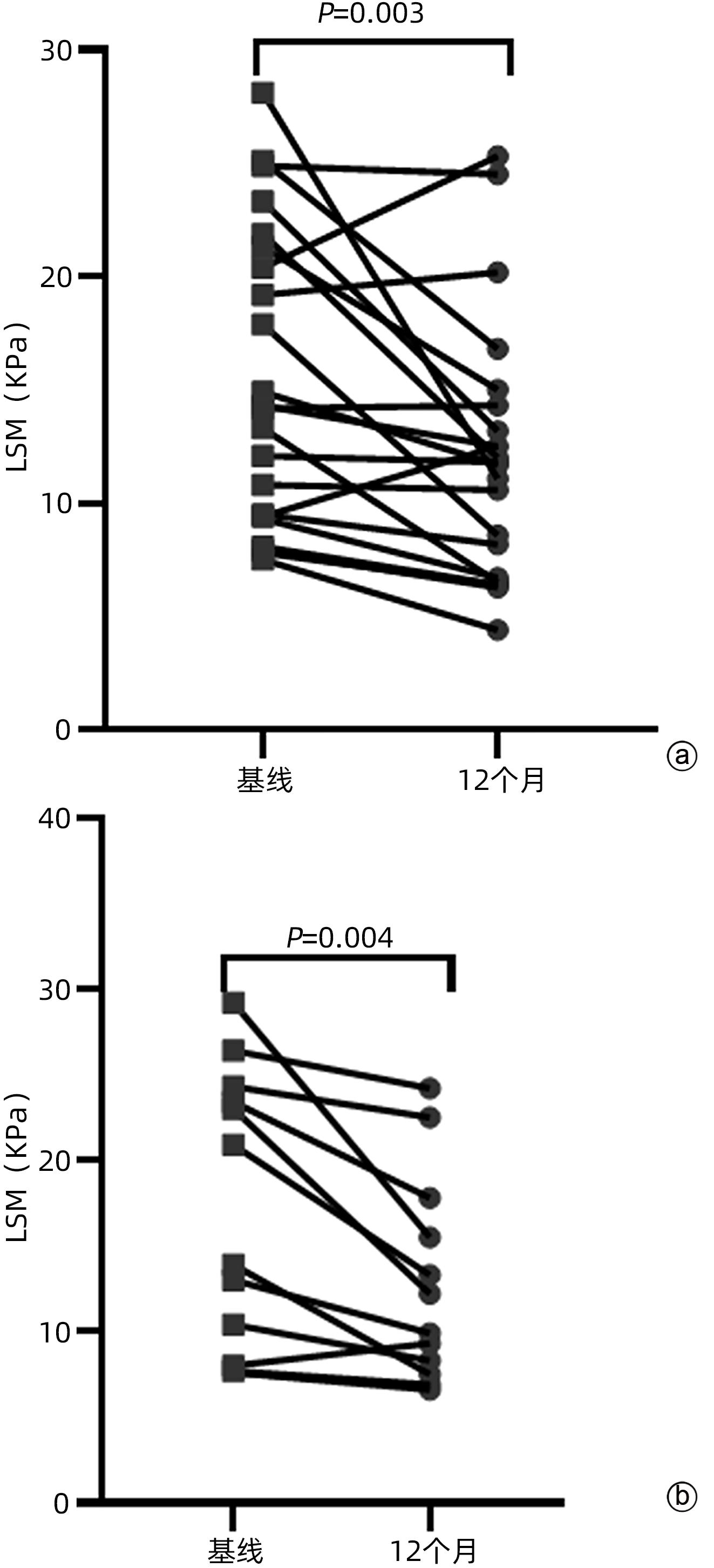
| [1] |
Inherited Metabolic Liver Disease Collaboration Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatolenticular degeneration(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 1): 9- 20. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20211217-00603. |
| [2] |
REN MS, ZHANG Z, CAI YL, et al. Comparison of long-term therapeutic effects between succimer and penicillamine in hepatolenticular degeneration[J]. Chin J New Drugs Clin Remed, 2000, 19( 3): 166- 169. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7669.2000.03.003. |
| [3] |
KALITA J, KUMAR V, RANJAN A, et al. Role of oxidative stress in the worsening of neurologic Wilson disease following chelating therapy[J]. Neuromolecular Med, 2015, 17( 4): 364- 372. DOI: 10.1007/s12017-015-8364-8. |
| [4] |
BREWER GJ, ASKARI F, DICK RB, et al. Treatment of Wilson’s disease with tetrathiomolybdate: V. Control of free copper by tetrathiomolybdate and a comparison with trientine[J]. Transl Res, 2009, 154( 2): 70- 77. DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2009.05.002. |
| [5] |
LI WJ, WANG XP. The therapeutic drug for Wilson’s disease, dimercaptosuccinic acid(sodium)[J]. World Clin Drugs, 2012, 33( 9): 574- 576.
李文杰, 王晓平. 肝豆状核变性治疗药物二巯丁二酸(钠)[J]. 世界临床药物, 2012, 33( 9): 574- 576.
|
| [6] |
KEMP W, LEVY M, WELTMAN M, et al. Australian Liver Association(ALA) expert consensus recommendations for the use of transient elastography in chronic viral hepatitis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30( 3): 453- 462. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12865. |
| [7] |
ZHOU SM, GUO LP, CAI WF, et al. Latest advances in the treatment of hepatolenticular degeneration[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 1): 218- 221. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.052. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
BREWER GJ, DICK RD, JOHNSON VD, et al. Treatment of Wilson’s disease with zinc: XV long-term follow-up studies[J]. J Lab Clin Med, 1998, 132( 4): 264- 278. DOI: 10.1016/s0022-2143(98)90039-7. |
| [12] |
Chinese Foundation for Hepatitis Prevention and Control; Chinese Society of Infectious Disease and Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Liver Disease Committee of Chinese Research Hospital Association. Consensus on clinical application of transient elastography detecting liver fibrosis: a 2018 update[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2019, 27( 3): 182- 191. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.03.004. |
| [13] |
ZHOU XX, PU XY, XIAO X, et al. Observation on the changes of clinical symptoms, blood and brain copper deposition in Wilson disease patients treated with dimercaptosuccinic acid for 2 years[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2020, 81: 448- 454. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.09.017. |



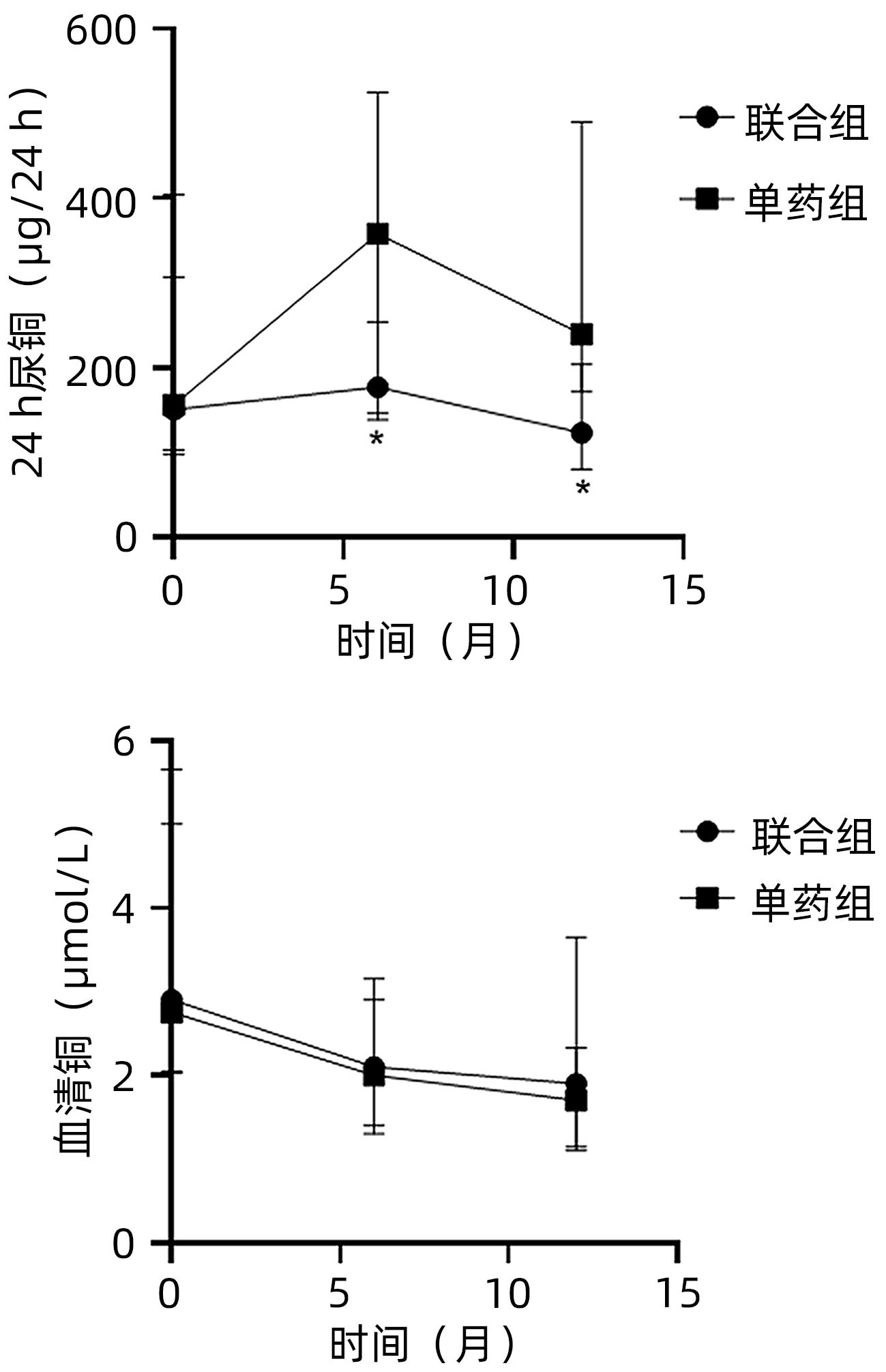




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: