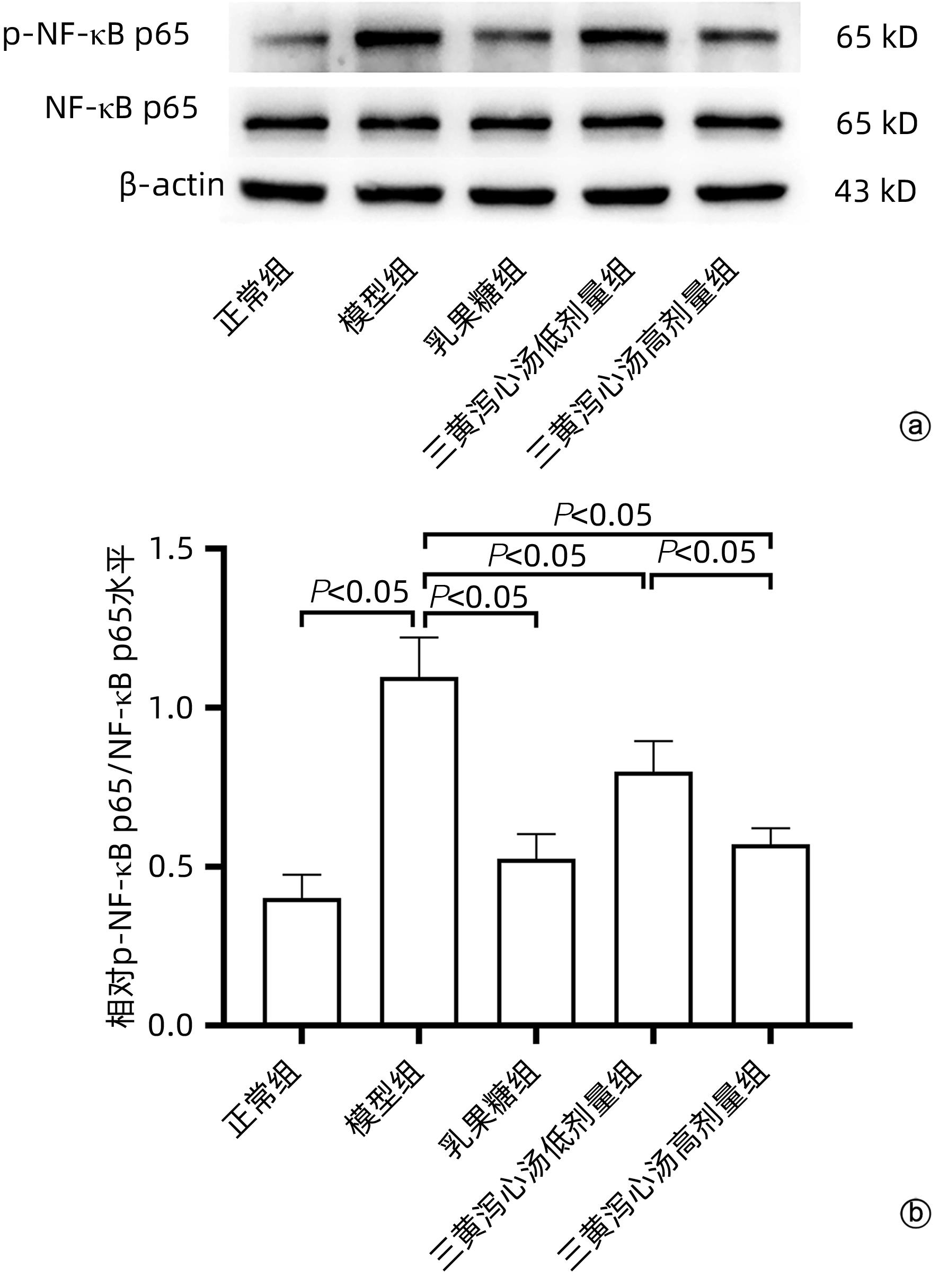
| [1] |
ROSE CF, AMODIO P, BAJAJ JS, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 6): 1526- 1547. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.013. |
| [2] |
SAID VJ, GARCIA-TRUJILLO E. Beyond lactulose: Treatment options for hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Gastroenterol Nurs, 2019, 42( 3): 277- 285. DOI: 10.1097/SGA.0000000000000376. |
| [3] |
YAO JQ, XIAO YQ, LIU Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect comparison of water and ethanol extracts of Sanhuang Xiexin Tang and component analysis of its active extracts[J]. Chin J Exp Med Formul, 2015, 21( 13): 31- 35. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2015130031. |
| [4] |
WANG YX, LIU WW, LI XP, et al. Determination of activity of Sanhuang Xiexin decoction in inhibiting drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vitro[J]. J Pract Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 34( 4): 500- 501. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2814.2018.04.096. |
| [5] |
YUE LJ, LIU C, ZHANG HJ, et al. Clinical effect of Sanhuang Xiexin decoction on patients with upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage and its influence on hemoglobin, urea nitrogen and Rockall score[J]. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 42( 5): 594- 596, 600. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2021.05.012. |
| [6] |
ZHOU XX, ZENG SL, YAN HP, et al. Retention enema therapy with rhubarb decoction in the adjuvant treatment of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Guangxi Univ Chin Med, 2022, 25( 1): 12- 16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4441.2022.01.003. |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
LIU MH, LI K, ZHENG HJ. Effect of Angong Niuhuang Pill on TNF-α/NF-κB signal pathway and neurological function in rats with hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Drugs& Clinic, 2021, 36( 11): 2217- 2223. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2021.11.001. |
| [9] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. |
| [10] |
LE YY, ZHANG RZ, XIAO WS, et al. Research progress in pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2022, 32( 5): 468- 472. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2022.05.023. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
SEPEHRINEZHAD A, ZARIFKAR A, NAMVAR G, et al. Astrocyte swelling in hepatic encephalopathy: molecular perspective of cytotoxic edema[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2020, 35( 4): 559- 578. DOI: 10.1007/s11011-020-00549-8. |
| [13] |
RAMA RAO KV, JAYAKUMAR AR, TONG X, et al. Marked potentiation of cell swelling by cytokines in ammonia-sensitized cultured astrocytes[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2010, 7: 66. DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-66. |
| [14] |
JAYAKUMAR AR, RAMA RAO KV, NORENBERG MD. Neuroinflammation in hepatic encephalopathy: mechanistic aspects[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2015, 5( Suppl 1): S21-S28. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.07.006. |
| [15] |
LU L, WU C, LU BJ, et al. BabaoDan cures hepatic encephalopathy by decreasing ammonia levels and alleviating inflammation in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 249: 112301. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112301. |
| [16] |
YANG C, TAN Y, LI F, et al. Intestinal microecology of mice exposed to TiO 2 nanoparticles and bisphenol A[J]. Foods, 2022, 11( 12): 1696. DOI: 10.3390/foods11121696. |
| [17] |
RAI R, SARASWAT VA, DHIMAN RK. Gut microbiota: its role in hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2015, 5( Suppl 1): S29-S36. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.12.003. |
| [18] |
AHLUWALIA V, BETRAPALLY NS, HYLEMON PB, et al. Impaired gut-liver-brain axis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 26800. DOI: 10.1038/srep26800. |
| [19] |
ZHOU Z, LI K, GUO J, et al. Green tea catechin EGCG ameliorates thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats via modulation of the microbiota-gut-liver axis[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2022: e2200821. DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.202200821. |
| [20] |
JIANG HN, MAO DW, YE QL, et al. Research progress in treatment of hepatic encephalopathy based on syndrome differentiation[J]. Shaanxi J Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 41( 11): 1678- 1680. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2020.11.042. |
| [21] |
FU DQ, XU L, GE EN, et al. Research of effective component dissolution rules of Sanhuang Xiexin Decoction[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 38( 10): 16- 19. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2020.10.004. |
| [22] |
LI L, WANG Y, ZHAO L, et al. Sanhuang xiexin decoction ameliorates secondary liver injury in DSS-induced colitis involve regulating inflammation and bile acid metabolism[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 299: 115682. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115682. |
| [23] |
MA BL, MA YM, YAN DM, et al. Effective constituents in Xiexin Decoction for anti-inflammation[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2009, 125( 1): 151- 156. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.05.035. |
| [24] |
MANZHALII E, VIRCHENKO O, FALALYEYEVA T, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy aggravated by systemic inflammation[J]. Dig Dis, 2019, 37( 6): 509- 517. DOI: 10.1159/000500717. |
| [25] |
ZHANG Y, CHEN W, MENG XL. The protective effect of Sanhuangxiexin Decoction against oxidative stress and inflammation injury of global cerebral ischemia reperfusion rats[J]. Pharmocol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2014, 30( 4): 1- 5. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2014.04.001. |



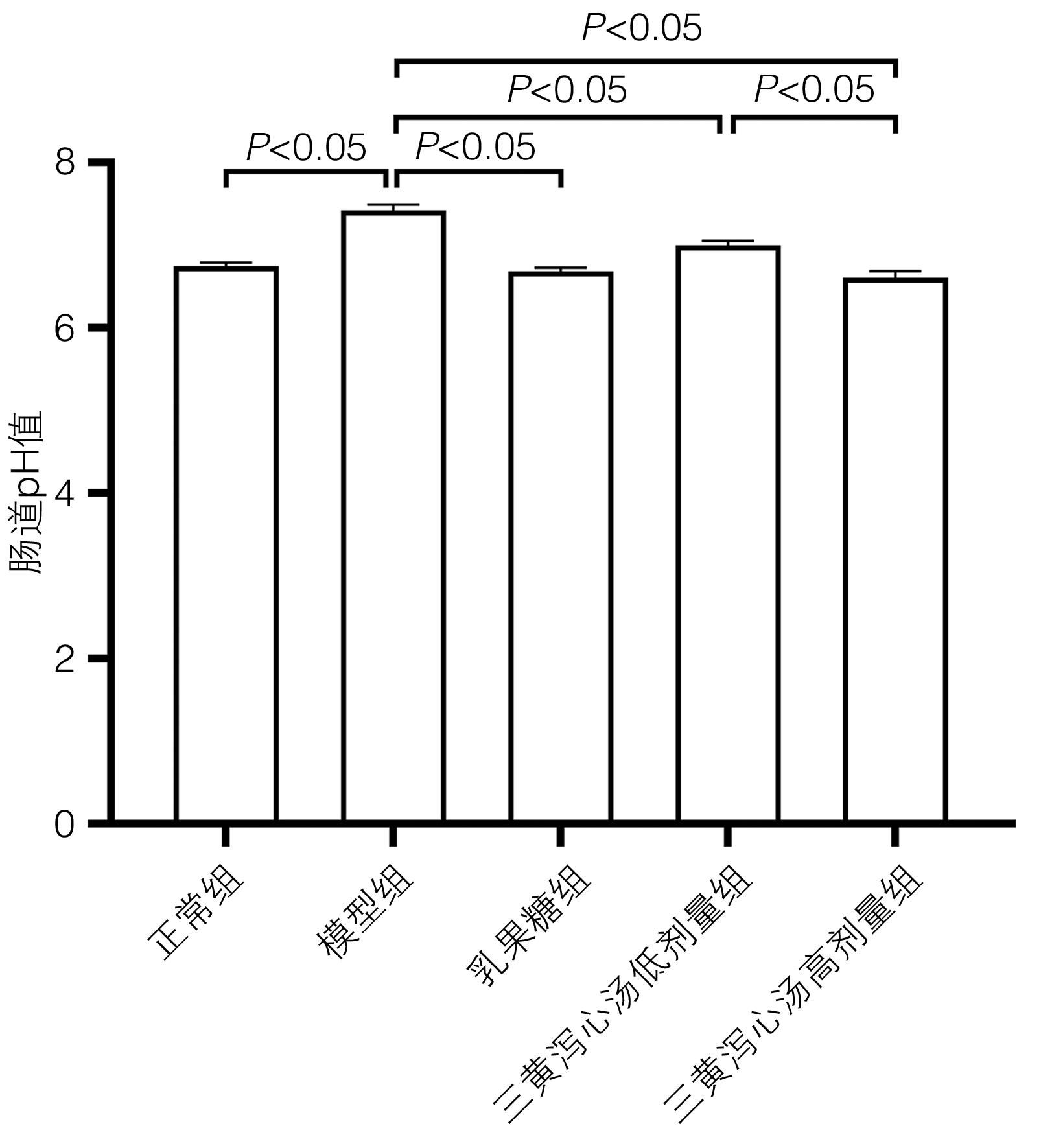




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: