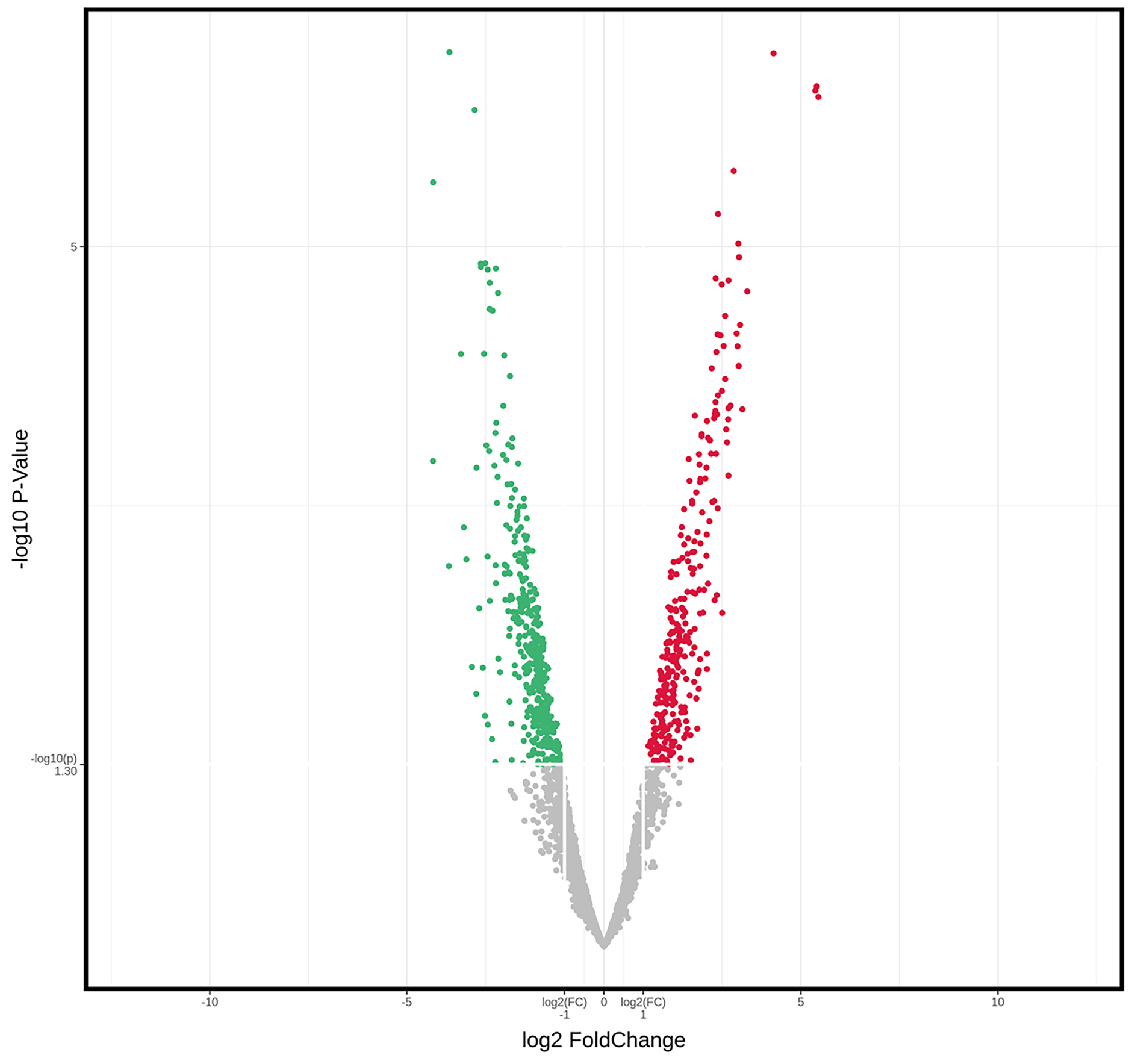
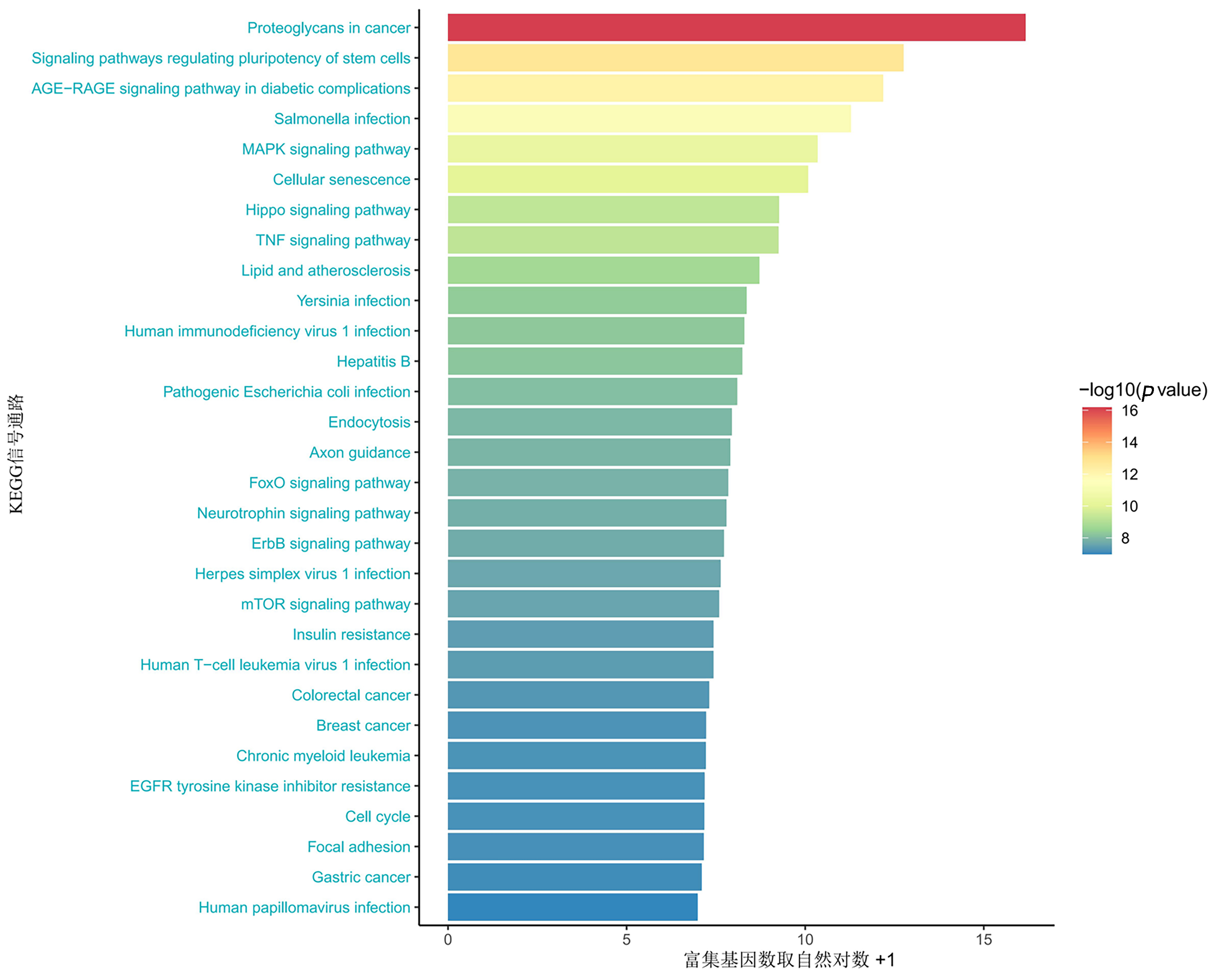
| [1] |
TANG Y, LIANG H, ZENG G, et al. Advances in new antivirals for chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135(5): 571-583. DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001994. |
| [2] |
ARROYO V, MOREAU R, JALAN R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(22): 2137-2145. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1914900. |
| [3] |
CONSOLE L, SCALISE M, INDIVERI C. Exosomes in inflammation and role as biomarkers[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 488: 165-171. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.11.009. |
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [5] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [6] |
GURUNATHAN S, KANG MH, JEYARAJ M, et al. Review of the isolation, characterization, biological function, and multifarious therapeutic approaches of exosomes[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(4): 307. DOI: 10.3390/cells8040307. |
| [7] |
MORI MA, LUDWIG RG, GARCIA-MARTIN R, et al. Extracellular miRNAs: from biomarkers to mediators of physiology and disease[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 30(4): 656-673. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.07.011. |
| [8] |
ZHANG J, LI S, LI L, et al. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function[J]. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2015, 13(1): 17-24. DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.001. |
| [9] |
CHEN W, YAN ZH, WANG YM, et al. Genome-wide microarray-based analysis of miRNAs expression in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2014, 13(1): 32-39. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(14)60004-7. |
| [10] |
HU J, XU Y, HAO J, et al. MiR-122 in hepatic function and liver diseases[J]. Protein Cell, 2012, 3(5): 364-371. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-012-2036-3. |
| [11] |
TANIMIZU N, KOBAYASHI S, ICHINOHE N, et al. Downregulation of miR122 by grainyhead-like 2 restricts the hepatocytic differentiation potential of adult liver progenitor cells[J]. Development, 2014, 141(23): 4448-4456. DOI: 10.1242/dev.113654. |
| [12] |
TU WL, YOU LR, TSOU AP, et al. Pten haplodeficiency accelerates liver tumor growth in miR-122a-Null mice via expansion of periportal hepatocyte-like cells[J]. Am J Pathol, 2018, 188(11): 2688-2702. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.07.019. |
| [13] |
KRAUSKOPF J, CAIMENT F, CLAESSEN SM, et al. Application of high-throughput sequencing to circulating microRNAs reveals novel biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2015, 143(2): 268-276. DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu232. |
| [14] |
BAI S, NASSER MW, WANG B, et al. MicroRNA-122 inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(46): 32015-32027. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016774. |
| [15] |
JOPLING CL, YI M, LANCASTER AM, et al. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific microRNA[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5740): 1577-1581. DOI: 10.1126/science.1113329. |
| [16] |
CHEN S, YANG L, PAN A, et al. Inhibitory effect on the hepatitis B cells through the regulation of miR-122-MAP3K2 signal pathway[J]. An Acad Bras Cienc, 2019, 91(2): e20180941. DOI: 10.1590/0001-3765201920180941. |
| [17] |
WEN Y, PENG SF, FU L, et al. Serum levels of miRNA in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2018, 17(2): 126-132. DOI: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.03.004. |
| [18] |
WU L, NGUYEN LH, ZHOU K, et al. Precise let-7 expression levels balance organ regeneration against tumor suppression[J]. Elife, 2015, 4: e09431. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.09431. |
| [19] |
MCDANIEL K, HUANG L, SATO K, et al. The let-7/Lin28 axis regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells in alcoholic liver injury[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(27): 11336-11347. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773291. |
| [20] |
MATSUURA K, AIZAWA N, ENOMOTO H, et al. Circulating let-7 levels in serum correlate with the severity of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C[J]. Open Forum Infect Dis, 2018, 5(11): ofy268. DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofy268. |
| [21] |
SANDHU GK, MCMILLIN M, FRAMPTON G, et al. Let-7f-dependent suppression of neuronal IGF1 by aberrant TGFβ1 signaling contributes to the neurological decline observed during acute liver failure[J]. J Gastroenterology, 2017, 152(5): S1066. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(17)33601-6. |
| [22] |
YANG S, CHEN Z, FAN D, et al. Retracted Article: MiR-182-5p and miR-96-5p increased hepatocellular carcinoma cell mobility, proliferation and cisplatin resistance partially by targeting RND3[J]. RSC Adv, 2018, 8(61): 34973-34983. DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07055e. |
| [23] |
CHANDEL R, DAS A, CHAWLA YK, et al. Mo1477 Progression of hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with the up regulation of rno-miR-96/182/183 cluster in liver of wistar rats[J]. J Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(4): S1125. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(16)33799-4 |
| [24] |
MANDAL R, HARDIN H, BAUS R, et al. Analysis of miR-96 and miR-133a expression in gastrointestinal neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Endocr Pathol, 2017, 28(4): 345-350. DOI: 10.1007/s12022-017-9504-5. |
| [25] |
SHI Y, JIA M, XU L, et al. miR-96 and autophagy are involved in the beneficial effect of grape seed proanthocyanidins against high-fat-diet-induced dyslipidemia in mice[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(4): 1222-1232. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.6318. |
| [26] |
BAJAJ JS, REDDY KR, O'LEARY JG, et al. Serum levels of metabolites produced by intestinal microbes and lipid moieties independently associated with acute-on-chronic liver failure and death in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159(5): 1715-1730. e12. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.019. |










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: