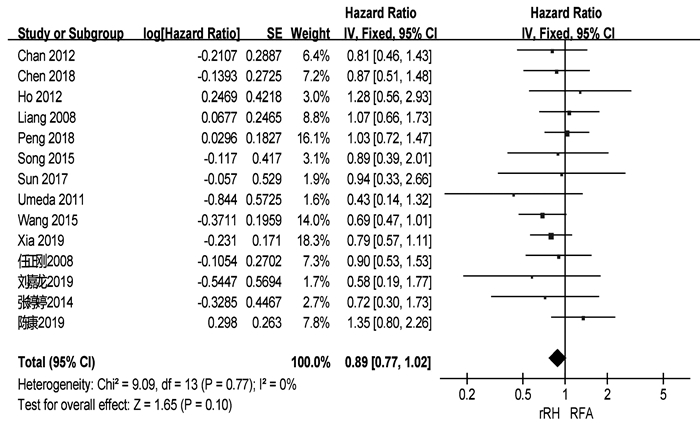
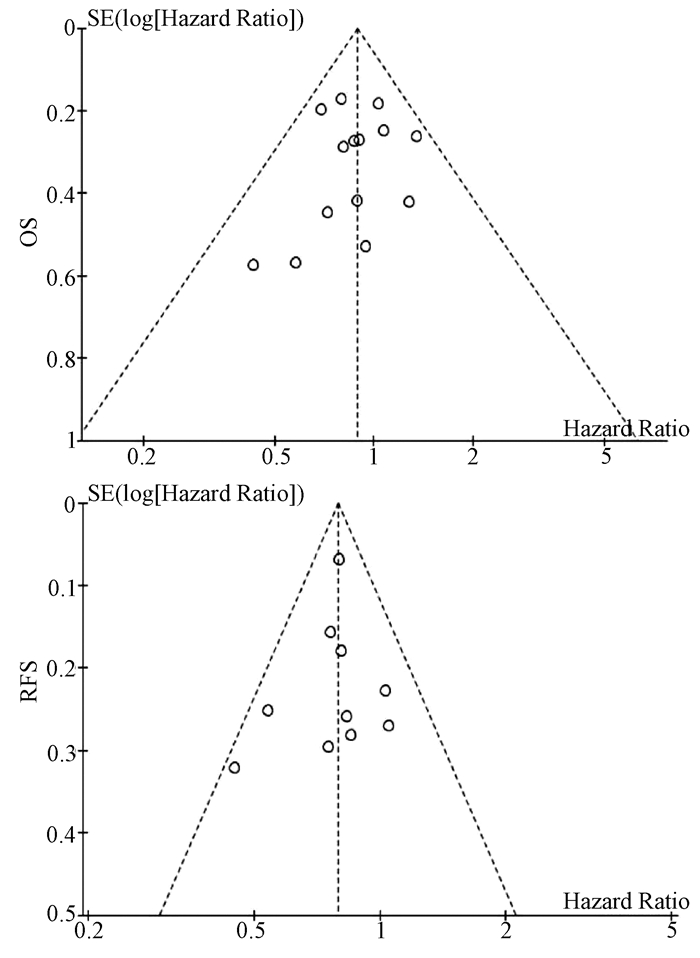
| [1] |
WANG YY, LIU JM, WANG LJ, et al. Prognostic value of tumor burden score in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Oncol Prev Treat, 2019, 11(5): 393-397. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5671.2019.05.06. |
| [2] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(1): 182-236. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019. |
| [3] |
WANG K, LIU G, LI J, et al. Early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy treated with re-hepatectomy, ablation or chemoembolization: A prospective cohort study[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2015, 41(2): 236-242. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2014.11.002. |
| [4] |
SUN WC, CHEN IS, LIANG HL, et al. Comparison of repeated surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for small recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after primary resection[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(61): 104571-104581. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21604. |
| [5] |
UMEDA Y, MATSUDA H, SADAMORI H, et al. A prognostic model and treatment strategy for intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection[J]. World J Surg, 2011, 35(1): 170-177. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-010-0794-8. |
| [6] |
SONG KD, LIM HK, RHIM H, et al. Repeated hepatic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection: A propensity score matching study[J]. Radiology, 2015, 275(2): 599-608. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14141568. |
| [7] |
LIANG HH, CHEN MS, PENG ZW, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus repeat hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2008, 15(12): 3484-3493. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-008-0076-y. |
| [8] |
HO CM, LEE PH, SHAU WY, et al. Survival in patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after primary hepatectomy: Comparative effectiveness of treatment modalities[J]. Surgery, 2012, 151(5): 700-709. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.12.015. |
| [9] |
CHAN AC, POON RT, CHEUNG TT, et al. Survival analysis of re-resection versus radiofrequency ablation for intrahepatic recurrence after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Surg, 2012, 36(1): 151-156. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-011-1323-0. |
| [10] |
CHEN S, PENG Z, XIAO H, et al. Combined radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection versus repeat hepatectomy for elderly patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after initial hepatic surgery[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2018, 34(7): 1029-1037. DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2017.1387941. |
| [11] |
CEN F. Analysis of curative effect of repeated hepatectomy for recurrent HCC[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 2016.
岑峰. 复发性肝癌行再次肝切除术治疗的疗效分析研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016.
|
| [12] |
CHEN K, LIU XY, TENG YX, et al. Rehepatectomyand radiofrequency ablation for patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Practic Surg, 2019, 39(10): 1060-1064. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.10.16. |
| [13] |
HUANG XH, HUANG Y, LIN KC, et al. The curative efficacy comparison of percntaneons radiofrequency ablation versus surgical re-resection for recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Abdominal Surg, 2013, 26(2): 93-95. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5591.2013. 02.008.
黄新辉, 黄尧, 林科灿, 等. 复发性小肝细胞癌射频消融与再手术切除疗效的分析[J]. 腹部外科, 2013, 26(2): 93-95. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5591.2013. 02.008.
|
| [14] |
LIANG HH, PENG ZW, CHEN MS, et al. Effects of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and repeat hepatectomy for the treatment of solitary recurrent hepatocelluar carcinoma with the diameter no more than 3 cm[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2011, 10(1): 36-39. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn. 1673-9752. 2011.01.010.
梁惠宏, 彭振维, 陈敏山, 等. 经皮射频消融与再手术治疗单个直径≤3 cm的复发性肝癌的疗效比较[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2011, 10(1): 36-39. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752. 2011.01.010.
|
| [15] |
REN ZG, GAN YH, FAN J, et al. Treatment of postoperative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma with radiofrequency ablation comparing with repeated surgical resection[J]. Chin J Surg, 2008, 46(21): 1614-1616. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-5815.2008.21.005. |
| [16] |
TIAN ZL. Investigate the efficacy between radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: An retrospective analysis of 57 cases[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Medical University, 2016.
田正灵. 射频消融与手术切除治疗复发性小肝细胞性肝癌的疗效比较分析(附57例病例分析)[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2016.
|
| [17] |
ZHANG H, XU XB, HE XJ, et al. Compare of the efficacy between re-operative and radiofrequency ablation on postoperative recurrent carcinoma[J]. Med J West China, 2013, 25(12): 1816-1818. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2013.12.019. |
| [18] |
ZHANG TT, LI KY, LUO HC, et al. Long-term outcomes of percutaneous microwave ablation versus repeat hepatectomy for treatment of late recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study[J]. Natl Med J China, 2014, 94(33): 2570-2572. DOI: 10.3760/cma. j.issn.0376-2491.2014.33.004.
张婷婷, 李开艳, 罗鸿昌, 等. 经皮微波消融和二次手术治疗晚期复发型小肝癌的长期疗效观察[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2014, 94(33): 2570-2572. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491. 2014.33.004.
|
| [19] |
PENG Z, WEI M, CHEN S, et al. Combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation versus hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after initial surgery: A propensity score matching study[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(8): 3522-3531. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-017-5166-4. |
| [20] |
LU LH, MEI J, KAN A, et al. Treatment optimization for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: Repeat hepatic resection versus radiofrequency ablation[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(9): 2997-3005. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2951. |
| [21] |
XIA Y, LI J, LIU G, et al. Long-term effects of repeat hepatectomy vs percutaneous radiofrequency ablation among patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2020, 6(2): 255-263. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4477. |
| [22] |
LIU JL, HUANG D, CAO L, et al. Laparoscopic hepatectomy versus radiofrequency ablation in treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective randomized control study based on interim follow-up analysis[J]. J Third Milit Med Univ, 2019, 41(5): 467-472. DOI: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.201811005. |
| [23] |
CHAN AC, CHAN SC, CHOK KS, et al. Treatment strategy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: Salvage transplantation, repeated resection, or radiofrequency ablation?[J]. Liver Transpl, 2013, 19(4): 411-419. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23605. |
| [24] |
CHEN R, GAN Y, GE N, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization versus radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after resection within barcelona clinic liver cancer stage 0/A: A retrospective comparative study[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2016, 27(12): 1829-1836. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.06.010. |
| [25] |
HIROKAWA F, HAYASHI M, MIYAMOTO Y, et al. Appropriate treatment strategy for intrahepatic recurrence after curative hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2011, 15(7): 1182-1187. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-011-1484-z. |
| [26] |
WANG N, ZHENG JL, JIANG L. Clinical effect of surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation in treatment of multiple liver cancer in different liver segments meeting the Milan criteria[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(4): 792-797. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.017. |
| [27] |
DUAN C, LIU M, ZHANG Z, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for the treatment of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma meeting Milan criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2013, 11(1): 190. DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-190. |
| [28] |
LIN SM, LIN CJ, LIN CC, et al. Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less[J]. Gut, 2005, 54(8): 1151-1156. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.045203. |
| [29] |
PENG ZW, ZHANG YJ, CHEN MS, et al. Risk factors of survival after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Surg Oncol, 2008, 17(1): 23-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.suronc.2007.08.002. |
| [30] |
LIVRAGHI T, LAZZARONI S, MELONI F. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur J Ultrasound, 2001, 13(2): 159-166. DOI: 10.1016/s0929- 8266(01)00128-8.
|
| [31] |
HUANG J, YAN L, CHENG Z, et al. A randomized trial comparing radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for HCC conforming to the Milan criteria[J]. Ann Surg, 2010, 252(6): 903-912. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181efc656. |
| [32] |
ZHONG JH, KE Y, GONG WF, et al. Hepatic resection associated with good survival for selected patients with intermediate and advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2014, 260(2): 329-340. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000236. |
| [33] |
LEE S, KANG TW, SONG KD, et al. Effect of microvascular invasion risk on early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery and radiofrequency ablation[J]. Ann Surg, 2019, 273(3): 564-571. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003268. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: