| [1] |
ESLAM M, NEWSOME PN, SARIN SK, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 1): 202- 209. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039. |
| [2] |
National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. |
| [3] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, KOENIG AB, ABDELATIF D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64( 1): 73- 84. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28431. |
| [4] |
Chinese Diabetes Society. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes in china(2020 edition)[J]. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 2021, 41( 5): 482- 548. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121383-20210825-08063. |
| [5] |
BUNGAU S, BEHL T, TIT DM, et al. Interactions between leptin and insulin resistance in patients with prediabetes, with and without NAFLD[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20( 6): 197. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9327. |
| [6] |
LONARDO A, BALLESTRI S, MARCHESINI G, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a precursor of the metabolic syndrome[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2015, 47( 3): 181- 190. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2014.09.020. |
| [7] |
ADAMS LA, ANSTEE QM, TILG H, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases[J]. Gut, 2017, 66( 6): 1138- 1153. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313884. |
| [8] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, de AVILA L, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 4): 793- 801. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. |
| [9] |
PORTILLO-SANCHEZ P, BRIL F, MAXIMOS M, et al. High prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and normal plasma aminotransferase levels[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 100( 6): 2231- 2238. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-1966. |
| [10] |
WILD SH, MORLING JR, MCALLISTER DA, et al. Type 2 diabetes and risk of hospital admission or death for chronic liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64( 6): 1358- 1364. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.01.014. |
| [11] |
LEE SH, PARK SY, CHOI CS. Insulin resistance: from mechanisms to therapeutic strategies[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2022, 46( 1): 15- 37. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280. |
| [12] |
SZENDROEDI J, YOSHIMURA T, PHIELIX E, et al. Role of diacylglycerol activation of PKCθ in lipid-induced muscle insulin resistance in humans[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014, 111( 26): 9597- 9602. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1409229111. |
| [13] |
MENG FS, WANG XY, QI F, et al. Analysis of the mechanism and factors of IR in T2DM and its prevention and treatment strategy[J]. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2023, 25( 2): 128- 132. DOI: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2023.02.026. |
| [14] |
SHI XT, XU YN, WANG M, et al. Research progress of adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. China Med Herald, 2022, 19( 19): 41- 44, 65.
石项天, 徐亚楠, 王猛, 等. 脂质因子在非酒精性脂肪肝病中作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2022, 19( 19): 41- 44,65.
|
| [15] |
TANASE DM, GOSAV EM, COSTEA CF, et al. The intricate relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM), insulin resistance(IR), and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020: 3920196. DOI: 10.1155/2020/3920196. |
| [16] |
MIKAMI K, ENDO T, SAWADA N, et al. Leptin/adiponectin ratio correlates with hepatic steatosis but not arterial stiffness in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japanese population[J]. Cytokine, 2020, 126: 154927. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154927. |
| [17] |
AHMED ES, MOHAMED HE, FARRAG MA. Luteolin loaded on zinc oxide nanoparticles ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with insulin resistance in diabetic rats via regulation of PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2022, 36: 3946320221137435. DOI: 10.1177/03946320221137435. |
| [18] |
YU Y, MAGUIRE TG, ALWINE JC. ChREBP, a glucose-responsive transcriptional factor, enhances glucose metabolism to support biosynthesis in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014, 111( 5): 1951- 1956. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1310779111. |
| [19] |
FARZANEGI P, DANA A, EBRAHIMPOOR Z, et al. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Eur J Sport Sci, 2019, 19( 7): 994- 1003. DOI: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1571114. |
| [20] |
YUAN Y, LIU Q, ZHAO F, et al. Holothuria leucospilota polysaccharides ameliorate hyperlipidemia in high-fat diet-induced rats via short-chain fatty acids production and lipid metabolism regulation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20( 19): 4738. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20194738. |
| [21] |
WU HZ, BALLANTYNE CM. Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 126( 11): 1549- 1564. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315896. |
| [22] |
YUNG JHM, GIACCA A. Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase(JNK) in obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 3): 706. DOI: 10.3390/cells9030706. |
| [23] |
DU H, DUAN SD, LEI R, et al. Astragalin inhibits insulin resistance and oxidative stress in palmitic acid-induced hepg2 cells[J]. Curr Top Nutraceutical Res, 2022, 20( 4): 635- 640. DOI: 10.37290/ctnr2641-452X.20:635-640. |
| [24] |
LEE J, WAN J, LEE L, et al. Study of the NLRP3 inflammasome component genes and downstream cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with carotid atherosclerosis[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16( 1): 217. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0595-2. |
| [25] |
CHEN YL, QIAO YC, XU Y, et al. Serum TNF-α concentrations in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and diabetic nephropathy patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Immunol Lett, 2017, 186: 52- 58. DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.04.003. |
| [26] |
SUN TT, LI JT, WEI HL, et al. Research advances in the role of the TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway in the regulation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 9): 2095- 2098. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.047. |
| [27] |
BAI SQ, NONG XL, ZHANG SQ, et al. Study on the effects of artesunate on liver of type 2 diabetic rats based on p38MAPK/IL-6 signal pathway[J]. J Guangxi Med Univ, 2022, 39( 4): 557- 563. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2022.04.008. |
| [28] |
HENDAWY AS, EL-LAKKANY NM, MANTAWY EM, et al. Vildagliptin alleviates liver fibrosis in NASH diabetic rats via modulation of insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammatory cascades[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 304: 120695. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120695. |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
ROSHANZAMIR F, MIRAGHAJANI M, ROUHANI MH, et al. The association between circulating fetuin-A levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2018, 41( 1): 33- 47. DOI: 10.1007/s40618-017-0697-8. |
| [31] |
MONTGOMERY MK, BAYLISS J, NIE S, et al. Deep proteomic profiling unveils arylsulfatase A as a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis inducible hepatokine and regulator of glycemic control[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13( 1): 1259. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28889-2. |
| [32] |
ZHANG LF, HAO YM. Study on selenoprotein p in type 2diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Baotou Med Coll, 2018, 34( 9): 95- 96. DOI: 10.16833/j.cnki.jbmc.2018.09.040. |
| [33] |
KE Y, XU C, LIN J, et al. Role of hepatokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Transl Int Med, 2019, 7( 4): 143- 148. DOI: 10.2478/jtim-2019-0029. |
| [34] |
GU L, ZHANG Y, ZHANG S, et al. Coix lacryma-JOBI seed oil reduces fat accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the activation of the p-AMPK/SePP1/apoER2 pathway[J]. J Oleo Sci, 2021, 70( 5): 685- 696. DOI: 10.5650/jos.ess20255. |
| [35] |
CHO YM, KIM DH, LEE KH, et al. The IRE1α-XBP1s pathway promotes insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes by increasing PPARγ activity[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2018, 50( 8): 1- 15. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-018-0131-0. |
| [36] |
REGULSKI MJ. Cellular senescence: what, why, and how[J]. Wounds, 2017, 29( 6): 168- 174.
|
| [37] |
DEEVSKA G, DOTSON PN, MITOV M, et al. Onset of senescence and steatosis in hepatocytes as a consequence of a shift in the diacylglycerol/ceramide balance at the plasma membrane[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 6): 1278. DOI: 10.3390/cells10061278. |
| [38] |
WAN Y, LIU Z, WU A, et al. Hyperglycemia promotes endothelial cell senescence through AQR/PLAU signaling axis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 5): 2879. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23052879. |
| [39] |
LIU Y, GUO J, ZHANG ML, et al. Study of fistular onion stalk extract activating mitochondrial metabolism on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rats by inducing pgc-1α[J]. Tianjin J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 38( 2): 247- 253. DOI: 10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2021.02.22. |
| [40] |
ENGELMANN C, TACKE F. The potential role of cellular senescence in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 2): 652. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020652. |
| [41] |
ROBBINS PD, JURK D, KHOSLA S, et al. Senolytic drugs: reducing senescent cell viability to extend health span[J]. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 2021, 61: 779- 803. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-050120-105018. |
| [42] |
NARASIMHAN A, FLORES RR, ROBBINS PD, et al. Role of cellular senescence in type ii diabetes[J]. Endocrinology, 2021, 162( 10): bqab136. DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqab136. |
| [43] |
MEIJNIKMAN AS, HERREMA H, SCHEITHAUER T, et al. Evaluating causality of cellular senescence in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3( 4): 100301. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100301. |
| [44] |
ZHANG CY, TAN XH, YANG HH, et al. COX-2/sEH dual inhibitor alleviates hepatocyte senescence in NAFLD mice by restoring autophagy through Sirt1/PI3K/AKT/mTOR[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 15): 8267. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158267. |
| [45] |
VACUROVA E, TRNOVSKA J, SVOBODA P, et al. Mitochondrially targeted tamoxifen alleviates markers of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13( 1): 1866. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29486-z. |



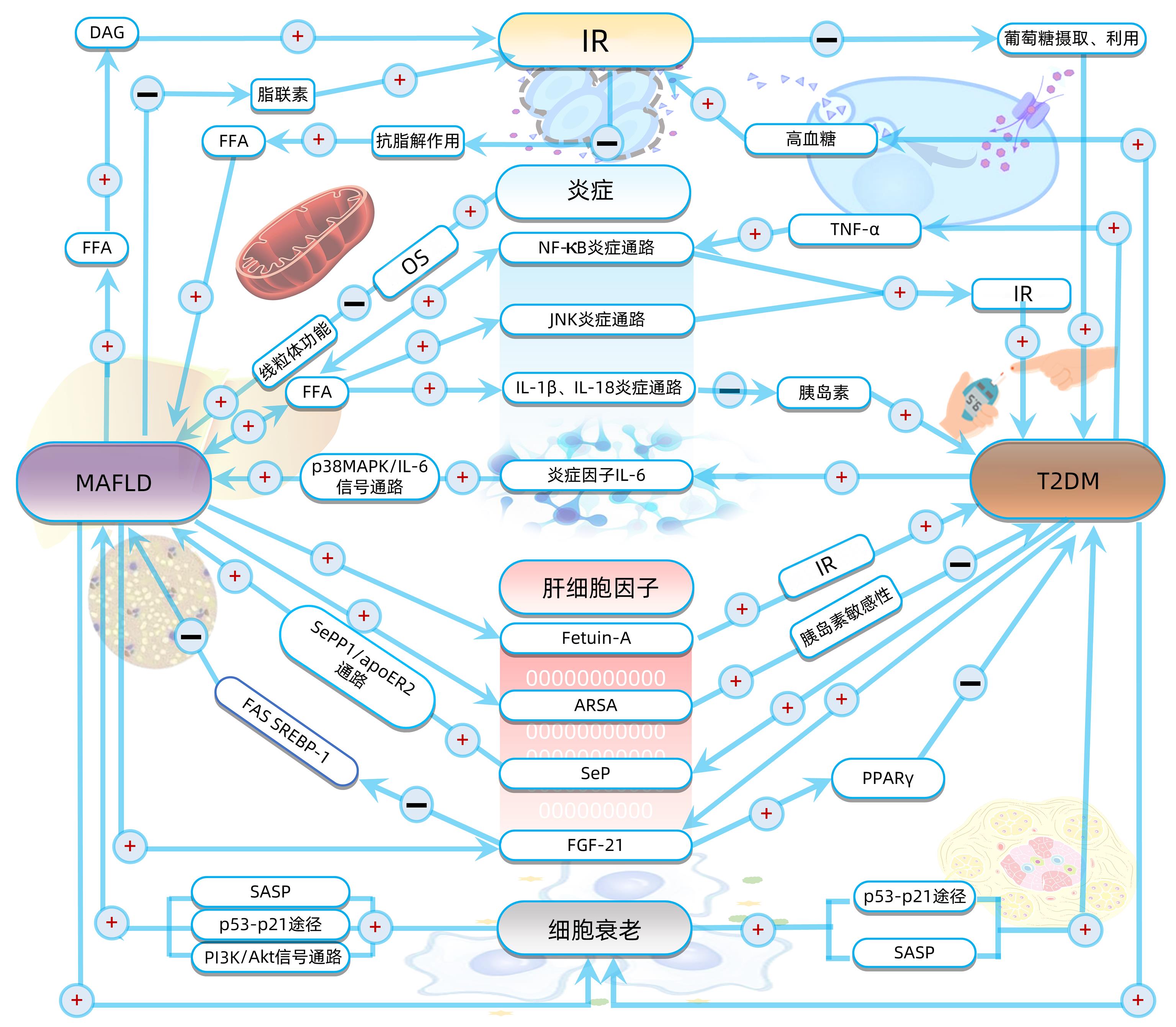




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: