| [1] |
DA COSTA AC, SANTA-CRUZ F, SENA BF, et al. Dedifferentiated liposarcoma of the gallbladder: First reported case[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2018, 16(1): 221. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-018-1520-5. |
| [2] |
LIU XW, CHENG Y, GONG JP. Value of percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy in treatment of hepatolithiasis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1640-1643. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.048. |
| [3] |
LU H, YANG H, WU L, et al. A novel prognostic model for diagnosing atypical bile duct hyperplasia in patients with intrahepatic lithiasis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(17): e15364. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015364. |
| [4] |
LI H, ZHENG J, CAI JY, et al. Laparoscopic VS open hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(43): 7791-7806. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7791. |
| [5] |
CHEN CH, LIN CL, KAO CH. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and cholelithiasis: A nationwide population-based cohort study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2018, 15(3): 513. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15030513. |
| [6] |
Biliary Tract Group, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. The 2011 Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatolithiasis[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House(PMPH), 2011.
中华医学会外科学分会胆道外科学组. 2011中国肝胆管结石病诊断治疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011.
|
| [7] |
XIA L, XIA YJ, ZHANG L, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Current status and thoughts[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(10): 2380-2385. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.10.048. |
| [8] |
CHEN ZS, TANG CW, TANG CH, et al. Research advances in the clinical diagnosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2638-2643. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.005. |
| [9] |
WANG ZC. Curative effect of ERCP on senile patients with choledocholithiasis and its effect on serum inflammatory factors[J]. Traum Crit Med, 2019, 7(4): 233-235. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2019.04.12. |
| [10] |
TIAN J, LI JW, CHEN J, et al. Laparoscopic hepatectomy with bile duct exploration for the treatment of hepatolithiasis: An experience of 116 cases[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2013, 45(6): 493-498. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.003. |
| [11] |
WANG P, SUN B, HUANG B, et al. Comparison between percutaneous transhepatic rigid cholangioscopic lithotripsy and conventional percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic surgery for hepatolithiasis treatment[J]. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech, 2016, 26(1): 54-59. DOI: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000222. |
| [12] |
LU GS, WEN HQ, LIU YM. A experimental study on formation of fistula after percutaneous transhepatic cholangiodrainage (PTCD)[J]. China J Endosc, 2004, 10(11): 44-46, 50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1989.2004.11.016. |
| [13] |
HAN ZM, SHENG YH, ZHANG FK. Comparison of clinical effects between two different paths of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy in treating complicated intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct stones[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2016, 24(6): 422-425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4761.2016.06.007. |
| [14] |
JIANG XF, ZHANG DW, LU HW, et al. Clinical effective analysis of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotrip by rigid choledochoscopy for 194 patients with intrahepatic stones[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2017, 37(8): 896-899. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2017.08.16. |
| [15] |
LIU XY, LIU XM, ZHI XT. Comparative effect analysis on hepatolith patients by two different path percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotripsy[J]. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg, 2015, 18(7): 530-532. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2015.07.009. |
| [16] |
TAO HS, WANG P, SUN BW, et al. One-Step multichannel percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotripsy applied in bilateral hepatolithiasis[J]. World J Surg, 2020, 44(5): 1586-1594. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-020-05368-7. |
| [17] |
WU C, YOU W, ZHANG L, et al. Clinical efficacy of percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy with one-step biliary fistulation for the treatment of hepatolithiasis[J]. Clin J Dig Surg, 2020, 19(8): 843-848. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20200603-00416. |



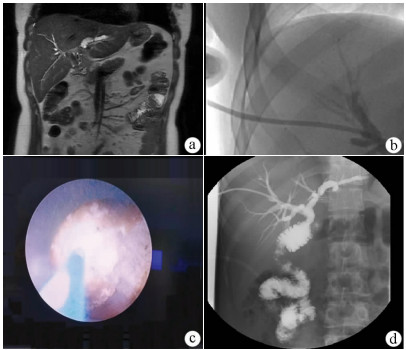




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: