| [1] |
IWAKIRI Y, TREBICKA J. Portal hypertension in cirrhosis: Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapy[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3(4): 100316. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100316. |
| [2] |
de FRANCHIS R, BOSCH J, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Baveno Ⅶ - Renewing consensus in portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(4): 959-974. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. |
| [3] |
GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. |
| [4] |
LEE E, KIM YJ, GOO DE, et al. Comparison of hepatic venous pressure gradient and endoscopic grading of esophageal varices[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(11): 3212-3219. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i11.3212. |
| [5] |
ELKRIEF L, RONOT M, ANDRADE F, et al. Non-invasive evaluation of portal hypertension using shear-wave elastography: analysis of two algorithms combining liver and spleen stiffness in 191 patients with cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 47(5): 621-630. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14488. |
| [6] |
DING NS, NGUYEN T, ISER DM, et al. Liver stiffness plus platelet count can be used to exclude high-risk oesophageal varices[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36(2): 240-245. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12916. |
| [7] |
KIM TY, JEONG WK, SOHN JH, et al. Evaluation of portal hypertension by real-time shear wave elastography in cirrhotic patients[J]. Liver Int, 2015, 35(11): 2416-2424. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12846. |
| [8] |
FLEMING KM, AITHAL GP, CARD TR, et al. The rate of decompensation and clinical progression of disease in people with cirrhosis: a cohort study[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 32(11-12): 1343-1350. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04473.x. |
| [9] |
LURIE Y, WEBB M, CYTTER-KUINT R, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(41): 11567-11583. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11567. |
| [10] |
KENNEDY P, WAGNER M, CASTÉRA L, et al. Quantitative elastography methods in liver disease: current evidence and future directions[J]. Radiology, 2018, 286(3): 738-763. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2018170601. |
| [11] |
CORPECHOT C, GAOUAR F, EL NAGGAR A, et al. Baseline values and changes in liver stiffness measured by transient elastography are associated with severity of fibrosis and outcomes of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(4): 970-979. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.030. |
| [12] |
SINGH S, FUJⅡ LL, MURAD MH, et al. Liver stiffness is associated with risk of decompensation, liver cancer, and death in patients with chronic liver diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 11(12): 1573-1584. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.07.034. |
| [13] |
BERZIGOTTI A, SEIJO S, ARENA U, et al. Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(1): 102-111. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.001. |
| [14] |
ABRALDES JG, BUREAU C, STEFANESCU H, et al. Noninvasive tools and risk of clinically significant portal hypertension and varices in compensated cirrhosis: The "Anticipate" study[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(6): 2173-2184. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28824. |
| [15] |
XIE Q, LI Z, TANG Z, et al. Value of liver/spleen stiffness combined with serum adenosine deaminase in predicting severe esophageal varices in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(6): 1314-1318. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.020. |
| [16] |
COSGROVE D, PISCAGLIA F, BAMBER J, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: Clinical applications[J]. Ultraschall Med, 2013, 34(3): 238-253. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1335375. |
| [17] |
D'ONOFRIO M, CROSARA S, de ROBERTIS R, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse of the liver[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(30): 4841-4849. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4841. |
| [18] |
GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. |
| [19] |
MIAO CC, ZHUGE YZ, ZHANG M, et al. Correlation analysis between liver and spleen stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse and hepatic venous pressure gradient[J]. Chin J Dig, 2017, 37(1): 30-34. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2017.01.009. |



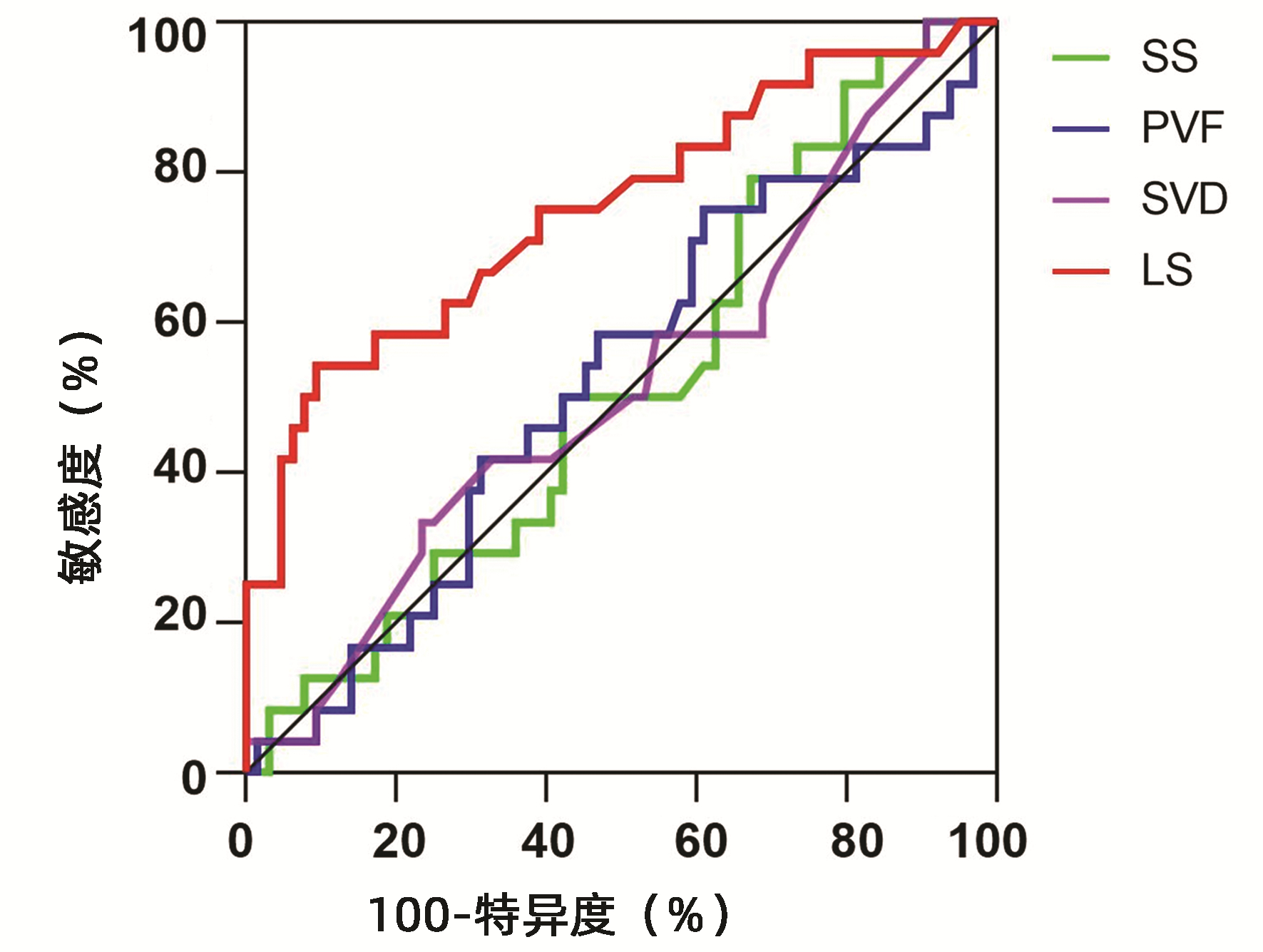




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: