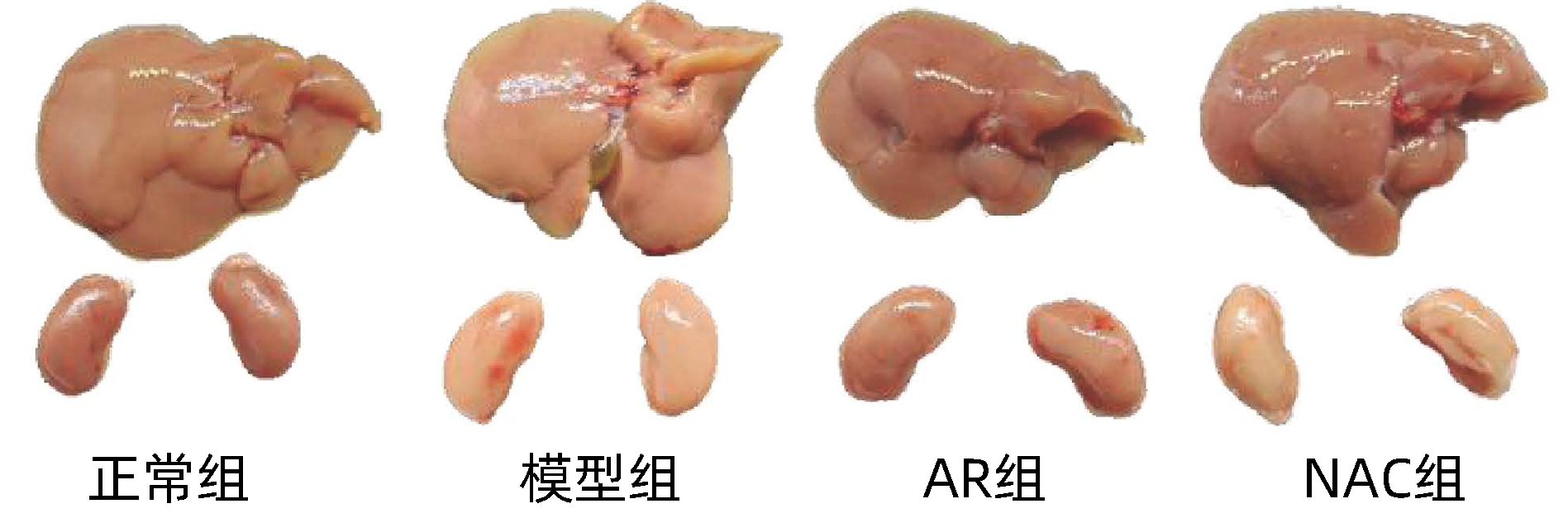
| [1] |
JI HJ, LI JY, WU SF, et al. Two new aristolochic acid analogues from the roots of Aristolochia contorta with significant cytotoxic activity[J]. Molecules, 2020, 26(1): 44. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010044. |
| [2] |
HAN JY, XIAN Z, ZHANG YS, et al. Systematic overview of aristolochic acids: Nephrotoxicity, carcinogenicity, and underlying mechanisms[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 648. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00648. |
| [3] |
ZHU GR, WANG J, HUANG K, et al. A transcriptomic analysis of acute hepatotoxicity induced by aristolochic acid Ⅰ in mice[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(10): 2389-2394. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.10.026. |
| [4] |
WANG F, WANG J, HUANG K, et al. Study on mechanism of aristolochic acid I induced acute kidney injury[J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2022, 34(5): 848-855. DOI: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2022.5.014. |
| [5] |
CAO YX, LI K, QIN XM, et al. Comparative study on different areas of Astragali Radix based on oligosaccharides characteristic map and immunological activity evaluation of partial acid hydrolyzed[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2020, 51(21): 5598-5606. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.21.025. |
| [6] |
HU NN, ZHANG XJ. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Inf Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 38(1): 76-82. DOI: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.210118. |
| [7] |
CUI Y, LI HS, SONG NN, et al. Metabonomics reveals that aristolochic acid Ⅰ affects β-oxidation of fatty acids, glucose metabolism and the TCA cycle in the mice liver[J]. Chin J Pharmacovigil, 2019, 16(8): 449-466. DOI: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.2019.08.001. |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
PENG Y, ZHU GR, MA YY, et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction and pharmacological validation of effects of Astragali Radix on acetaminophen-induced liver injury[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 697644. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.697644. |
| [10] |
LUO JH, YANG YB. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on oxidative stress in acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2012, 18(19): 170-175. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2012.19.052. |
| [11] |
WANG J, ZHAO S, REN BH. Protective effect and mechanism of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity[J]. Chin J Immunol, 2020, 36(4): 390-394. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.04.002. |
| [12] |
WANG D, QI J, PAN XQ, et al. The antagonistic effect and mechanism of N-acetylcysteine on acrylamide-induced hepatic and renaltoxicity[J]. Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis, 2016, 34(1): 13-17.
王敦, 齐健, 潘校琦, 等. N-乙酰半胱氨酸拮抗丙烯酰胺的肝肾毒性及机制[J]. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2016, 34(1): 13-17.
|
| [13] |
WU N, GAO X, YE ZH, et al. Inheritance and innovation of theory of homogeny of liver and kidney for LI Hanmin[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 36(3): 619-622. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2018.03.025. |
| [14] |
ANGER EE, YU F, LI J. Aristolochic acid-induced nephrotoxicity: Molecular mechanisms and potential protective approaches[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(3): 1157. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21031157. |
| [15] |
DAI ZC, WANG XH, PENG RX, et al. Induction of IL-6Rα by ATF3 enhances IL-6 mediated sorafenib and regorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2022, 524: 161-171. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.024. |
| [16] |
CLEMENS MM, KENNON-MCGILL S, VAZQUEZ JH, et al. Exogenous phosphatidic acid reduces acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice by activating hepatic interleukin-6 signaling through inter-organ crosstalk[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11(12): 3836-3846. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.08.024. |
| [17] |
CHEN W, YUAN H, CAO WM, et al. Blocking interleukin-6 trans-signaling protects against renal fibrosis by suppressing STAT3 activation[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(14): 3980-3991. DOI: 10.7150/thno.32352. |
| [18] |
ZHENG C, HUANG L, LUO W, et al. Inhibition of STAT3 in tubular epithelial cells prevents kidney fibrosis and nephropathy in STZ-induced diabetic mice[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(11): 848. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-2085-0. |
| [19] |
SINCLAIR S. Chinese herbs: A clinical review of Astragalus, Ligusticum, and Schizandrae[J]. Altern Med Rev, 1998, 3(5): 338-344.
|
| [20] |
JIANG H, GU SL, ZHANG YT, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Astragalus membranaceus[J]. J Anhui Univ Chin Med, 2020, 39(5): 93-96. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7246.2020.05.022. |
| [21] |
LI Y, MA W. Analysis on the medication rule of Chinese medicine in the treatment of interstitial pneumonia based on data mining[J]. Chin Med Herald, 2023, 20(14): 146-150. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.14.31. |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
AI G, WANG M, ZHU JL, et al. Preliminary study on the clinical efficacy of N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of patients with chronic icteric hepatitis B[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2020, 23(3): 336-339. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.03.009. |
| [25] |
MAGNER K, ILIN JV, CLARK EG, et al. Meta-analytic techniques to assess the association between N-acetylcysteine and acute kidney injury after contrast administration: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(7): e2220671. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.20671. |
| [26] |
LI QW, LIAO JZ, CHEN WJ, et al. NAC alleviative ferroptosis in diabetic nephropathy via maintaining mitochondrial redox homeostasis through activating SIRT3-SOD2/Gpx4 pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 187: 158-170. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.05.024. |



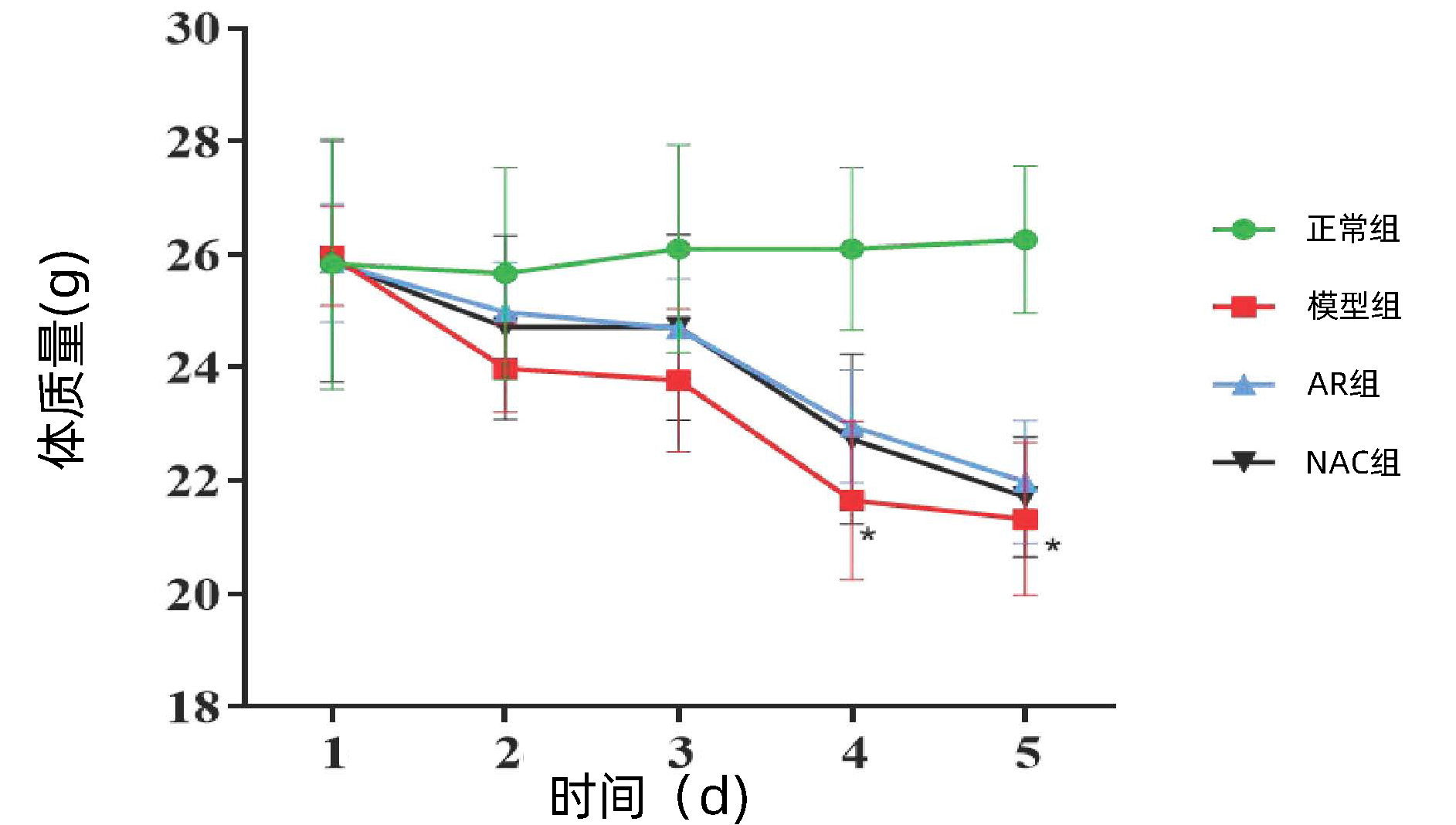




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: