2017, 316: 1- 10. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.04.005. [46] van HUL N, LANTHIER N, ESPAÑOL SUÑER R, et al. Kupffer cells influence parenchymal invasion and phenotypic orientation, but not the proliferation, of liver progenitor cells in a murine model of liver injury[J]. Am J Pathol, 2011, 179( 4): 1839- 1850. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.042. -



 PDF下载 ( 1010 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1010 KB)

 下载:
下载: