| [1] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standardization for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(2): 1-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02. |
| [2] |
LU C, RONG D, ZHANG B, et al. Current perspectives on the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and opportunities[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 130. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-1047-6. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
BIAN J, LIN J, LONG J, et al. T lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma immune microenvironment: insights into human immunology and immunotherapy[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(12): 4585-4606.
|
| [5] |
ZHANG W, LIU X, ZHU Y, et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of Th17/Treg balance in health and disease[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2021, 51(9): 2137-2150. DOI: 10.1002/eji.202048794. |
| [6] |
CHO HJ, CHEONG JY. Role of immune cells in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(15): 8011. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22158011. |
| [7] |
XIE J, WANG M, CHENG A, et al. The role of SOCS proteins in the development of virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Virol J, 2021, 18(1): 74. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-021-01544-w. |
| [8] |
SHARMA J, LARKIN J 3rd. Therapeutic implication of SOCS1 modulation in the treatment of autoimmunity and cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 324. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00324. |
| [9] |
YOSHIMURA A, ITO M, MISE-OMATA S, et al. SOCS: negative regulators of cytokine signaling for immune tolerance[J]. Int Immunol, 2021, 33(12): 711-716. DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxab055. |
| [10] |
LIAU N, LAKTYUSHIN A, LUCET IS, et al. The molecular basis of JAK/STAT inhibition by SOCS1[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 1558. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04013-1. |
| [11] |
SHARMA J, COLLINS TD, ROACH T, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 mimetic peptides attenuate lymphocyte activation in the MRL/lpr mouse autoimmune model[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 6354. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86017-4. |
| [12] |
CHEN H, WU Y, LI K, et al. Optimization of phosphotyrosine peptides that target the SH2 domain of SOCS1 and block substrate ubiquitination[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2022, 17(2): 449-462. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00884. |
| [13] |
SEIF F, KHOSHMIRSAFA M, AAZAMI H, et al. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2017, 15(1): 23. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-017-0177-y. |
| [14] |
IIZUKA-KOGA M, NAKATSUKASA H, ITO M, et al. Induction and maintenance of regulatory T cells by transcription factors and epigenetic modifications[J]. J Autoimmun, 2017, 83: 113-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.07.002. |
| [15] |
NI X, WANG Q, GU J, et al. Clinical and basic research progress on Treg-induced immune tolerance in liver transplantation[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 535012. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.535012. |
| [16] |
ILANGUMARAN S, BOBBALA D, RAMANATHAN S. SOCS1: Regulator of T cells in autoimmunity and cancer[J]. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 2017, 410: 159-189. DOI: 10.1007/82_2017_63. |
| [17] |
TAKAHASHI R, NAKATSUKASA H, SHIOZAWA S, et al. SOCS1 is a key molecule that prevents regulatory T cell plasticity under inflammatory conditions[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 199(1): 149-158. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600441. |
| [18] |
RAMSDELL F, ZIEGLER SF. FOXP3 and scurfy: how it all began[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2014, 14(5): 343-349. DOI: 10.1038/nri3650. |
| [19] |
SOBAH ML, LIONGUE C, WARD AC. SOCS proteins in immunity, inflammatory diseases, and immune-related cancer[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2021, 8: 727987. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.727987. |
| [20] |
YOSHIMURA A, SUZUKI M, SAKAGUCHI R, et al. SOCS, inflammation, and autoimmunity[J]. Front Immunol, 2012, 3: 20. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00020. |
| [21] |
WANG WZ, XIANG XX. Immunological mechanism of Treg/Th17 and Th1/Th2 balance in autoimmune hepatitis and new targets for diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(8): 1874-1877. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.051. |
| [22] |
CHIKUMA S, KANAMORI M, MISE-OMATA S, et al. Suppressors of cytokine signaling: Potential immune checkpoint molecules for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(4): 574-580. DOI: 10.1111/cas.13194. |
| [23] |
TANAKA K, ICHIYAMA K, HASHIMOTO M, et al. Loss of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in helper T cells leads to defective Th17 differentiation by enhancing antagonistic effects of IFN-gamma on STAT3 and Smads[J]. J Immunol, 2008, 180(6): 3746-3756. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.3746. |
| [24] |
ZHANG H, JIANG Z, ZHANG L. Dual effect of T helper cell 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cell (Treg) in liver pathological process: From occurrence to end stage of disease[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 69: 50-59. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.005. |
| [25] |
TANG GJ. The role of Th17/Treg cell imbalance in the progression of chronic hepatitis B diseases[D]. Kunming: Kunming Medical University, 2021. DOI: 10.27202/d.cnki.gkmyc.2021.000104. |
| [26] |
TANG GJ, YOU J, LIU HE, et al. Role of T helper 17 cell/regulatory T cell imbalance in the progression of HBV-related liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(2): 414-418. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.035. |
| [27] |
QIU J, ZHOU F, LI X, et al. Changes and clinical significance of detailed peripheral lymphocyte subsets in evaluating the immunity for cancer patients[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 209-219. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S221586. |
| [28] |
GRANITO A, MURATORI L, LALANNE C, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in viral and autoimmune liver diseases: Role of CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + regulatory T cells in the immune microenvironment[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(22): 2994-3009. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2994. |
| [29] |
ZAHRAN AM, NAFADY-HEGO H, MANSOR SG, et al. Increased frequency and FOXP3 expression of human CD8 +CD25 High+ T lymphocytes and its relation to CD4 regulatory T cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hum Immunol, 2019, 80(7): 510-516. DOI: 10.1016/j.humimm.2019.03.014. |
| [30] |
DING W, XU X, QIAN Y, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018, 97(50): e13301. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013301. |
| [31] |
ZHOU L, WANG J, LYU SC, et al. PD-L1+NEUT, Foxp3+Treg, and NLR as new prognostic marker with low survival benefits value in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 15330338211045820. DOI: 10.1177/15330338211045820. |
| [32] |
HU ZQ, XIN HY, LUO CB, et al. Associations among the mutational landscape, immune microenvironment, and prognosis in Chinese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2021, 70(2): 377-389. DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02685-7. |
| [33] |
ZHANG L, YANG Z, ZHANG S, et al. Polyploidy spectrum correlates with immunophenotype and shapes hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence following liver transplantation[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2022, 15: 217-233. DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S345681. |
| [34] |
LIU F, LIU W, SANIN DE, et al. Heterogeneity of exhausted T cells in the tumor microenvironment is linked to patient survival following resection in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2020, 9(1): 1746573. DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1746573. |
| [35] |
BOZWARD AG, WARRICKER F, OO YH, et al. Natural killer cells and regulatory T cells cross talk in hepatocellular carcinoma: Exploring therapeutic options for the next decade[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 643310. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.643310. |
| [36] |
ZHOU L, PAN LC, ZHENG YG, et al. Novel strategy of sirolimus plus thymalfasin and huaier granule on tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the UCSF criteria following liver transplantation: A single center experience[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 16(4): 4407-4417. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9226. |
| [37] |
NALBANT A. IL-17, IL-21, and IL-22 cytokines of T helper 17 cells in cancer[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2019, 39(1): 56-60. DOI: 10.1089/jir.2018.0057. |
| [38] |
LIANG KH, LAI MW, LIN YH, et al. Plasma interleukin-17 and alpha-fetoprotein combination effectively predicts imminent hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence in liver cirrhotic patients[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1): 177. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01761-1. |
| [39] |
ZHOU Y, XU X, DING J, et al. Dynamic changes of T-cell subsets and their relation with tumor recurrence after microwave ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2018, 14(1): 40-45. DOI: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_775_17. |
| [40] |
HE Y, HWANG S, AHMED YA, et al. Immunopathobiology and therapeutic targets related to cytokines in liver diseases[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18(1): 18-37. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-00580-w. |
| [41] |
LEE J, LOZANO-RUIZ B, YANG FM, et al. The multifaceted role of Th1, Th9, and Th17 cells in immune checkpoint inhibition therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 625667. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.625667. |
| [42] |
HAN Y, LIU D, LI L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(3): 727-742.
|
| [43] |
YARCHOAN M, XING D, LUAN L, et al. Characterization of the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 23(23): 7333-7339. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0950. |
| [44] |
The International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association, Liver Surgery Group of Chinese Medical Association Surgery Branch, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Liver Cancer Expert Committee. Chinese multidisciplinary expert consensus on combined immunotherapy based on immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma (2021 version)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(7): 740-753. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210603-00260. |
| [45] |
DING J, XU K, SUN S, et al. SOCS1 blocks G1-S transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing the stability of the CyclinD1/CDK4 complex in the nucleus[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(4): 3962-3975. DOI: 10.18632/aging.102865. |
| [46] |
ZHENG X, DONG L, WANG K, et al. MiR-21 Participates in the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway-mediated imbalance of Th17/Treg cells in patients after gastric cancer resection[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2019, 26(3): 884-893. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-018-07117-6. |
| [47] |
YANG Z, ZHU H, ZHANG L, et al. DNA methylation of SOCS1/2/3 predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(3): 1773-1782. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05271-3. |
| [48] |
CABRAL L, REYES P, CROCÈ LS, et al. The Relevance of SOCS1 methylation and epigenetic therapy in diverse cell populations of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2021, 11(10): 1825. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11101825. |



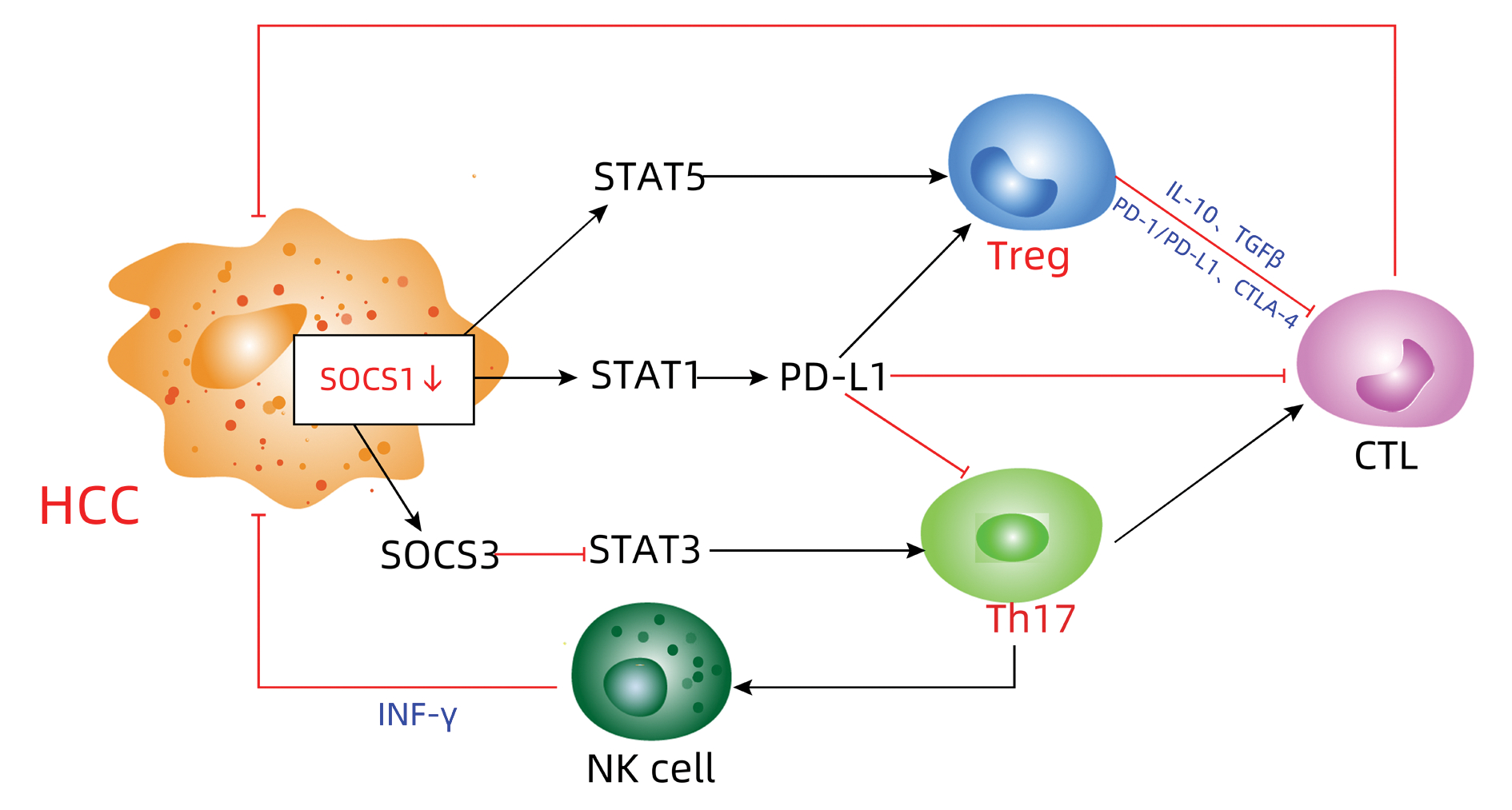




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
