| [1] |
BAKI JA, TAPPER EB. Contemporary epidemiology of cirrhosis[J]. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol, 2019, 17(2): 244-253. DOI: 10.1007/s11938-019-00228-3. |
| [2] |
TAPPER EB, PARIKH ND. Mortality due to cirrhosis and liver cancer in the United States, 1999-2016: observational study[J]. BMJ, 2018, 362: k2817. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.k2817. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
LISMAN T, CALDWELL SH, BURROUGHS AK, et al. Hemostasis and thrombosis in patients with liver disease: the ups and downs[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 53(2): 362-371. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.01.042. |
| [5] |
NG KJ, LEE YK, HUANG MY, et al. Risks of venous thromboembolism in patients with liver cirrhosis: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2015, 13(2): 206-213. DOI: 10.1111/jth.12805. |
| [6] |
ZOCCO MA, DI STASIO E, de CRISTOFARO R, et al. Thrombotic risk factors in patients with liver cirrhosis: correlation with MELD scoring system and portal vein thrombosis development[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 51(4): 682-689. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.013. |
| [7] |
ABDEL-RAZIK A, MOUSA N, ELHELALY R, et al. De-novo portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: risk factors and correlation with the Model for End-stage Liver Disease scoring system[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 27(5): 585-592. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000325. |
| [8] |
STINE JG, WANG J, SHAH PM, et al. Decreased portal vein velocity is predictive of the development of portal vein thrombosis: A matched case-control study[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38(1): 94-101. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13500. |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
XU X, GUO X, DE STEFANO V, et al. Nonselective beta-blockers and development of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13(4): 468-481. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09951-6. |
| [11] |
QI X, HAN G, YE C, et al. Splenectomy causes 10-fold increased risk of portal venous system thrombosis in liver cirrhosis patients[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22: 2528-2550. DOI: 10.12659/msm.898866. |
| [12] |
CARNEVALE R, RAPARELLI V, NOCELLA C, et al. Gut-derived endotoxin stimulates factor VⅢ secretion from endothelial cells. Implications for hypercoagulability in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(5): 950-956. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.002. |
| [13] |
RAPARELLI V, BASILI S, CARNEVALE R, et al. Low-grade endotoxemia and platelet activation in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(2): 571-581. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28853. |
| [14] |
HUANG X, FAN X, ZHANG R, et al. Systemic inflammation and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with gastroesophageal varices[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 32(3): 401-405. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001526. |
| [15] |
PALARETI G, COSMI B, LEGNANI C, et al. D-dimer to guide the duration of anticoagulation in patients with venous thromboembolism: a management study[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(2): 196-203. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-548065. |
| [16] |
Group of Portal Hypertension, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric varices bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension (2015 edition)[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2016, 31(2): 167-170. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2016.02.032. |
| [17] |
TSOCHATZIS EA, SENZOLO M, GERMANI G, et al. Systematic review: portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 31(3): 366-374. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04182.x. |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
STINE JG, SHAH PM, CORNELLA SL, et al. Portal vein thrombosis, mortality and hepatic decompensation in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015, 7(27): 2774-2780. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i27.2774. |
| [20] |
QI X, SU C, REN W, et al. Association between portal vein thrombosis and risk of bleeding in liver cirrhosis: A systematic review of the literature[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2015, 39(6): 683-691. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.02.012. |
| [21] |
ZUO HW, SHA QM, SUN J, et al. Risk factors of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(1): 63-67. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.013. |
| [22] |
INTAGLIATA NM, ARGO CK, STINE JG, et al. Concepts and controversies in haemostasis and thrombosis associated with liver disease: Proceedings of the 7th International Coagulation in Liver Disease Conference[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2018, 118(8): 1491-1506. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1666861. |
| [23] |
de FRANCHIS R; Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 743-752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. |
| [24] |
XU X, ZHANG C, SHI C, et al. Antiviral therapy effectively improves liver hemodynamics as evidenced by serum biomarker and contrast-enhanced ultrasound examinations in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. PeerJ, 2018, 6: e5484. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.5484. |
| [25] |
PAYANCÉ A, RAUTOU PE. Cirrhosis regression: extrahepatic angiogenesis and liver hyperarterialization persist[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2018, 132(12): 1341-1343. DOI: 10.1042/CS20180129. |
| [26] |
HSIEH YH, HUANG HC, CHANG CC, et al. Nucleos(t)ide analogs do not independently influence hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension beyond viral suppression in CBDL-induced cirrhotic rat[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2018, 367(2): 260-266. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.118.250431. |
| [27] |
HE Y, HU ZF, LI P, et al. Experimental study of saikosaponin-d (SSd) on lipid peroxidation of hepatic fibrosis on rat[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2008, 33(8): 915-919. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.2008.08.013. |
| [28] |
ZHU HL, ZHANG GB, ZHANG C. Effect and mechanism of Bupleuri injection on multiple organ injury in endotoxin-inducing disseminated inravascular coagulation rat[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2012, 32(23): 5196-5199. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2012.23.043. |
| [29] |
DAS D, BISWAL S, BARHWAL KK, et al. Methanolic root extract of Codonopsis clematidea prevents hypoxia induced procoagulant state by inhibition of GPIb receptor regulated Lyn kinase activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 59: 152903. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152903. |
| [30] |
LIU M. Study about the brain protective effect and its mechanism of CPPS on cycloheximide induced memory consolidation disorder in mice[D]. Zhangjiakou: Hebei North University, 2020.
刘梅. 党参多糖对环已酰亚胺所致记忆巩固障碍小鼠脑保护作用及其机制研究[D]. 张家口: 河北北方学院, 2020.
|
| [31] |
CHENG Y, ZHANG YY, HUANG T, et al. Effect of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide on fatigue in exhausted mice[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(16): 3498-3501. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.16.031. |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
SUN C, SU S, ZHU Y, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza stem-leaf active components of salvianolic acids and flavonoids improved the hemorheological disorder and vascular endothelial function on microcirculation dysfunction rats[J]. Phytother Res, 2020, 34(7): 1704-1720. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.6652. |
| [34] |
CAO H, ZHANG L, SUN ZB, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza prevents deep vein thrombosis via antioxidative effects in endothelial cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 11(5): 3593-3600. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3153. |
| [35] |
ZHOU Q, ZHANG ZH, ZHANG XL, et al. Spectrum-effect correlation-based study on anticoagulant activity enhancement induced by ingredients of wine-processed Salvia miltiorrhiza[J]. Chin Tradit Patent Med, 2021, 43(4): 954-958. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.04.023. |
| [36] |
LIN XR, LIU X, LU CY. Effects of tanshinol and tanshinone ⅡA on diffuse intravascular coagulation in rats[J]. Chin Tradit Patent Med, 2016, 38(12): 2673-2676. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2016.12.030. |
| [37] |
WANG Q, JIANG LL, XIAO TS, et al. Study on the active parts of Salvia miltiorrhiza inhibiting coagulation factors Xa and ⅡA[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2013, 24(5): 1153-1154. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2013.05.055. |
| [38] |
SHI H, SHI H, REN F, et al. Naringin in Ganshuang Granule suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells for anti-fibrosis effect by inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2017, 21(3): 500-509. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12994. |
| [39] |
LU F, GENG JB, ZHANG JW, et al. Effect of entecavir plus Ganshuang granule on fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 41(4): 624-629. DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2021.03.015. |
| [40] |
LIU YM, SHI HB, LIU YR, et al. Protective effect of Ganshuang Granules on liver cirrhosis by suppressing regulatory T cells in mouse model[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 25(1): 51-58. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-015-2430-9. |
| [41] |
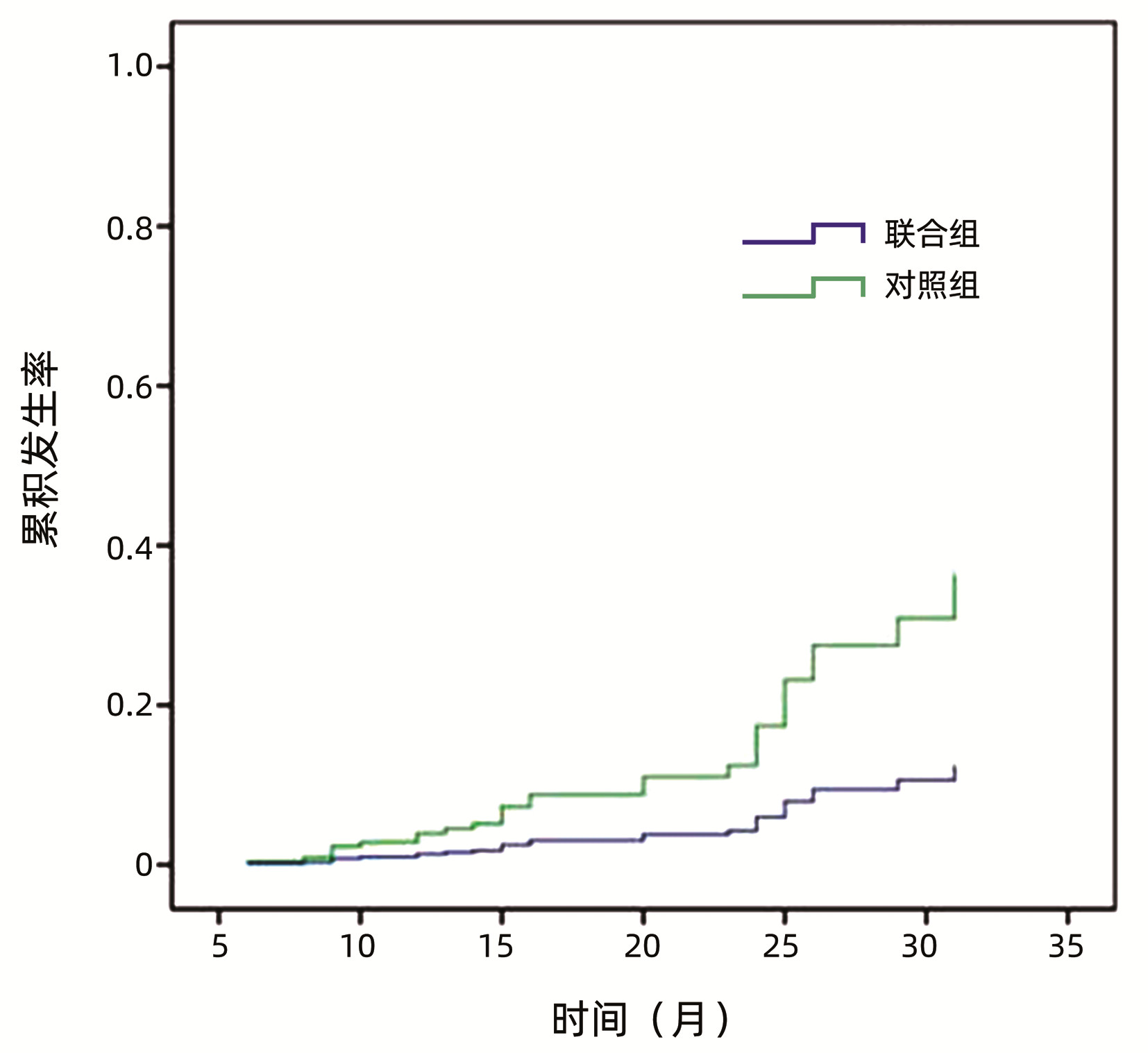
LIU L, LI JY, LIU CY, et al. Effect of Tenofovir combined with Ganshuang granule on hemodynamics of portal vein system in hepatitis B liver cirrhosis[J]. J Kunming Med Univ, 2021, 42(11): 134-139. DOI: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211125. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: