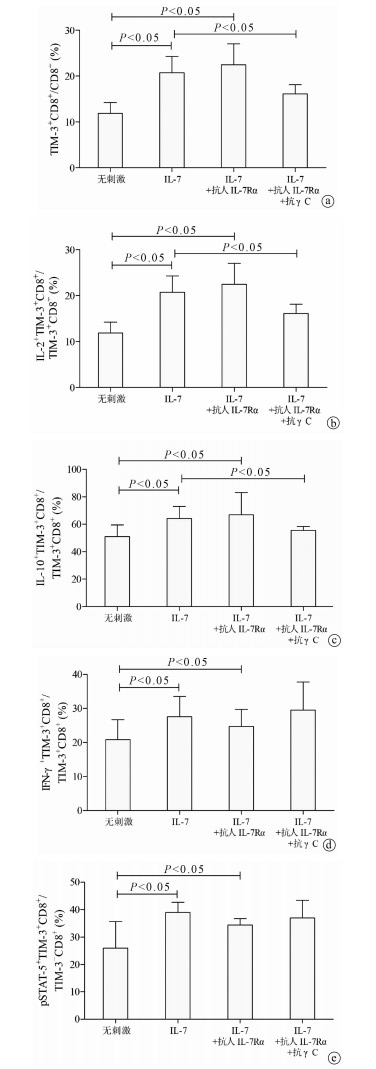
| [1] |
TOE JG, PELLEGRINI M, MAK TW. Promoting immunity during chronic infection—the therapeutic potential of common gamma-chain cytokines[J]. Mol Immunol, 2013, 56(1-2): 38-47. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.04.008. |
| [2] |
TRINITÉ B, CHAN CN, LEE CS, et al. HIV-1 Vpr- and reverse transcription-induced apoptosis in resting peripheral blood CD4 T cells and protection by common gamma-chain cytokines[J]. J Virol, 2016, 90(2): 904-916. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01770-15. |
| [3] |
DAS M, ZHU C, KUCHROO VK. Tim-3 and its role in regulating anti-tumor immunity[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 276(1): 97-111. DOI: 10.1111/imr.12520. |
| [4] |
MUJIB S, JONES RB, LO C, et al. Antigen-independent induction of Tim-3 expression on human T cells by the common γ-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 is associated with proliferation and is dependent on the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway[J]. J Immunol, 2012, 188(8): 3745-3756. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102609. |
| [5] |
DONG J, YANG XF, WANG LX, et al. Modulation of tim-3 expression by antigen-dependent and -independent factors on T cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 98. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00098. |
| [6] |
DONG J, YANG XF, SHEN HJ, et al. Regulatory effect of gamma-chain cytokines on expression of TIM3 on CD8 + T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(2): 205-208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.02.015. |
| [7] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Socirty of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: A 2015 update[J]. J Chin Hepatol, 2015, 31(12): 1941-1960. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.12.002. |
| [8] |
HEIM K, NEUMANN-HAEFELIN C, THIMME R, et al. Heterogeneity of HBV-Specific CD8 + T-Cell failure: Implications for immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2240. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02240. |
| [9] |
ZHANG Y, ZHENG J. Functions of immune checkpoint molecules beyond immune evasion[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1248: 201-226. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5-9. |
| [10] |
WYKES MN, LEWIN SR. Immune checkpoint blockade in infectious diseases[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(2): 91-104. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.112. |
| [11] |
CHO H, KANG H, LEE HH, et al. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) in viral hepatitis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(7). DOI: 10.3390/ijms18071517. |
| [12] |
ZHANG ZN, ZHU ML, CHEN YH, et al. Elevation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression on T cells appears early in HIV infection, and differential Tim-3 and PD-1 expression patterns can be induced by common γ -chain cytokines[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015: 916936. DOI: 10.1155/2015/916936. |
| [13] |
LIN JX, LEONARD WJ. The common cytokine receptor γ chain family of cytokines[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2018, 10(9): a028449. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028449. |
| [14] |
TOE JG, PELLEGRINI M, MAK TW. Promoting immunity during chronic infection—the therapeutic potential of common gamma-chain cytokines[J]. Mol Immunol, 2013, 56(1-2): 38-47. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.04.008. |
| [15] |
SHEN Z, LIU J, WU J, et al. IL-21-based therapies induce clearance of hepatitis B virus persistence in mouse models[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(13): 3798-3811. DOI: 10.7150/thno.35331. |
| [16] |
SHEN Z, WU J, GAO Z, et al. Characterization of IL-21-expressing recombinant hepatitis B virus (HBV) as a therapeutic agent targeting persisting HBV infection[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(12): 5600-5612. DOI: 10.7150/thno.44715. |
| [17] |
ZHANG ZH, JIANG BC, LIU XH, et al. Interleukin-7 regulates T follicular helper cell function in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Viral Immunol, 2018, 31(6): 417-425. DOI: 10.1089/vim.2018.0010. |
| [18] |
HOU H, KANG Y, ZENG Y, et al. Interleukin-7 augments CD8 + T cells function and promotes viral clearance in chronic hepatitis C virus infection[J]. Cytokine, 2018, 102: 26-33. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.12.014. |
| [19] |
TENG D, DING L, CAI B, et al. Interleukin-7 enhances anti-tumor activity of CD8 + T cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cytokine, 2019, 118: 115-123. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.04.003. |
| [20] |
YIN W, XU L, SUN R, et al. Interleukin-15 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication via IFN-β production in a C57BL/6 mouse model[J]. Liver Int, 2012, 32(8): 1306-1314. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02773.x. |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
PENG H, TIAN Z. NK cells in liver homeostasis and viral hepatitis[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2018, 61(12): 1477-1485. DOI: 10.1007/s11427-018-9407-2. |



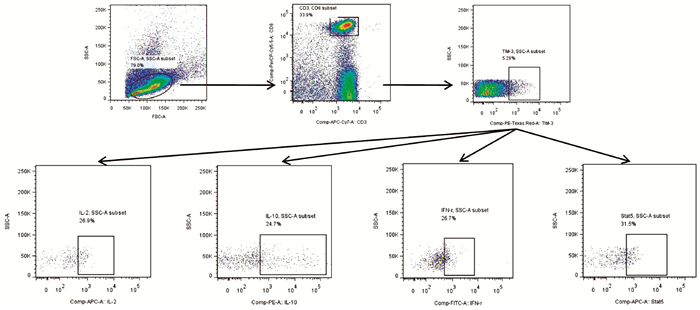




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: