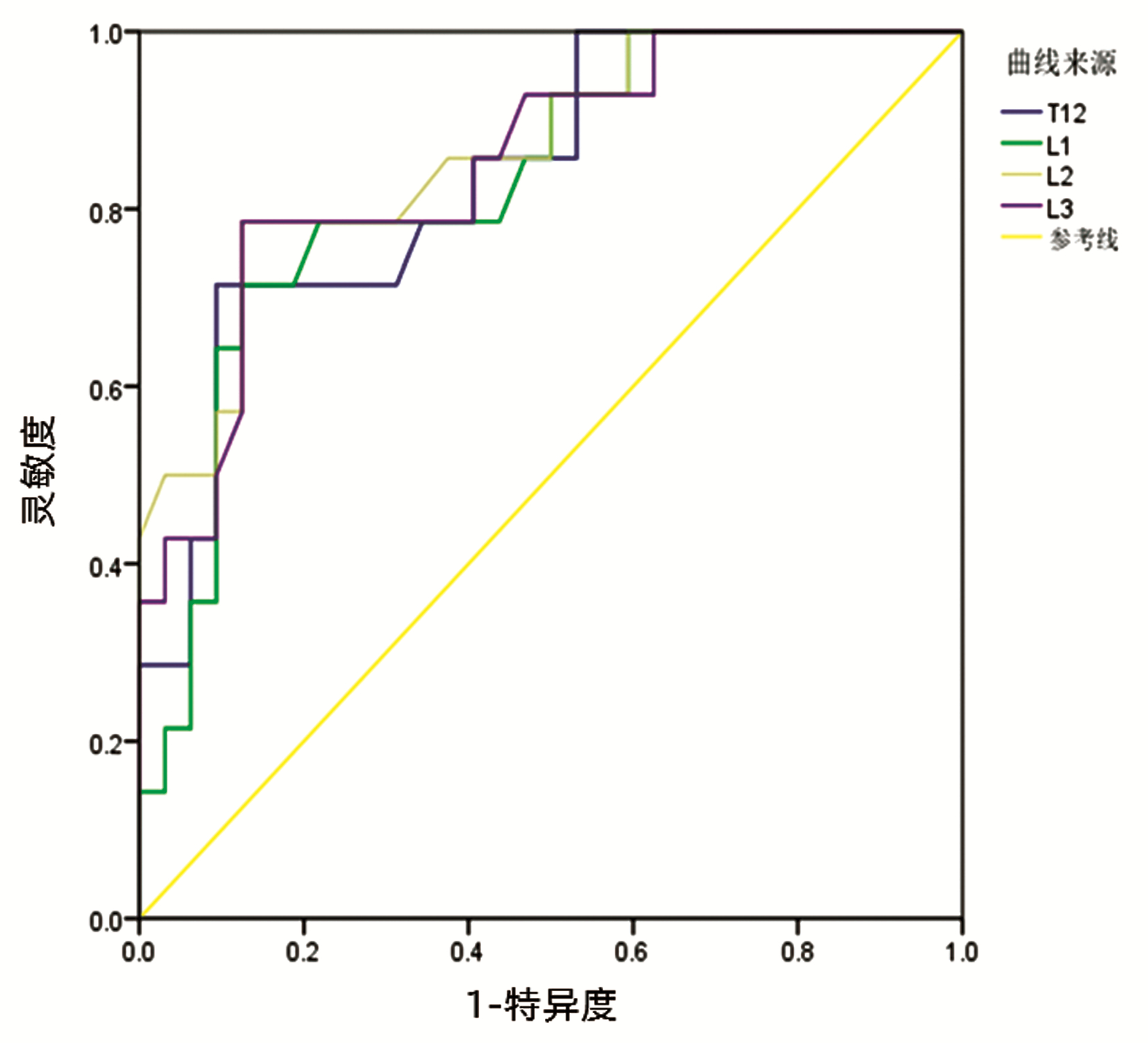
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
LUXON BA. Bone disorders in chronic liver diseases[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2011, 13(1): 40-48. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-010-0166-4. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [5] |
HAYASHI M, ABE K, FUJITA M, et al. Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis in chronic liver disease[J]. Hepatol Res, 2018, 48(11): 893-904. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13192. |
| [6] |
SCHREIBER JJ, ANDERSON PA, ROSAS HG, et al. Hounsfield units for assessing bone mineral density and strength: a tool for osteoporosis management[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2011, 93(11): 1057-1063. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00160. |
| [7] |
NISHIKAWA H, SHIRAKI M, HIRAMATSU A, et al. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria[J]. Hepatol Res, 2016, 46(10): 951-963. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12774. |
| [8] |
WANG YF, SUN MX, XUE H, et al. Understanding the China Blue Paper on Obesity Prevention and Control and policy implications and recommendations for obesity prevention and control in China[J]. Chin J Rrev Med, 2019, 53(9): 875-884. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.09.003. |
| [9] |
BYRNE DD, NEWCOMB CW, CARBONARI DM, et al. Risk of hip fracture associated with untreated and treated chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 61(2): 210-218. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.001. |
| [10] |
REID IR. Targeting sclerostin in postmenopausal osteoporosis: Focus on romosozumab and blosozumab[J]. BioDrugs, 2017, 31(4): 289-297. DOI: 10.1007/s40259-017-0229-2. |
| [11] |
FORESTA C, SCHIPILLITI M, CIARLEGLIO FA, et al. Male hypogonadism in cirrhosis and after liver transplantation[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2008, 31(5): 470-478. DOI: 10.1007/BF03346393. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
SMITH AD. Screening of bone density at CT: An overlooked opportunity[J]. Radiology, 2019, 291(2): 368-369. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2019190434. |
| [15] |
BAO J, ZOU D, LI WS. Research progress on lumbar CT attenuation value in assessing bone mineral density of patients with lumbar degenerative diseases[J]. Chin J Spine and Spinal Core, 2020, 30(8): 745-750. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-406X.2020.08.12. |
| [16] |
LEE S, CHUNG CK, OH SH, et al. Correlation between bone mineral density measured by dual-energy X-Ray absorptiometry and hounsfield units measured by diagnostic CT in lumbar spine[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2013, 54(5): 384-389. DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.5.384. |
| [17] |
HAO RR, WANG H, WANG HY, et al. Analysis of risk factors for senile sarcopenia and its relationship with NAFLD[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2020, 19(15): 1588-1591. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.15.006. |
| [18] |
CHEN LR, YANG ZY. Research progress of intervention therapy for sarcopenia and understanding of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(15): 3389-3392. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.15.063. |
| [19] |
HOU JC, ZHANG YM. Progress of skeletal muscle mass evaluation, diagnosis and treatment of sarcopenia in patients with liver disease[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2020, 26(11): 873-877. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113884-20200304-00112. |
| [20] |
CAREY EJ, LAI JC, SONNENDAY C, et al. A north american expert opinion statement on sarcopenia in liver transplantation[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(5): 1816-1829. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30828. |
| [21] |
GOLSE N, BUCUR PO, CIACIO O, et al. A new definition of sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl, 2017, 23(2): 143-154. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24671. |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
CHEN CH, LIN CL, KAO CH. Association between chronic hepatitis B virus infection and risk of osteoporosis: A nationwide population-based study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015, 94(50): e2276. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002276. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: