| [1] |
|
| [2] |
LIU K, HUANG A, NIE J, et al. IL-35 regulates the function of immune cells in tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 683332. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.683332. |
| [3] |
XIN PL, JIE LF, CHENG Q, et al. Pathogenesis and function of interleukin-35 in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 655114. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655114. |
| [4] |
LI X, LIU X, WANG W. IL-35: A novel immunomodulator in hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 614847. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.614847. |
| [5] |
HU S, LIAN PP, HU Y, et al. The role of IL-35 in the pathophysiological processes of liver disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 569575. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.569575. |
| [6] |
TAIT WOJNO ED, HUNTER CA, STUMHOFER JS. The immunobiology of the Interleukin-12 family: Room for discovery[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50(4): 851-870. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.011. |
| [7] |
COLLISON LW, WORKMAN CJ, KUO TT, et al. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function[J]. Nature, 2007, 450(7169): 566-569. DOI: 10.1038/nature06306. |
| [8] |
BEHZADI P, BEHZADI E, RANJBAR R. IL-12 family cytokines: General characteristics, pathogenic microorganisms, receptors, and signalling pathways[J]. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung, 2016, 63(1): 1-25. DOI: 10.1556/030.63.2016.1.1. |
| [9] |
DIXON KO, van der KOOIJ SW, VIGNALI DA, et al. Human tolerogenic dendritic cells produce IL-35 in the absence of other IL-12 family members[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2015, 45(6): 1736-1747. DOI: 10.1002/eji.201445217. |
| [10] |
COLLISON LW, DELGOFFE GM, GUY CS, et al. The composition and signaling of the IL-35 receptor are unconventional[J]. Nat Immunol, 2012, 13(3): 290-299. DOI: 10.1038/ni.2227. |
| [11] |
DAMBUZA IM, HE C, CHOI JK, et al. IL-12p35 induces expansion of IL-10 and IL-35-expressing regulatory B cells and ameliorates autoimmune disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 719. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00838-4. |
| [12] |
LIU J, HAO S, CHEN X, et al. Human placental trophoblast cells contribute to maternal-fetal tolerance through expressing IL-35 and mediating iT(R)35 conversion[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 4601. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12484-z. |
| [13] |
WANG W, WEI C, CHENG Z, et al. Aberrant Th2 immune responses are associated with a reduced frequency of IL-35-induced regulatory T cells after allergen exposure in patients with allergic asthma[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2020, 12(6): 1029-1045. DOI: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.6.1029. |
| [14] |
GUO H, ZHAO N, GAO H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin-35 propagate immunosuppressive effects in mice[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2017, 86(5): 389-395. DOI: 10.1111/sji.12613. |
| [15] |
LI Y, PAN X, PENG X, et al. Adenovirus-mediated interleukin-35 gene transfer suppresses allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma[J]. Inflamm Res, 2015, 64(10): 767-774. DOI: 10.1007/s00011-015-0858-1. |
| [16] |
TEYMOURI M, PIRRO M, FALLARINO F, et al. IL-35, a hallmark of immune-regulation in cancer progression, chronic infections and inflammatory diseases[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018, 143(9): 2105-2115. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31382. |
| [17] |
XUE H, LIN F, TAN H, et al. Overrepresentation of IL-10-expressing B cells suppresses cytotoxic CD4 + T cell activity in HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(5): e0154815. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154815. |
| [18] |
DAMO M, JOSHI NS. T(reg) cell IL-10 and IL-35 exhaust CD8(+) T cells in tumors[J]. Nat Immunol, 2019, 20(6): 674-675. DOI: 10.1038/s41590-019-0389-y. |
| [19] |
CHENG ST, YUAN D, LIU Y, et al. Interleukin-35 level is elevated in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2018, 15(2): 188-194. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.21957. |
| [20] |
RIBEIRO C, MARTINELLI KG, de MELLO V, et al. Cytokine, genotype, and viral load profile in the acute and chronic hepatitis B[J]. Viral Immunol, 2020, 33(10): 620-627. DOI: 10.1089/vim.2020.0176. |
| [21] |
ZHOU Y, ZHANG H, LI Y. IL-35 expression in peripheral blood CD4(+) T cells from chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients directly correlates with virus load[J]. Cytokine, 2015, 73(1): 169-175. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.003. |
| [22] |
TAO NN, GONG R, CHEN X, et al. Interleukin-35 stimulates hepatitis B virus transcription and replication by targeting transcription factor HNF4α[J]. J Gen Virol, 2018, 99(5): 645-654. DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001050. |
| [23] |
YANG J, MA C, ZHAO Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus core particles containing a conserved region of the G Protein Combined with Interleukin-35 protected mice against respiratory syncytial virus infection without vaccine-enhanced immunopathology[J]. J Virol, 2020, 94(13): e00007-20. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00007-20. |
| [24] |
LIU Y, LUO Y, ZHU T, et al. Regulatory B cells dysregulated T cell function in an IL-35-dependent way in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 653198. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.653198. |
| [25] |
WAN Z, ZHOU Z, LIU Y, et al. Regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in viral infection[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2020, 91(5): e12873. DOI: 10.1111/sji.12873. |
| [26] |
SHAO X, MA J, JIA S, et al. Interleukin-35 suppresses antiviral immune response in chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 472. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00472. |
| [27] |
YANG L, JIA S, SHAO X, et al. Interleukin-35 modulates the balance between viral specific CD4(+)CD25(+) CD127(dim/-) regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Virol J, 2019, 16(1): 48. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-019-1158-0. |
| [28] |
TENG DK, LIU Y, LV YF, et al. Elevated interleukin-35 suppresses liver inflammation by regulation of T helper 17 cells in acute hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 70: 252-259. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.02.048. |
| [29] |
MCLANE LM, ABDEL-HAKEEM MS, WHERRY EJ. CD8 T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection and cancer[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2019, 37: 457-495. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055318. |
| [30] |
LI X, TIAN L, DONG Y, et al. IL-35 inhibits HBV antigen-specific IFN-γ-producing CTLs in vitro[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2015, 129(5): 395-404. DOI: 10.1042/CS20140511. |
| [31] |
DONG Y, LI X, YU Y, et al. JAK/STAT signaling is involved in IL-35-induced inhibition of hepatitis B virus antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 252: 117663. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117663. |
| [32] |
XIANG XG, XIE Q. IL-35: A potential therapeutic target for controlling hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Dig Dis, 2015, 16(1): 1-6. DOI: 10.1111/1751-2980.12218. |
| [33] |
LUO M, PENG H, CHEN P, et al. The immunomodulatory role of interleukin-35 in fibrotic diseases[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2019, 15(4): 431-439. DOI: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1564041. |
| [34] |
LI T, HUANG Y, LIU P, et al. Lower plasma levels of IL-35 in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 2018, 244(2): 123-131. DOI: 10.1620/tjem.244.123. |
| [35] |
SHI M, WEI J, DONG J, et al. Function of interleukin-17 and -35 in the blood of patients with hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 11(1): 121-126. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2681. |
| [36] |
HU H, FU Y, LI M, et al. Interleukin-35 pretreatment attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced heart injury by inhibition of inflammation, apoptosis and fibrotic reactions[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 86: 106725. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106725. |
| [37] |
TSUDA M, ZHANG W, YANG GX, et al. Deletion of interleukin (IL)-12p35 induces liver fibrosis in dominant-negative TGFβ receptor type Ⅱ mice[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57(2): 806-816. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25829. |
| [38] |
WANG W, GUO H, LI H, et al. Interleukin-35 Gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells protect concanavalin A-induced fulminant hepatitis by decreasing the interferon gamma level[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2018, 29(2): 234-241. DOI: 10.1089/hum.2017.171. |
| [39] |
KODA Y, NAKAMOTO N, CHU PS, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells protect against immune-mediated acute liver injury via IL-35[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129(8): 3201-3213. DOI: 10.1172/JCI125863. |
| [40] |
CHEN L, SUN W, WANG Y, et al. Lower levels of interleukin-35 in patients with prophase of liver failure are associated with progression to liver failure[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10(8): 9174-9183. DOI: 10.21037/apm-21-1680. |
| [41] |
YANG L, ZHANG Q, SONG J, et al. Interleukin-35 suppresses CD8(+) T cell activity in patients with viral hepatitis-induced acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2020, 65(12): 3 614-3623. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06077-w. |
| [42] |
GAO Y, LIANG ZJ, FU J. Influence of interleukin-35 on peripheral CD8 + T cell function in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(9): 2011-2016. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.025. |
| [43] |
KOURKO O, SEAVER K, ODOARDI N, et al. IL-27, IL-30, and IL-35: A cytokine triumvirate in cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 969. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00969. |
| [44] |
LIU K, HUANG A, NIE J, et al. IL-35 regulates the function of immune cells in tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 683332. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.683332. |
| [45] |
XUE W, YAN D, KAN Q. Interleukin-35 as an emerging player in tumor microenvironment[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(9): 2074-2082. DOI: 10.7150/jca.29170. |
| [46] |
LONG J, GUO H, CUI S, et al. IL-35 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells is associated with tumor progression[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(29): 45678-45686. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10141. |
| [47] |
FU YP, YI Y, CAI XY, et al. Overexpression of interleukin-35 associates with hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness and recurrence after curative resection[J]. Br J Cancer, 2016, 114(7): 767-776. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2016.47. |
| [48] |
HE Y, PEI JH, LI XQ, et al. IL-35 promotes EMT through STAT3 activation and induces MET by promoting M2 macrophage polarization in HCC[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Communl, 2021, 559: 35-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.050. |
| [49] |
LIU X, REN H, GUO H, et al. Interleukin-35 has a tumor-promoting role in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2021, 203(2): 219-229. DOI: 10.1111/cei.13535. |
| [50] |
YANG L, SHAO X, JIA S, et al. Interleukin-35 dampens CD8(+) T cells activity in patients with non-viral hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1032. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01032. |
| [51] |
ZHANG Q, YANG L, LIU S, et al. Interleukin-35 suppresses interleukin-9-secreting CD4(+) T cell activity in patients with hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 645835. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645835. |
| [52] |
YAZDANI Z, RAFIEI A, GOLPOUR M, et al. IL-35, a double-edged sword in cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2020, 121(3): 2064-2076. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.29441. |



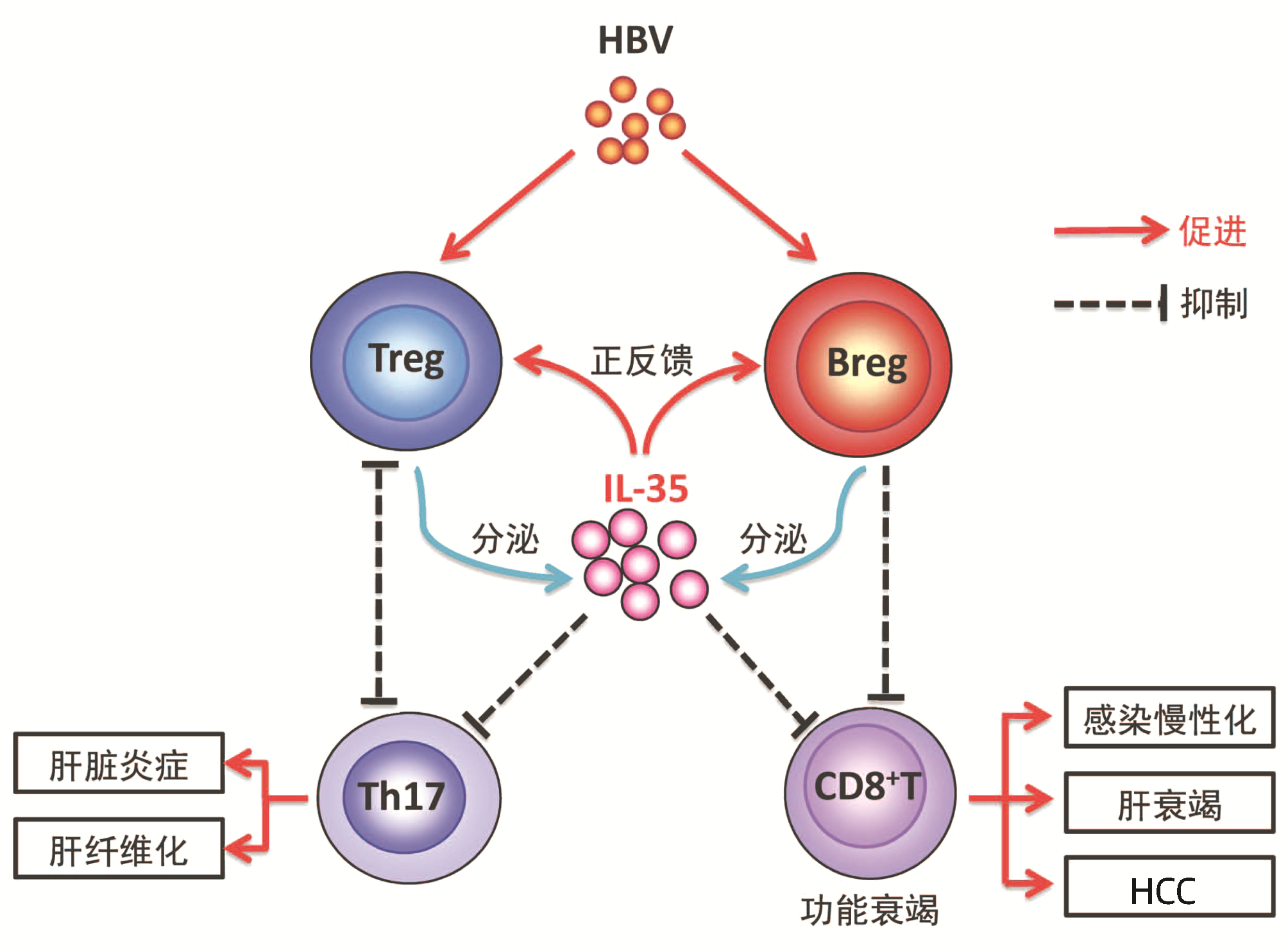




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: