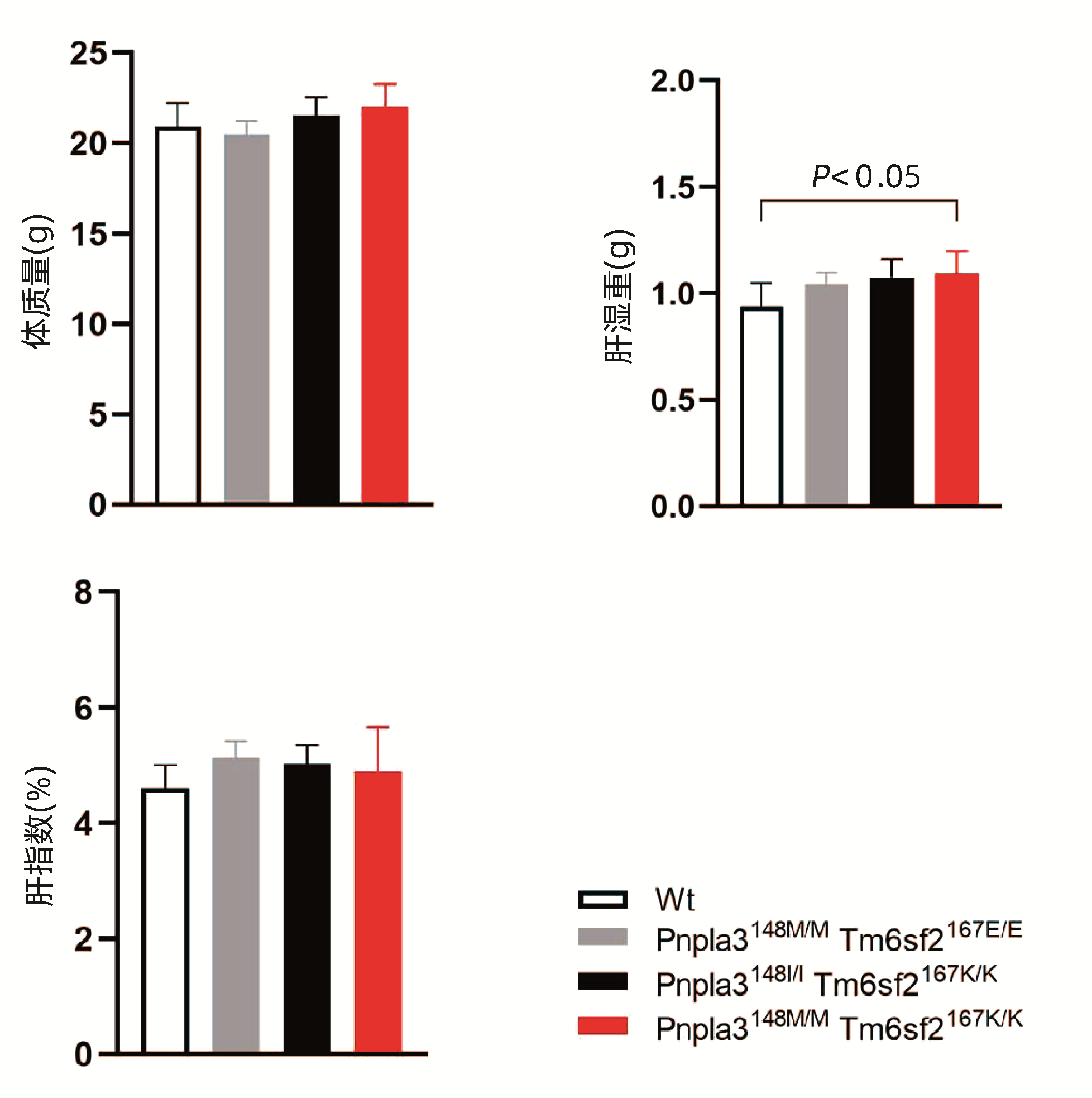
| [1] |
FRIEDMAN SL, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI BA, RINELLA M, et al. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24(7): 908-922. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9. |
| [2] |
YOUNOSSI Z, ANSTEE QM, MARIETTI M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15(1): 11-20. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109. |
| [3] |
ARON-WISNEWSKY J, VIGLIOTTI C, WITJES J, et al. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(5): 279-297. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-0269-9. |
| [4] |
WATT MJ, MIOTTO PM, de NARDO W, et al. The liver as an endocrine organ-linking NAFLD and insulin resistance[J]. Endocr Rev, 2019, 40(5): 1367-1393. DOI: 10.1210/er.2019-00034. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
TILG H, MOSCHEN AR, RODEN M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 14(1): 32-42. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.147. |
| [7] |
TRÉPO E, ROMEO S, ZUCMAN-ROSSI J, et al. PNPLA3 gene in liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(2): 399-412. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.03.011. |
| [8] |
BASU RAY S. PNPLA3-I148M: a problem of plenty in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Adipocyte, 2019, 8(1): 201-208. DOI: 10.1080/21623945.2019.1607423. |
| [9] |
KOZLITINA J, SMAGRIS E, STENDER S, et al. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nat Genet, 2014, 46(4): 352-356. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2901. |
| [10] |
O'HARE EA, YANG R, YERGES-ARMSTRONG LM, et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 impacts lipid processing in liver and small intestine[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(5): 1526-1542. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29021. |
| [11] |
STEFAN N, HÄRING HU, CUSI K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2019, 7(4): 313-324. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30154-2. |
| [12] |
IOANNOU GN. Epidemiology and risk-stratification of NAFLD-associated HCC[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(6): 1476-1484. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.012. |
| [13] |
LI JF, ZHENG EQ, XIE M. Association between rs738409 polymorphism in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) gene and hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility: Evidence from case-control studies[J]. Gene, 2019, 685: 143-148. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.012. |
| [14] |
WANG X, LIU Z, WANG K, et al. Additive effects of the risk alleles of PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a Chinese population[J]. Front Genet, 2016, 7: 140. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00140. |
| [15] |
XU M, LI Y, ZHANG S, et al. Interaction of TM6SF2 E167K and PNPLA3 I148M variants in NAFLD in northeast China[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2019, 18(3): 456-460. DOI: 10.1016/j.aohep.2018.10.005. |
| [16] |
ZHANG J, MA XF, WANG YF, et al. Hepatocyte-specific TM6SF2 knockout aggravates hepatic steatosis in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(11): 2612-2616. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.11.024. |
| [17] |
LAZARUS JV, ANSTEE QM, HAGSTRÖM H, et al. Defining comprehensive models of care for NAFLD[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(10): 717-729. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00477-7. |
| [18] |
CHEN L, DU S, LU L, et al. The additive effects of the TM6SF2 E167K and PNPLA3 I148M polymorphisms on lipid metabolism[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(43): 74209-74216. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18474. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: