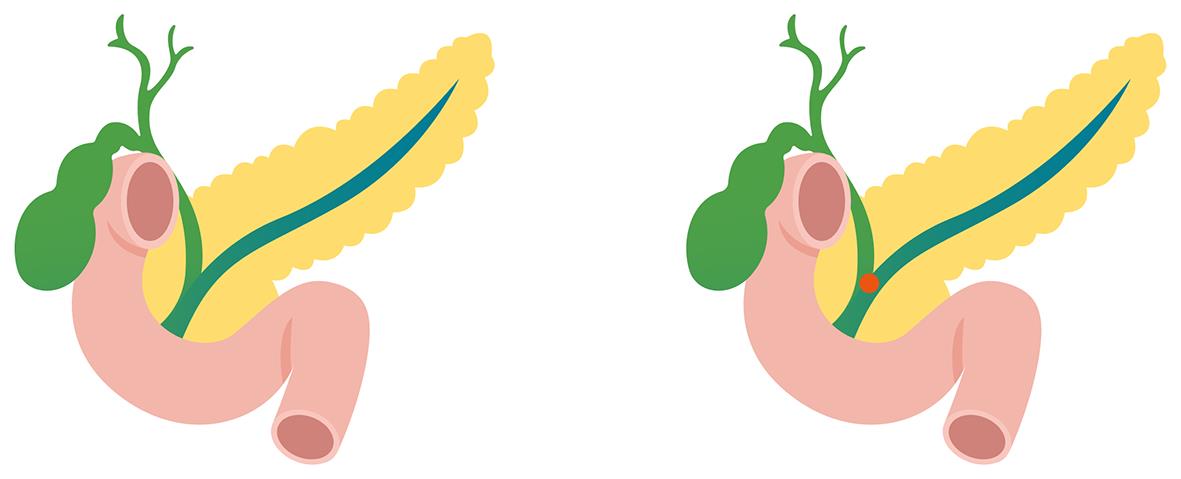
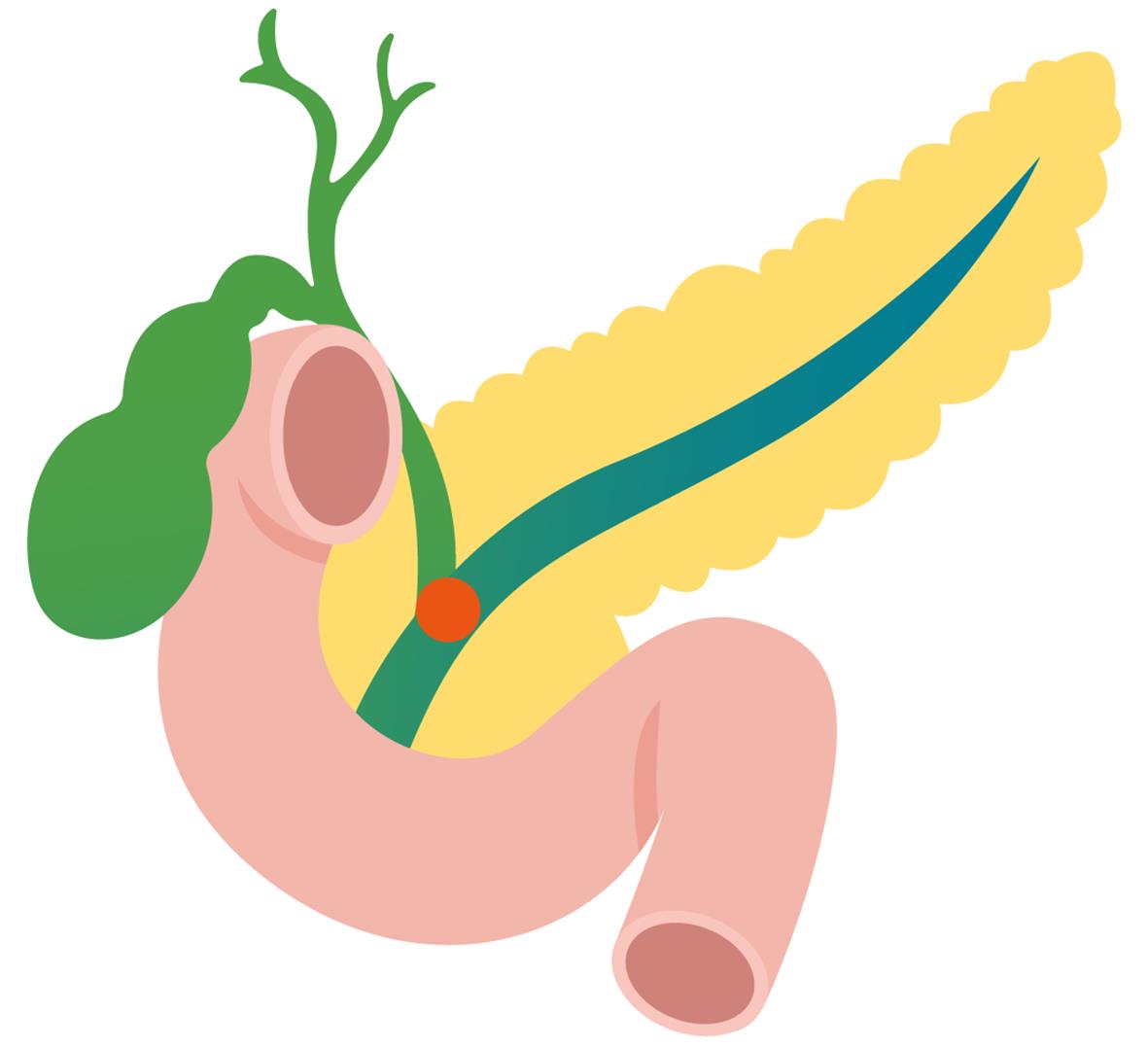
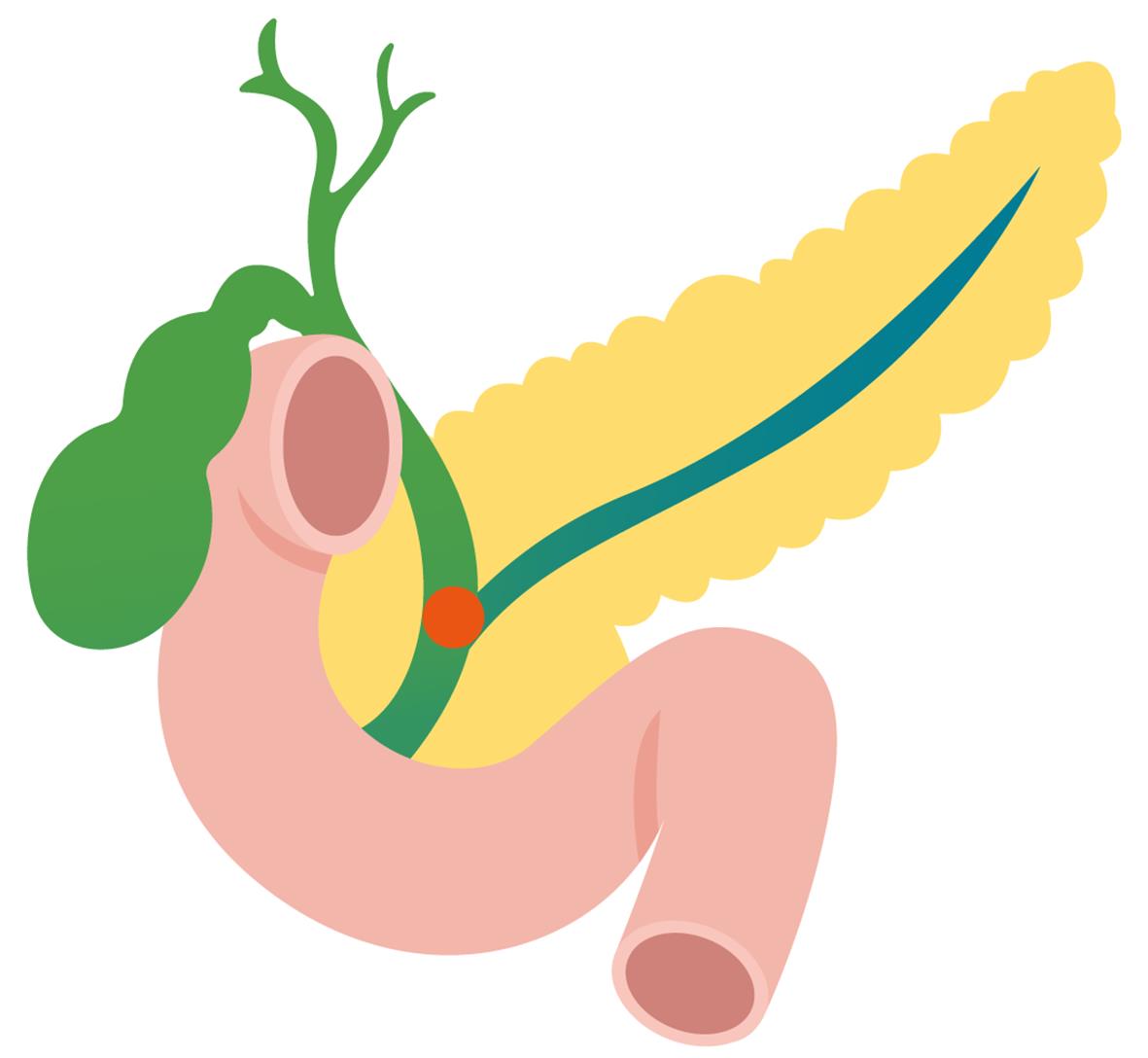
胰管高压导致高脂血症性急性胰腺炎的发病机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240134
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:张平负责课题设计;张平、冯佳晨进行查阅文献并起草论文,论文撰写及修改、校阅论文。
The pathogenesis of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis caused by pancreatic duct hypertension
-
摘要: 高脂血症性急性胰腺炎与其他病因的急性胰腺炎相比,重症率更高,预后更难预测,发病机制复杂且不清晰。目前已知的发病机制可能与血清游离脂肪酸升高有关,但降低血脂的治疗方案并未降低本病的发病率。近期,胰管高压是急性胰腺炎重要的发病机制被进一步证实,而最新研究进展表明高脂血症可通过引起胰管增生、形成胆胰管汇合部蛋白栓、损伤胰管的分泌功能来导致胰管堵塞,胰管堵塞又可引起胰管高压。本文综述了高脂血症在导致胰管堵塞方面的最新研究和进展,并强调胰管高压是高脂血症性急性胰腺炎重要的发病机制之一,这将为研究高脂血症性急性胰腺炎的发病机制提供新的思路。Abstract: Compared with acute pancreatitis caused by other factors, hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis often has a higher rate of severe conditions, greater difficulties in predicting prognosis, and a more complex and unclear pathogenesis. At present, the pathogenesis of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis may be associated with the elevation of serum free fatty acids, but the lipid-lowering treatment regimens do not reduce the incidence rate of this disease. Recent studies have further confirmed that pancreatic duct hypertension is an important pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. The latest research advances have shown that hyperlipidemia can lead to pancreatic duct obstruction by causing pancreatic duct hyperplasia, forming protein embolism at the biliary-pancreatic junction, and damaging the secretory function of the pancreatic duct, while pancreatic duct obstruction can in turn cause pancreatic duct obstruction. This article reviews the latest research advances in hyperlipidemia in causing pancreatic duct obstruction and emphasizes that pancreatic duct hypertension is one of the important pathogeneses of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis, which will provide new ideas for exploring the pathogenesis of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis.
-
Key words:
- Pancreatitis /
- Pancreatic duct hypertension /
- Hyperlipidemias
-
[1] BOXHOORN L, VOERMANS RP, BOUWENSE SA, et al. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396( 10252): 726- 734. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31310-6. [2] GARG PK, SINGH VP. Organ failure due to systemic injury in acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156( 7): 2008- 2023. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.041. [3] JOHNSON CD, BESSELINK MG, CARTER R. Acute pancreatitis[J]. BMJ, 2014, 349: g4859. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g4859. [4] SU W, GUO F. Triglyceride-controlling during acute phase of hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 1): 89- 93. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221220-00755.苏伟, 郭丰. 高甘油三酯血症性胰腺炎急性期的血脂控制[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22( 1): 89- 93. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221220-00755. [5] YANG AL, MCNABB-BALTAR J. Hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20( 5): 795- 800. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.06.005. [6] LI Q, HOU CQ, PENG YP, et al. Diabetes and younger age are vital and independent risk factors for acute pancreatitis in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 2620750. DOI: 10.1155/2019/2620750. [7] JIN M, BAI XY, CHEN XF, et al. A 16-year trend of etiology in acute pancreatitis: The increasing proportion of hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis and its adverse effect on prognosis[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2019, 13( 6): 947- 953. e 1. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.09.005. [8] ZAFRIR B, SALIBA W, JUBRAN A, et al. Severe hypertriglyceridemia-related pancreatitis: Characteristics and predictors of recurrence[J]. Pancreas, 2019, 48( 2): 182- 186. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001235. [9] JIN Q, YANG J, MA HL, et al. Value of different scoring systems in predicting the severity and prognosis of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 11): 2551- 2557. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.022.金秋, 杨婧, 马红琳, 等. 不同评分系统预测高脂血症性急性胰腺炎严重程度及预后的价值分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 11): 2551- 2557. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.022. [10] GUBENSEK J, BUTUROVIC-PONIKVAR J, ROMOZI K, et al. Factors affecting outcome in acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis treated with plasma exchange: An observational cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9( 7): e102748. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102748. [11] VALDIVIELSO P, RAMÍREZ-BUENO A, EWALD N. Current knowledge of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2014, 25( 8): 689- 694. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.08.008. [12] KISS L, FŰR G, PISIPATI S, et al. Mechanisms linking hypertriglyceridemia to acute pancreatitis[J]. Acta Physiol, 2023, 237( 3): e13916. DOI: 10.1111/apha.13916. [13] WANG B, XU XB, JIN XX, et al. Effects of ω-3 fatty acids on toll-like receptor 4 and nuclear factor κB p56 in the pancreas of rats with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2017, 46( 10): 1267- 1274. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000935. [14] SU YR, HONG YP, MEI FC, et al. High-fat diet aggravates the intestinal barrier injury via TLR4-RIP3 pathway in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2019, 2019: 2512687. DOI: 10.1155/2019/2512687. [15] SIMHA V. Management of hypertriglyceridemia[J]. BMJ, 2020: m3109. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.m3109. [16] HARVEY MH, WEDGWOOD KR, AUSTIN JA, et al. Pancreatic duct pressure, duct permeability and acute pancreatitis[J]. Br J Surg, 1989, 76( 8): 859- 862. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800760832. [17] LERCH MM, SALUJA AK, RÜNZI M, et al. Pancreatic duct obstruction triggers acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the opossum[J]. Gastroenterology, 1993, 104( 3): 853- 861. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91022-a. [18] ROMAC JM, SHAHID RA, SWAIN SM, et al. Piezo1 is a mechanically activated ion channel and mediates pressure induced pancreatitis[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9( 1): 1715. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04194-9. [19] SWAIN SM, ROMAC JM, SHAHID RA, et al. TRPV4 channel opening mediates pressure-induced pancreatitis initiated by Piezo1 activation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130( 5): 2527- 2541. DOI: 10.1172/JCI134111. [20] WEN L, JAVED TA, YIMLAMAI D, et al. Transient high pressure in pancreatic ducts promotes inflammation and alters tight junctions via calcineurin signaling in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155( 4): 1250- 1263.e5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.036. [21] LERCH MM, AGHDASSI AA, SENDLER M. Cell signaling of pancreatic duct pressure and its role in the onset of pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159( 3): 827- 831. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.027. [22] NORDSTOGA K, SØRBY R, OLIVECRONA G, et al. Pancreatitis in hyperlipemic mink(Mustela vison)[J]. Vet Pathol, 2012, 49( 3): 557- 561. DOI: 10.1177/0300985811417248. [23] KANEKO K, ANDO H, SEO T, et al. Proteomic analysis of protein plugs: Causative agent of symptoms in patients with choledochal cyst[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2007, 52( 8): 1979- 1986. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-006-9398-4. [24] KAMISAWA T, KANEKO K, ITOI T, et al. Pancreaticobiliary maljunction and congenital biliary dilatation[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 2( 8): 610- 618. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30002-X. [25] ZHAO CS, YAO WJ, WANG ZZ, et al. Efficacy of pancreatic duct stenting in treatment of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: A report of 33 cases[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2021, 30( 9): 1023- 1030. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2021.09.005.赵成思, 姚维杰, 王佐正, 等. 胰管支架治疗高三酰甘油血症性胰腺炎的疗效: 附33例报告[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2021, 30( 9): 1023- 1030. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2021.09.005. [26] WANG J, YANG CX. Discussion on the occurrence, prevention and treatment of biliary pancreatitis via analyzing the anatomy of choledocho-pancreatico-duodenal junction[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2020, 40( 11): 1263- 1265. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.11.09.王坚, 杨传鑫. 从胆胰肠结合部解剖谈胆源性胰腺炎发生与防治[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40( 11): 1263- 1265. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.11.09. [27] LEE MG, MUALLEM S. Pancreatitis: The neglected duct[J]. Gut, 2008, 57( 8): 1037- 1039. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2008.150961. [28] MORAN O. The gating of the CFTR channel[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2017, 74( 1): 85- 92. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2390-z. [29] MALÉTH J, BALÁZS A, PALLAGI P, et al. Alcohol disrupts levels and function of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to promote development of pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148( 2): 427- 439.e16. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.002. [30] LARUSCH J, JUNG J, GENERAL IJ, et al. Mechanisms of CFTR functional variants that impair regulated bicarbonate permeation and increase risk for pancreatitis but not for cystic fibrosis[J]. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10( 7): e1004376. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004376. -



 PDF下载 ( 671 KB)
PDF下载 ( 671 KB)

 下载:
下载: