| [1] |
SHIZUMA T. Spontaneous bacterial and fungal peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis: A literature review[J]. World J Hepatol, 2018, 10(2): 254-266. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.254. |
| [2] |
GAO XM, LENG XQ. Research advances of serological markers for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Med Innov China, 2022, 19(28): 173-176. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2022.28.042. |
| [3] |
METWALLY K, FOUAD T, ASSEM M, et al. Predictors of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhotic ascites[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6(4): 372-376. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00001. |
| [4] |
POPOIAG RE, SUCEVEANU AI, SUCEVEANU AP, et al. Predictors of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in Romanian adults with liver cirrhosis: Focus on the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(3): 983. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10415. |
| [5] |
HAN CJ, LI WH, WU ZX, et al. Role of NLR, LMR and PNI in anti-infective therapy of liver cirrhosis related spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Int J Lab Med, 2022, 43(24): 3012-3015, 3021. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2022.24.015. |
| [6] |
OETTL K, BIRNER-GRUENBERGER R, SPINDELBOECK W, et al. Oxidative albumin damage in chronic liver failure: Relation to albumin binding capacity, liver dysfunction and survival[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59(5): 978-983. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.013. |
| [7] |
OIKONOMOU T, GOULIS I, KIAPIDOU S, et al. The significance of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Ann Gastroenterol, 2020, 33(6): 667-674. DOI: 10.20524/aog.2020.0534. |
| [8] |
Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for alcoholic liver disease: a 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(5): 939-946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.006. |
| [9] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology CMA, XU XY, DUAN ZP, et al. Chinese guidelines on the management of ascites and its related complications in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13(1): 1-21. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-09923-2. |
| [10] |
BHANDARI R, KHALIQ K, RAVAT V, et al. Chronic alcoholic liver disease and mortality risk in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Analysis of 6, 530 hospitalizations[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12(5): e8189. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.8189. |
| [11] |
BETRAPALLY NS, GILLEVET PM, BAJAJ JS. Gut microbiome and liver disease[J]. Transl Res, 2017, 179: 49-59. DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.07.005. |
| [12] |
MARCIANO S, DÍAZ JM, DIRCHWOLF M, et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis: Incidence, outcomes, and treatment strategies[J]. Hepat Med, 2019, 11: 13-22. DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S164250. |
| [13] |
SORT P, NAVASA M, ARROYO V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 1999, 341(6): 403-409. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199908053410603. |
| [14] |
BIGGINS SW, ANGELI P, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74(2): 1014-1048. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31884. |
| [15] |
WEHMEYER MH, KROHM S, KASTEIN F, et al. Prediction of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic ascites by a simple scoring system[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2014, 49(5): 595-603. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2013.848471. |
| [16] |
ILIAZ R, OZPOLAT T, BARAN B, et al. Predicting mortality in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis using routine inflammatory and biochemical markers[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 30(7): 786-791. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001111. |
| [17] |
DONLON NE, MOHAN H, FREE R, et al. Predictive value of CRP/albumin ratio in major abdominal surgery[J]. Ir J Med Sci, 2020, 189(4): 1465-1470. DOI: 10.1007/s11845-020-02238-y. |
| [18] |
KANO H, MIDORIKAWA Y, SONG PP, et al. High C-reactive protein/albumin ratio associated with reduced survival due to advanced stage of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Biosci Trends, 2020, 14(4): 304-309. DOI: 10.5582/bst.2020.03167. |
| [19] |
KINOSHITA A, ONODA H, IMAI N, et al. The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, a novel inflammation-based prognostic score, predicts outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2015, 22(3): 803-810. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-014-4048-0. |
| [20] |
PIOTROWSKI D, SCZEWSKA-PIOTROWSKA A, JAROSZEWICZ J, et al. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio as the best simple predictor of bacterial infection in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 17(5): 1727. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17051727. |
| [21] |
HUANG SS, XIE DM, CAI YJ, et al. C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio is a predictor of hepatitis B virus related decompensated cirrhosis: Time-dependent receiver operating characteristics and decision curve analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 29(4): 472-480. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000807. |



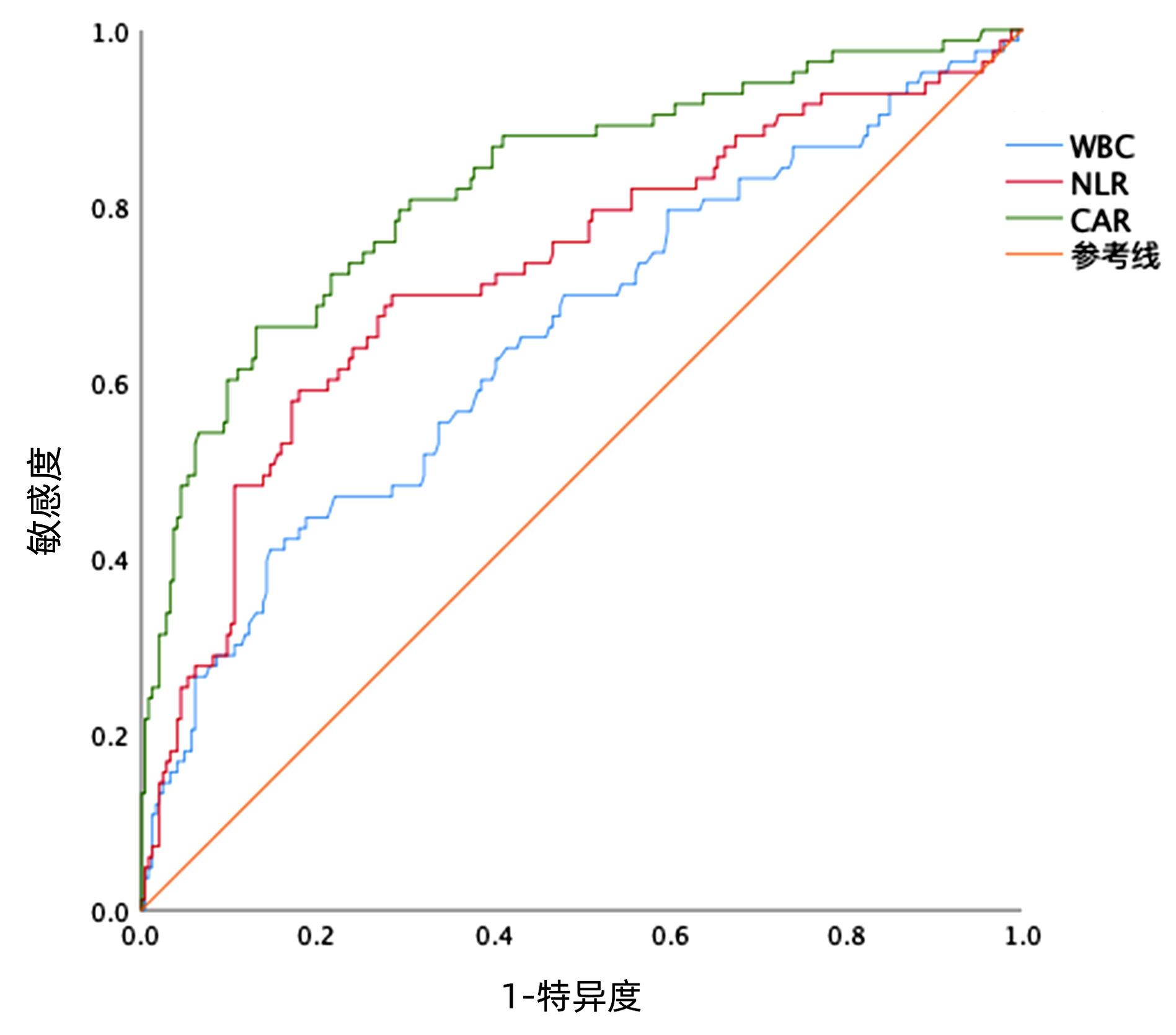




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: