| [1] |
BUNCHORNTAVAKUL C, REDDY KR. Review article: malnutrition/sarcopenia and frailty in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 51( 1): 64- 77. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15571. |
| [2] |
PONZIANI FR, GASBARRINI A. Sarcopenia in patients with advanced liver disease[J]. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2018, 19( 7): 681- 691. DOI: 10.2174/1389203718666170428121647. |
| [3] |
ANAND A, MOHTA S, AGARWAL S, et al. European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People(EWGSOP2) criteria with population-based skeletal muscle index best predicts mortality in Asians with cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2022, 12( 1): 52- 60. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.03.015. |
| [4] |
PRADO CM, LIEFFERS JR, MCCARGAR LJ, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2008, 9( 7): 629- 635. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70153-0. |
| [5] |
CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2020, 21( 3): 300- 307. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012 |
| [6] |
CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis[J]. Age Ageing, 2019, 48( 1): 16- 31. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afy169. |
| [7] |
YIN Y, QI XS, YANG YP. Assessment and management of nutritional status in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Med J Chin PLA, 2023, 48( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2023.01.0013. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
QIU J, THAPALIYA S, RUNKANA A, et al. Hyperammonemia in cirrhosis induces transcriptional regulation of myostatin by an NF-κB-mediated mechanism[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110( 45): 18162- 18167. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1317049110. |
| [10] |
DENG W, CHEN Q, GONG ZJ. Research progress on the pathogenesis of sarcopenia in end-stage liver disease[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 31( 8): 942- 946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2022.08.020. |
| [11] |
SINCLAIR M, GROSSMANN M, HOERMANN R, et al. Testosterone therapy increases muscle mass in men with cirrhosis and low testosterone: A randomised controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65( 5): 906- 913. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.06.007. |
| [12] |
MOCTEZUMA-VELÁZQUEZ C, LOW G, MOURTZAKIS M, et al. Association between low testosterone levels and sarcopenia in cirrhosis: A cross-sectional study[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2018, 17( 4): 615- 623. DOI: 10.5604/01.3001.0012.0930. |
| [13] |
SINCLAIR M, GOW PJ, GROSSMANN M, et al. Review article: sarcopenia in cirrhosis——aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43( 7): 765- 777. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13549. |
| [14] |
MARZETTI E, CALVANI R, CESARI M, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and sarcopenia of aging: from signaling pathways to clinical trials[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2013, 45( 10): 2288- 2301. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.024. |
| [15] |
ROMANELLO V, GUADAGNIN E, GOMES L, et al. Mitochondrial fission and remodelling contributes to muscle atrophy[J]. EMBO J, 2010, 29( 10): 1774- 1785. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.60. |
| [16] |
EBADI M, BHANJI RA, MAZURAK VC, et al. Sarcopenia in cirrhosis: from pathogenesis to interventions[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2019, 54( 10): 845- 859. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-019-01605-6. |
| [17] |
TUTTLE C, THANG L, MAIER AB. Markers of inflammation and their association with muscle strength and mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2020, 64: 101185. DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101185. |
| [18] |
PAN L, XIE W, FU X, et al. Inflammation and sarcopenia: A focus on circulating inflammatory cytokines[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2021, 154( 15): 111544. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111544 |
| [19] |
BANO G, TREVISAN C, CARRARO S, et al. Inflammation and sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Maturitas, 2017, 96: 10- 15. DOI: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.11.006. |
| [20] |
ABRIGO J, GONZALEZ F, AGUIRRE F, et al. Cholic acid and deoxycholic acid induce skeletal muscle atrophy through a mechanism dependent on TGR5 receptor[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236( 1): 260- 272. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29839. |
| [21] |
O’BRIEN A, CHINA L, MASSEY KA, et al. Bile duct-ligated mice exhibit multiple phenotypic similarities to acute decompensation patients despite histological differences[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36( 6): 837- 846. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12876. |
| [22] |
BHANJI RA, MOCTEZUMA-VELAZQUEZ C, DUARTE-ROJO A, et al. Myosteatosis and sarcopenia are associated with hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12( 4): 377- 386. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-9875-9. |
| [23] |
MEYER F, BANNERT K, WIESE M, et al. Molecular mechanism contributing to malnutrition and sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 15): 5357. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155357 |
| [24] |
FAN J, KOU X, JIA S, et al. Autophagy as a potential target for sarcopenia[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2016, 231( 7): 1450- 1459. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25260. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
BHAT M, KALAM R, QADRI SS, et al. Vitamin D deficiency-induced muscle wasting occurs through the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and is partially corrected by calcium in male rats[J]. Endocrinology, 2013, 154( 11): 4018- 4029. DOI: 10.1210/en.2013-1369. |
| [27] |
GIRGIS CM, CHA KM, HOUWELING PJ, et al. Vitamin D receptor ablation and vitamin D deficiency result in reduced grip strength, altered muscle fibers, and increased myostatin in mice[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2015, 97( 6): 602- 610. DOI: 10.1007/s00223-015-0054-x. |
| [28] |
HANAI T, SHIRAKI M, MIWA T, et al. Effect of loop diuretics on skeletal muscle depletion in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49( 1): 82- 95. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13244. |
| [29] |
MANDAI S, FURUKAWA S, KODAKA M, et al. Loop diuretics affect skeletal myoblast differentiation and exercise-induced muscle hypertrophy[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7( 1): 1- 9. DOI: 10.1038/srep46369. |
| [30] |
NAKANO I, TSUDA M, KINUGAWA S, et al. Loop diuretic use is associated with skeletal muscle wasting in patients with heart failure[J]. J Cardiol, 2020, 76( 1): 109- 114. DOI: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2020.01.003. |
| [31] |
ISHIKAWA S, NAITO S, IIMORI S, et al. Loop diuretics are associated with greater risk of sarcopenia in patients with non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13( 2): e0192990. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192990. |
| [32] |
LIU XL, HUANG JM, LIU JH, et al. Clinical value of the third lumbar skeletal muscle index in patients with cirrhosis and sarcopenia[J] Jiangxi Med J, 2021, 56( 12): 2183- 2184, 2190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2021.12.024. |
| [33] |
KANG SH, JEONG WK, BAIK SK, et al. Impact of sarcopenia on prognostic value of cirrhosis: going beyond the hepatic venous pressure gradient and MELD score[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2018, 9( 5): 860- 870. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12333. |
| [34] |
KIM G, KANG SH, KIM MY, et al. Prognostic value of sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12( 10): e0186990. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186990. |
| [35] |
LI X, FU YM, SUN Y, et al. Research progress in correlation between vitamin D and sarcopenia in the elderly[J]. Med Recapitulate, 2021, 27( 3): 436- 441. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.03.004. |
| [36] |
UCHITOMI R, OYABU M, KAMEI Y. Vitamin D and sarcopenia: Potential of vitamin D supplementation in sarcopenia prevention and treatment[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12( 10): 3189. DOI: 10.3390/nu12103189 |
| [37] |
KUMAR A, DAVULURI G, SILVA R, et al. Ammonia lowering reverses sarcopenia of cirrhosis by restoring skeletal muscle proteostasis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65( 6): 2045- 2058. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29107. |
| [38] |
LIU YY, CHEN DF, YAN QX. Current status of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 191- 195. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.033. |
| [39] |
MOHTA S, ANAND A, SHARMA S, et al. Randomised clinical trial: effect of adding branched chain amino acids to exercise and standard-of-care on muscle mass in cirrhotic patients with sarcopenia[J]. Hepatol Int, 2022, 16( 3): 680- 690. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-022-10334-7. |
| [40] |
AAMANN L, DAM G, BORRE M, et al. Resistance training increases muscle strength and muscle size in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18( 5): 1179- 1187. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.058 |
| [41] |
THOMPSON JL, BUTTERFIELD GE, GYLFADOTTIR UK, et al. Effects of human growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I, and diet and exercise on body composition of obese postmenopausal women[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1998, 83( 5): 1477- 1484. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.83.5.4826. |
| [42] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Clinical guidelines on nutrition in end-stage liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 6): 1222- 1230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.010. |
| [43] |
HEY P, GOW P, TESTRO AG, et al. Nutraceuticals for the treatment of sarcopenia in chronic liver disease[J]. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 2021, 41: 13- 22. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.11.015. |
| [44] |
BURTON LA, MCMURDO ME, STRUTHERS AD. Mineralocorticoid antagonism: a novel way to treat sarcopenia and physical impairment in older people?[J]. Clin Endocrinol(Oxf), 2011, 75( 6): 725- 729. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04148.x. |
| [45] |
NAMBA M, HIRAMATSU A, AIKATA H, et al. Management of refractory ascites attenuates muscle mass reduction and improves survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2020, 55( 2): 217- 226. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-019-01623-4. |



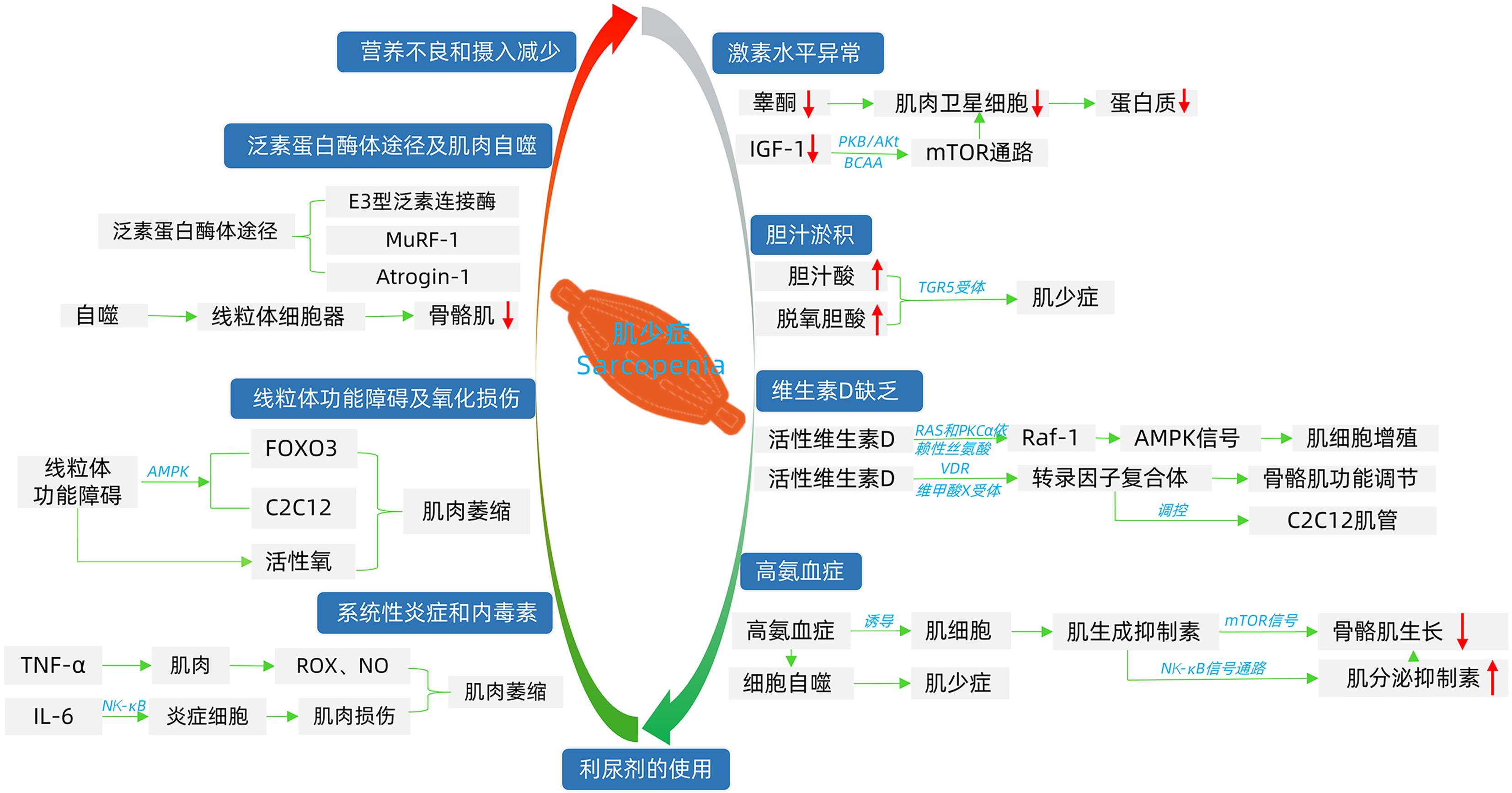




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: