-
摘要: 本文综述了全球和中国消除乙型肝炎的新进展。虽然全球乙型肝炎疾病负担正在下降,但各国消除乙型肝炎的进展差异较大,在疾病负担最严重的20个国家中,孟加拉国、印度、印度尼西亚、日本和俄罗斯取得显著进展。中国继续保持新生儿乙型肝炎疫苗高覆盖率,首剂及时接种率为95.6%,3剂接种率为99.6%。从2016年到2022年,中国慢性乙型肝炎患者的诊断率由19%升至24%,治疗率由11%升至15%,但与世界卫生组织提出的2023年目标仍有较大距离。全球和中国仍需继续努力,砥砺奋进,加速实现2030年消除病毒性肝炎的宏伟目标。Abstract: This paper summarizes the latest progress in the elimination of hepatitis B worldwide and in China. Although the global burden of hepatitis B is decreasing, there is a large difference in the progress towards elimination across different countries, and among the 20 countries with the heaviest disease burden, Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Japan, and Russia have achieved substantial progress. China continues to maintain a high HBV vaccination coverage for neonates, with an inoculation rate of 95.6% for timely birth dose and 99.6% for 3 doses. From 2016 to 2022, the diagnosis rate of patients with chronic hepatitis B in China have increased from 19% to 24%, and treatment rate have increased from 11% to 15%; however, there is still a big gap compared with the WHO targets by 2030. Further efforts are needed to eliminate viral hepatitis by 2030 globally and in China.
-
Key words:
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- Diagnosis /
- Therapeutics /
- Public Health
-
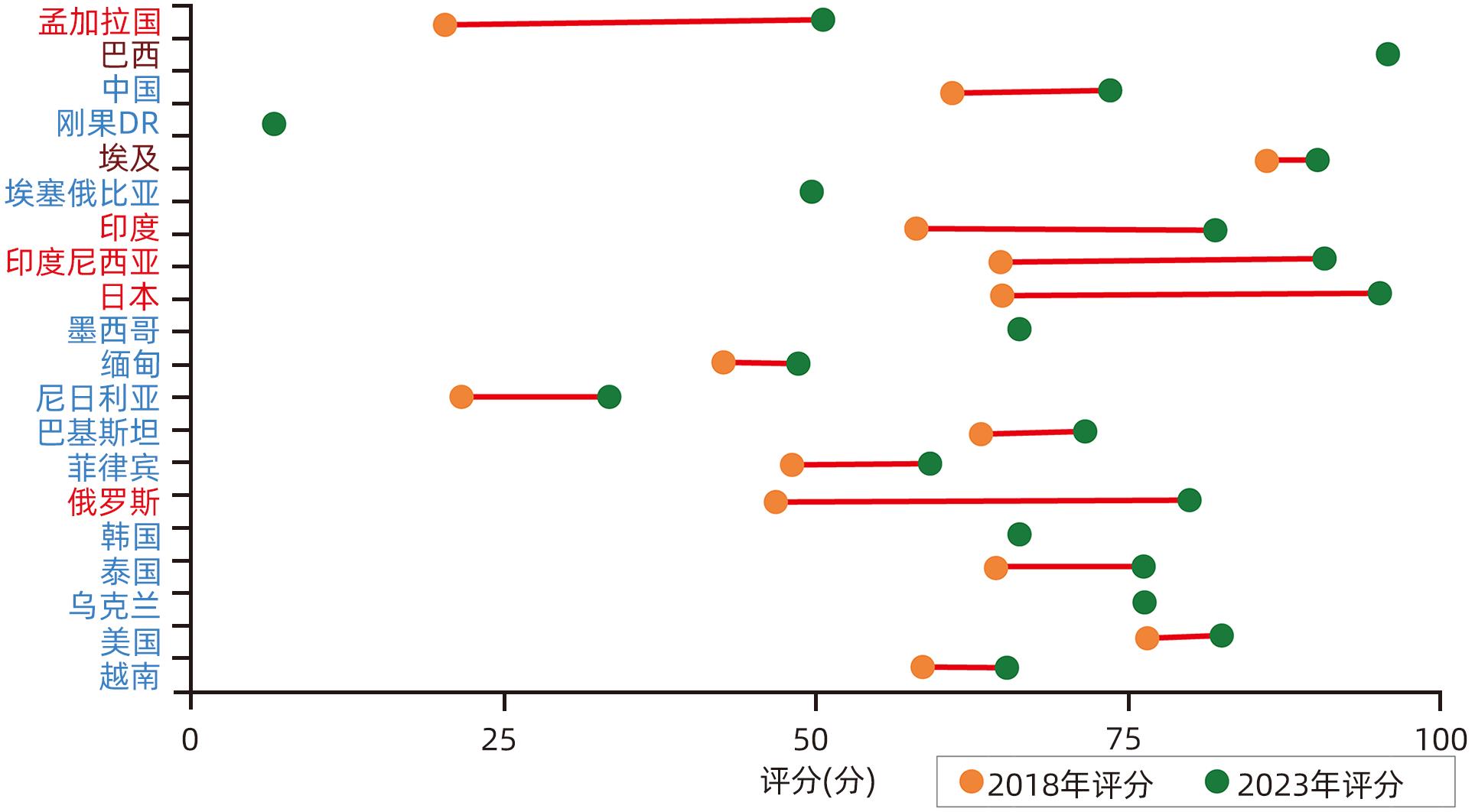
图 2 The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology委员会对全球病毒性肝炎疾病负担最严重的20个国家2018—2023年消除病毒性肝炎相关政策的评分
Figure 2. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission’s scores on policies related to the elimination of viral hepatitis from 2018 to 2023 for the 20 countries with the highest disease burden of viral hepatitis worldwide
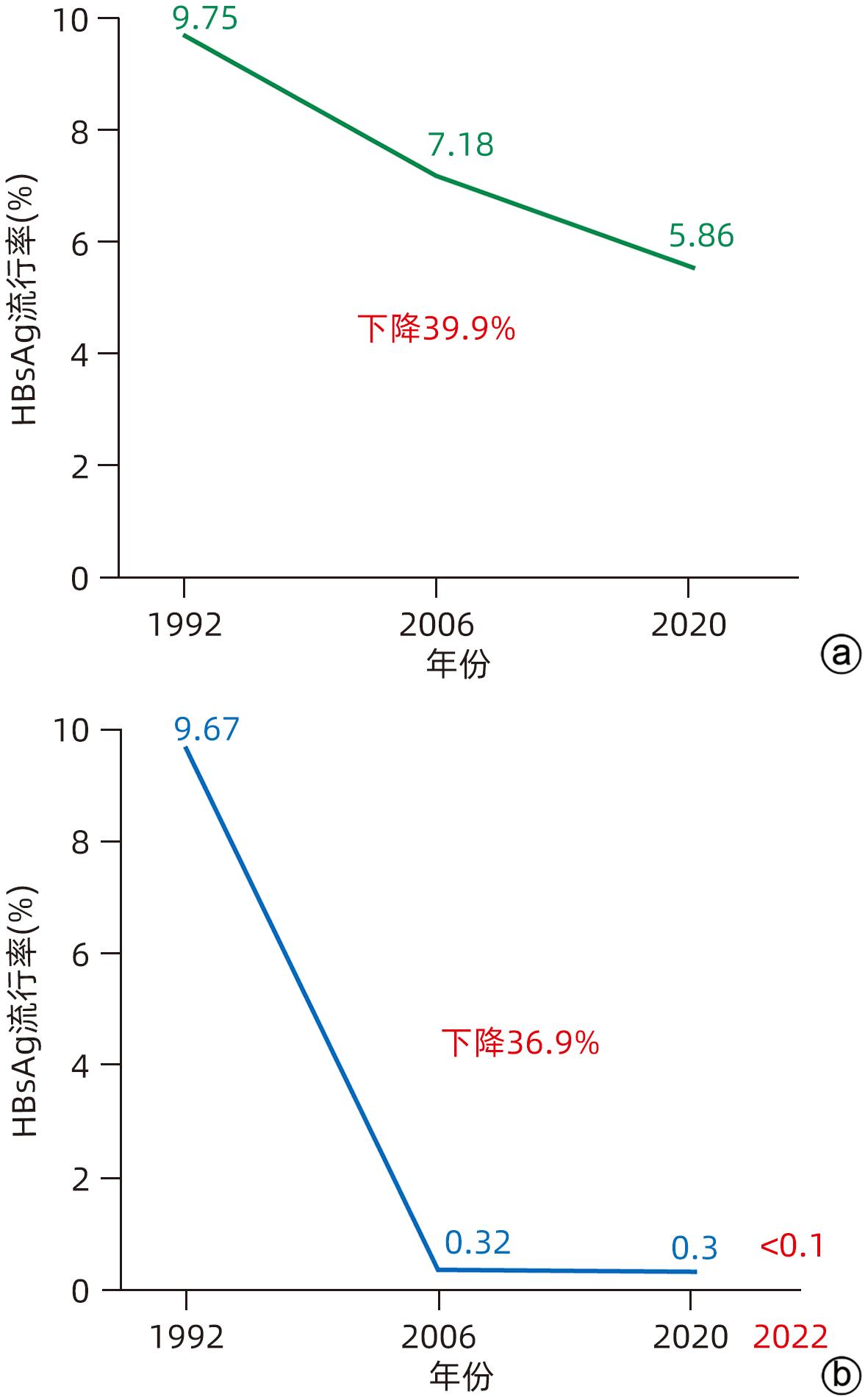
表 1 全球消除乙型肝炎进展
Table 1. Worldwide progress in elimination of hepatitis B
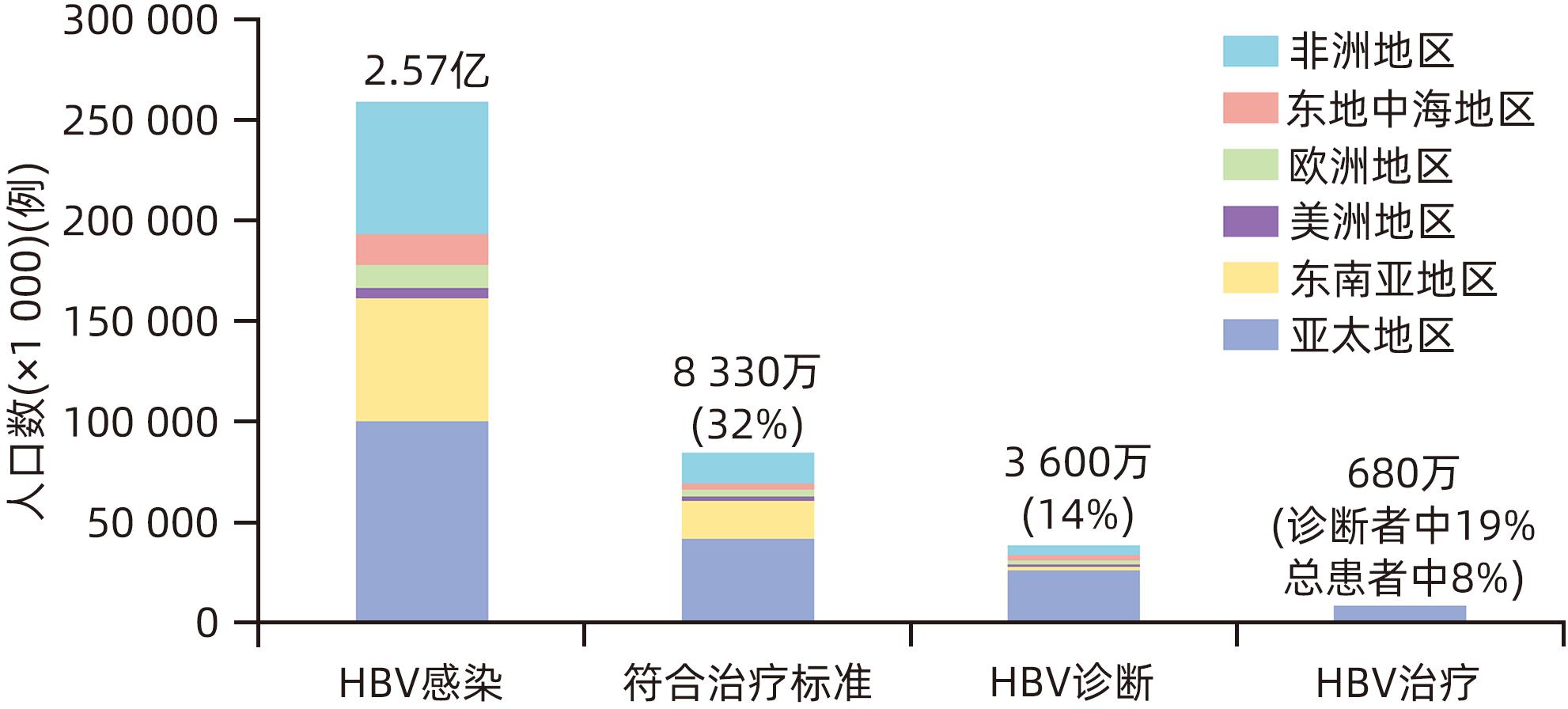
项目 2019年 2022年 HBsAg阳性人数(例) 2.96亿 2.57亿 一般人群HBsAg流行率 3.8% 3.2% <5岁HBsAg流行率 0.9% 0.7%(560万) 死亡人数(例) 82万 无资料 诊断人数(例) 3 040万 3 600万(14%) 治疗人数(例) 660万 680万(8%) 3针乙型肝炎疫苗覆盖率 86% 85% 首针及时接种率 43% 46% HBIG接种率 13% 14% 孕妇抗病毒预防率 <1% 3% 注:HBIG,乙型肝炎免疫球蛋白。 表 2 2017—2023年美国消除乙型肝炎进展
Table 2. Progress in elimination of hepatitis B in the United States, 2017—2023

表 3 2022年全球与中国消除乙型肝炎进展比较
Table 3. Comparison of progress in elimination of hepatitis B worldwide and in China, 2022
项目 全球 中国 HBsAg阳性人数(例) 2.57亿 7 975万 一般人群HBsAg流行率 3.2% 5.6% <5岁HBsAg流行率 0.7%(560万) <0.1%(8万) 死亡人数(例) 无资料 无资料 诊断人数(例) 3 600万(14%) 1 913万(24%) 治疗人数(例) 680万(8%) 508万(15%) 3针乙型肝炎疫苗覆盖率 85% 99% 首针及时接种率 46% 95% HBIG接种率 14% 100% 孕妇抗病毒预防率 3% 26% -
[1] World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report, 2017[EB/OL]. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ [2] World Health Organization. Global health sector strategies on, respectively, HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections for the period 2022- 2030[EB/OL]. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/hq-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-library/full-final-who-ghss-hiv-vh-sti_1-june2022.pdf?sfvrsn=7c074b36_9. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/hq-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-library/full-final-who-ghss-hiv-vh-sti_1-june2022.pdf?sfvrsn=7c074b36_9 [3] World Health Organization. Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016- 2021: Towards ending viral hepatitis[EB/OL]. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/246177/1/WHO-HIV-2016.06-eng,pdf?ua= 1. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/246177/1/WHO-HIV-2016.06-eng [4] GBD 2019 Hepatitis B Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7( 9): 796- 829. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00124-8. [5] CUI FQ, BLACH S, MANZENGO MINGIEDI C, et al. Global reporting of progress towards elimination of hepatitis B and hepatitis C[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 8( 4): 332- 342. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00386-7. [6] COLLABORATORS PO. Global prevalence, cascade of care, and prophylaxis coverage of hepatitis B in 2022: A modelling study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 8( 10): 879- 907. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00197-8. [7] World Health Organization. Progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections 2021: accountability for the global health sector strategies, 2016-2021: actions for impact. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2021. [8] CDA Foundation. https://cdafound.org/dashboard/polaris/dashboard.html. https://cdafound.org/dashboard/polaris/dashboard.html [9] World Health Organization/UNICEF. WHO/UNICEF joint reporting process[EB/OL]. Geneva, 2019. https://www.who.int/treams/immunization- vaccines. https://www.who.int/treams/immunization- vaccines [10] COOKE GS, FLOWER B, CUNNINGHAM E, et al. Progress towards elimination of viral hepatitis: A Lancet Gastroenterology& Hepatology Commission update[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 9( 4): 346- 365. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00321-7. [11] US Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023 Viral hepatitis national progress report. 2024[EB/OL]. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/policy/npr/2023/index.htm https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/policy/npr/2023/index.htm [12] SU X, ZHENG L, ZHANG HM, et al. Secular trends of acute viral hepatitis incidence and mortality in China, 1990 to 2019 and its prediction to 2030: The global burden of disease study 2019[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2022, 9: 842088. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.842088. [13] YUE TT, ZHANG QQ, CAI T, et al. Trends in the disease burden of HBV and HCV infection in China from 1990-2019[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2022, 122: 476- 485. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.017. [14] SHI JF, CAO MM, WANG YT, et al. Is it possible to halve the incidence of liver cancer in China by 2050?[J]. Int J Cancer, 2021, 148( 5): 1051- 1065. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33313. [15] CUI FQ, SHEN LP, LI L, et al. Prevention of chronic hepatitis B after 3 decades of escalating vaccination policy, China[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2017, 23( 5): 765- 772. DOI: 10.3201/eid2305.161477. [16] LIANG X, BI SL, YANG WZ, et al. Epidemiological serosurvey of hepatitis B in China—declining HBV prevalence due to hepatitis B vaccination[J]. Vaccine, 2009, 27( 47): 6550- 6557. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.08.048. [17] LIU J, LIANG WN, JING WZ, et al. Countdown to 2030: Eliminating hepatitis B disease, China[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2019, 97( 3): 230- 238. DOI: 10.2471/BLT.18.219469. [18] ZHANG GM, MIAO N, ZHENG H, et al. Incidence by age and region of hepatitis B reported in China from 2005 to 2016[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2018, 24( 2): 121- 126. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2018.02.001.张国民, 缪宁, 郑徽, 等. 中国2005—2016年乙型病毒性肝炎报告发病的年龄和地区特征[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2018, 24( 2): 121- 126. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2018.02.001. [19] SO S, TERRAULT N, CONNERS EE. Universal adult hepatitis B screening and vaccination as the path to elimination[J]. JAMA, 2023, 329( 19): 1639- 1640. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.2806. [20] CONNERS EE, PANAGIOTAKOPOULOS L, HOFMEISTER MG, et al. Screening and testing for hepatitis B virus infection: CDC recommendations-United States, 2023[J]. MMWR Recomm Rep, 2023, 72( 1): 1- 25. DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.rr7201a1. [21] SU TH, KAO JH. Improving clinical outcomes of chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 9( 2): 141- 154. DOI: 10.1586/17474124.2015.960398. -



 PDF下载 ( 886 KB)
PDF下载 ( 886 KB)

 下载:
下载: