| [1] |
STINTON LM, SHAFFER EA. Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer[J]. Gut Liver, 2012, 6(2): 172-187. DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.2.172. |
| [2] |
SHABANZADEH DM. Incidence of gallstone disease and complications[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2018, 34(2): 81-89. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000418. |
| [3] |
LAMBERTS MP. Indications of cholecystectomy in gallstone disease[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2018, 34(2): 97-102. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000419. |
| [4] |
PENG YY, TAN YY. Analysis of the role of Cajal interstitial cells in the formation of gallstones[J]. Labeled Immunoassays Clin Med, 2016, 23(7): 817-819. DOI: 10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2016.07.028. |
| [5] |
ZHAO JN, FAN Y, WU SD. Advances in the relationship between Cajal-like interstitial cells of the gallbladder and cholesterol stone formation in the gallbladder[J]. Med Recapitulate, 2019, 25(21): 4180-4184, 4190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.21.004. |
| [6] |
XU JH, FAN Y. Effect of cholesterol on Cajal-like interstitial cells of guinea pig gallbladder isolated and cultured in vitro[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2019, 32(11): 1457-1461. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2019.11.001. |
| [7] |
YU Y, YIN X, TANG QL, et al. Study on the regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway-related factor genes by Dahuang Lingxian formula to affect the inflammatory response of bile duct cells[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2020, 31(5): 1034-1037. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.05.003. |
| [8] |
WANG QJ, TANG QL, YU Y, et al. Dahuang Lingxian formula capsule regulates TGF-β1 mRNA and Smad2 in bile duct endothelial cells[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2014, 25(12): 2833-2835. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2014.12.006. |
| [9] |
FENG H, WANG F, WANG C. C-Kit expression in the gallbladder of guinea pig with chronic calculous cholecystitis and the effect of Artemisia capillaris Thunb on interstitial cells of Cajal[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2016, 19(7): 720-725.
|
| [10] |
CHEN Q. Experimental methodology of Chinese pharmacology[M]. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House, 1994: 215.
陈奇. 中药药理学实验方法学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1994: 215.
|
| [11] |
ANSTÖTZ M, LEE SK, NEBLETT TI, et al. Experience-dependent regulation of Cajal-retzius cell networks in the developing and adult mouse hippocampus[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2018, 28(2): 672-687. DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhx153. |
| [12] |
ORTIZ-HIDALGO C, de LEON BOJORGE B, ALBORES-SAAVEDRA J. Stromal tumor of the gallbladder with phenotype of interstitial cells of Cajal: a previously unrecognized neoplasm[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2000, 24(10): 1420-1423. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-200010000-00013. |
| [13] |
LAVOIE B, BALEMBA OB, NELSON MT, et al. Morphological and physiological evidence for interstitial cell of Cajal-like cells in the guinea pig gallbladder[J]. J Physiol, 2007, 579(Pt 2): 487-501. DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.122861. |
| [14] |
PASTERNAK A, GAJDA M, GIL K, et al. Evidence of interstitial Cajal-like cells in human gallbladder[J]. Folia Histochem Cytobiol, 2012, 50(4): 581-585. DOI: 10.5603/19673. |
| [15] |
CHEN L, YU B. Telocytes and interstitial cells of Cajal in the biliary system[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(7): 3323-3329. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13643. |
| [16] |
FAUSSONE-PELLEGRINI MS, VANNUCCHI MG, LEDDER O, et al. Plasticity of interstitial cells of Cajal: a study of mouse colon[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2006, 325(2): 211-217. DOI: 10.1007/s00441-006-0174-8. |
| [17] |
MEI F, HAN J, HUANG Y, et al. Plasticity of interstitial cells of cajal: a study in the small intestine of adult Guinea pigs[J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2009, 292(7): 985-993. DOI: 10.1002/ar.20928. |
| [18] |
TORIHASHI S, NISHI K, TOKUTOMI Y, et al. Blockade of kit signaling induces transdifferentiation of interstitial cells of cajal to a smooth muscle phenotype[J]. Gastroenterology, 1999, 117(1): 140-148. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70560-3. |
| [19] |
MEI F, ZHU J, GUO S, et al. An age-dependent proliferation is involved in the postnatal development of interstitial cells of Cajal in the small intestine of mice[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2009, 131(1): 43-53. DOI: 10.1007/s00418-008-0515-7. |
| [20] |
HUIZINGA JD, THUNEBERG L, KLVPPEL M, et al. W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity[J]. Nature, 1995, 373(6512): 347-349. DOI: 10.1038/373347a0. |
| [21] |
ISOZAKI K, HIROTA S, NAKAMA A, et al. Disturbed intestinal movement, bile reflux to the stomach, and deficiency of c-kit-expressing cells in Ws/Ws mutant rats[J]. Gastroenterology, 1995, 109(2): 456-464. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90333-x. |
| [22] |
ISOZAKI K, HIROTA S. Gain-of-function mutations of receptor tyrosine kinases in gastrointestinal stromal tumors[J]. Curr Genomics, 2006, 7(8): 469-475. DOI: 10.2174/138920206779315755. |
| [23] |
MA WW, LI CQ, YU HL, et al. The oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol increases oxidative stress and regulate Nrf2 signaling pathway in astrocyte cells[J]. Neurochem Res, 2015, 40(4): 758-766. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-015-1524-2. |
| [24] |
CHUA NK, COATES HW, BROWN AJ. Cholesterol, cancer, and rebooting a treatment for athlete's foot[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2018, 10(437): eaat3741. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat3741. |
| [25] |
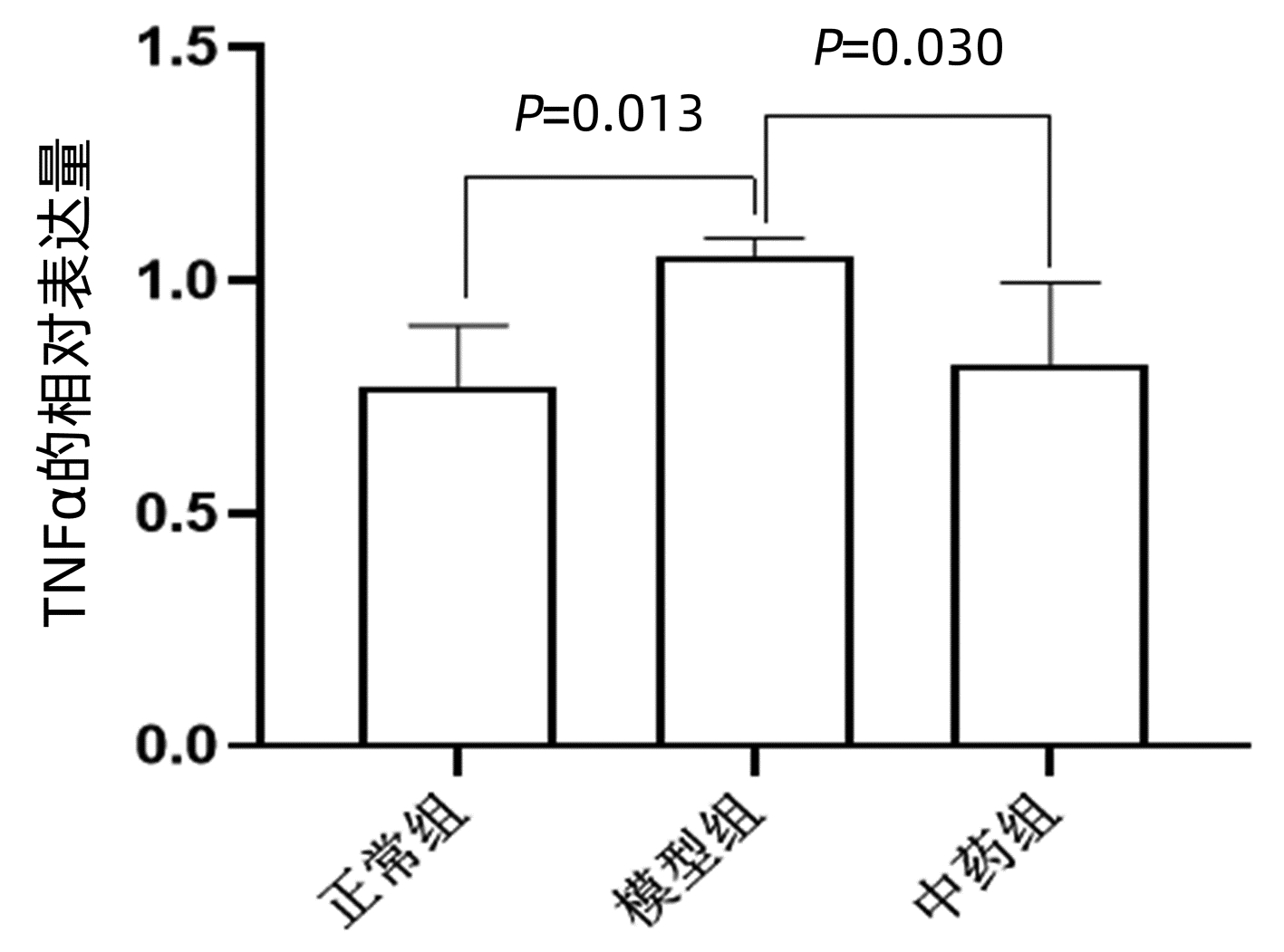
WAN JF, CHU SF, ZHOU X, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid protects interstitial Cajal-like cells in the gallbladder from undergoing apoptosis by inhibiting TNF-α expression[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2018, 39(9): 1493-1500. DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.206. |



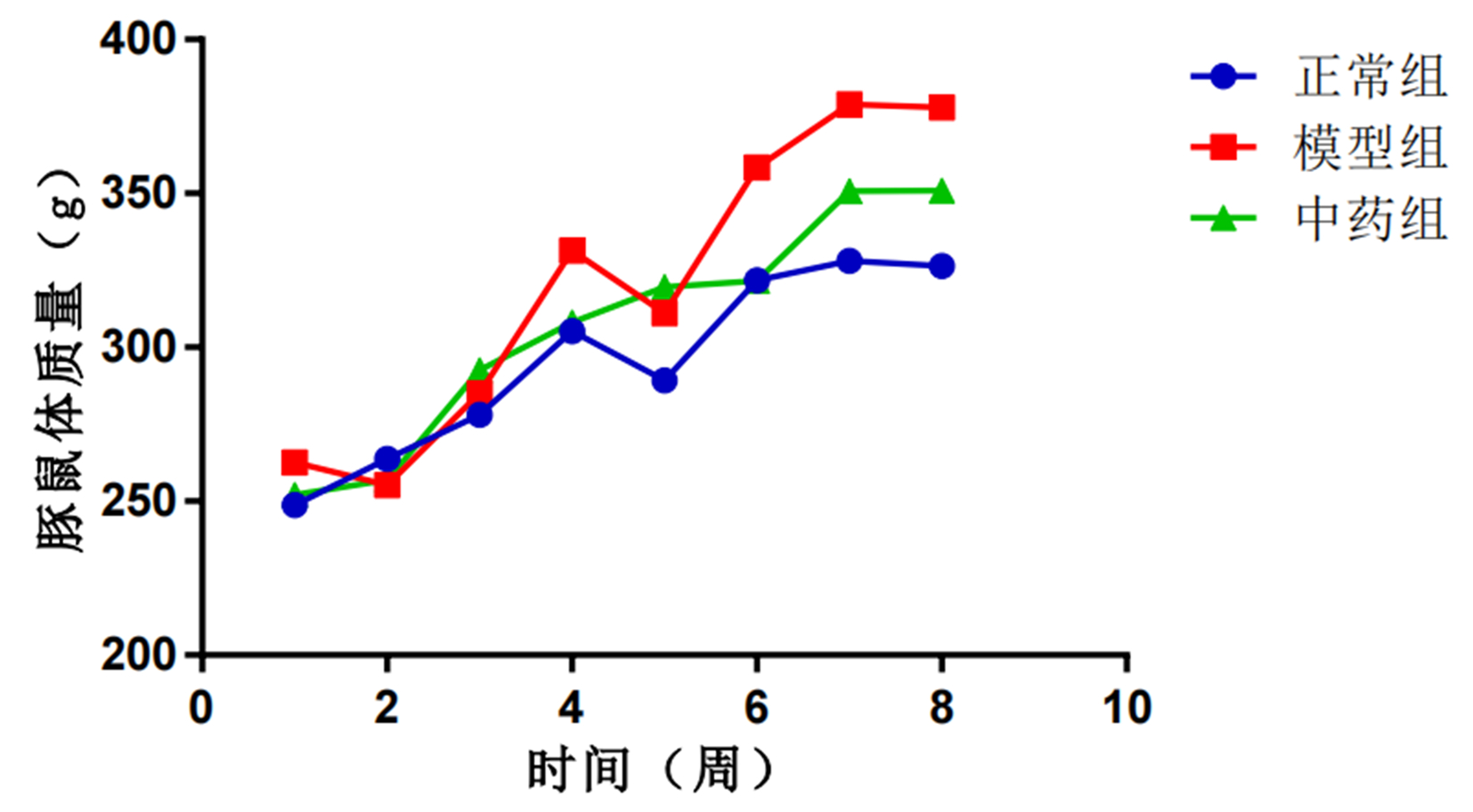




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: