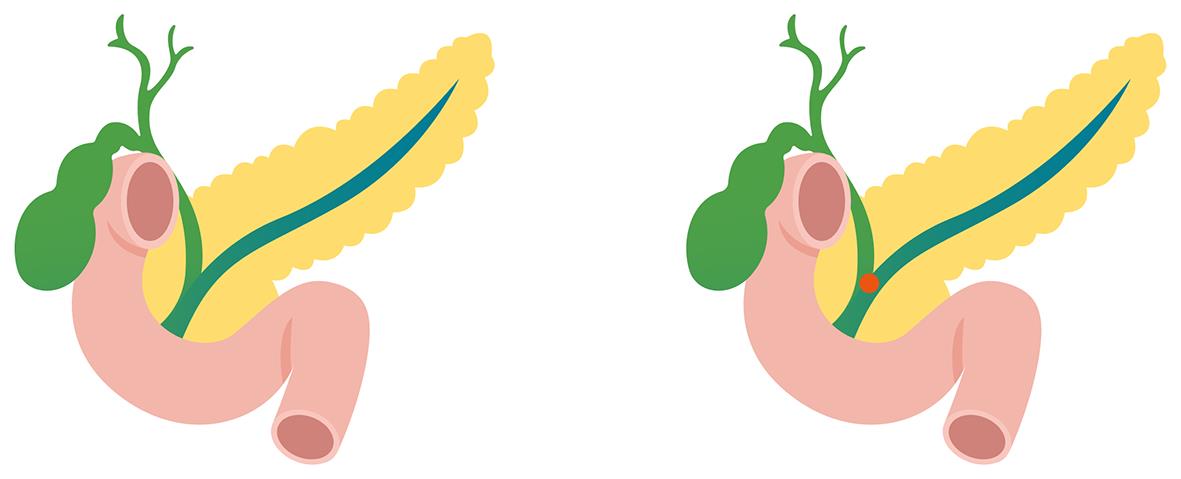
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
GARG PK, SINGH VP. Organ failure due to systemic injury in acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156( 7): 2008- 2023. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.041. |
| [3] |
JOHNSON CD, BESSELINK MG, CARTER R. Acute pancreatitis[J]. BMJ, 2014, 349: g4859. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g4859. |
| [4] |
SU W, GUO F. Triglyceride-controlling during acute phase of hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 1): 89- 93. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221220-00755. |
| [5] |
YANG AL, MCNABB-BALTAR J. Hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20( 5): 795- 800. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.06.005. |
| [6] |
LI Q, HOU CQ, PENG YP, et al. Diabetes and younger age are vital and independent risk factors for acute pancreatitis in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 2620750. DOI: 10.1155/2019/2620750. |
| [7] |
JIN M, BAI XY, CHEN XF, et al. A 16-year trend of etiology in acute pancreatitis: The increasing proportion of hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis and its adverse effect on prognosis[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2019, 13( 6): 947- 953. e 1. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.09.005. |
| [8] |
ZAFRIR B, SALIBA W, JUBRAN A, et al. Severe hypertriglyceridemia-related pancreatitis: Characteristics and predictors of recurrence[J]. Pancreas, 2019, 48( 2): 182- 186. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001235. |
| [9] |
JIN Q, YANG J, MA HL, et al. Value of different scoring systems in predicting the severity and prognosis of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 11): 2551- 2557. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.022. |
| [10] |
GUBENSEK J, BUTUROVIC-PONIKVAR J, ROMOZI K, et al. Factors affecting outcome in acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis treated with plasma exchange: An observational cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9( 7): e102748. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102748. |
| [11] |
VALDIVIELSO P, RAMÍREZ-BUENO A, EWALD N. Current knowledge of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2014, 25( 8): 689- 694. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.08.008. |
| [12] |
KISS L, FŰR G, PISIPATI S, et al. Mechanisms linking hypertriglyceridemia to acute pancreatitis[J]. Acta Physiol, 2023, 237( 3): e13916. DOI: 10.1111/apha.13916. |
| [13] |
WANG B, XU XB, JIN XX, et al. Effects of ω-3 fatty acids on toll-like receptor 4 and nuclear factor κB p56 in the pancreas of rats with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2017, 46( 10): 1267- 1274. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000935. |
| [14] |
SU YR, HONG YP, MEI FC, et al. High-fat diet aggravates the intestinal barrier injury via TLR4-RIP3 pathway in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2019, 2019: 2512687. DOI: 10.1155/2019/2512687. |
| [15] |
SIMHA V. Management of hypertriglyceridemia[J]. BMJ, 2020: m3109. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.m3109. |
| [16] |
HARVEY MH, WEDGWOOD KR, AUSTIN JA, et al. Pancreatic duct pressure, duct permeability and acute pancreatitis[J]. Br J Surg, 1989, 76( 8): 859- 862. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800760832. |
| [17] |
LERCH MM, SALUJA AK, RÜNZI M, et al. Pancreatic duct obstruction triggers acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the opossum[J]. Gastroenterology, 1993, 104( 3): 853- 861. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91022-a. |
| [18] |
ROMAC JM, SHAHID RA, SWAIN SM, et al. Piezo1 is a mechanically activated ion channel and mediates pressure induced pancreatitis[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9( 1): 1715. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04194-9. |
| [19] |
SWAIN SM, ROMAC JM, SHAHID RA, et al. TRPV4 channel opening mediates pressure-induced pancreatitis initiated by Piezo1 activation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130( 5): 2527- 2541. DOI: 10.1172/JCI134111. |
| [20] |
WEN L, JAVED TA, YIMLAMAI D, et al. Transient high pressure in pancreatic ducts promotes inflammation and alters tight junctions via calcineurin signaling in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155( 4): 1250- 1263.e5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.036. |
| [21] |
LERCH MM, AGHDASSI AA, SENDLER M. Cell signaling of pancreatic duct pressure and its role in the onset of pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159( 3): 827- 831. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.027. |
| [22] |
NORDSTOGA K, SØRBY R, OLIVECRONA G, et al. Pancreatitis in hyperlipemic mink( Mustela vison)[J]. Vet Pathol, 2012, 49( 3): 557- 561. DOI: 10.1177/0300985811417248. |
| [23] |
KANEKO K, ANDO H, SEO T, et al. Proteomic analysis of protein plugs: Causative agent of symptoms in patients with choledochal cyst[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2007, 52( 8): 1979- 1986. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-006-9398-4. |
| [24] |
KAMISAWA T, KANEKO K, ITOI T, et al. Pancreaticobiliary maljunction and congenital biliary dilatation[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 2( 8): 610- 618. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30002-X. |
| [25] |
ZHAO CS, YAO WJ, WANG ZZ, et al. Efficacy of pancreatic duct stenting in treatment of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: A report of 33 cases[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2021, 30( 9): 1023- 1030. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2021.09.005. |
| [26] |
WANG J, YANG CX. Discussion on the occurrence, prevention and treatment of biliary pancreatitis via analyzing the anatomy of choledocho-pancreatico-duodenal junction[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2020, 40( 11): 1263- 1265. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.11.09. |
| [27] |
LEE MG, MUALLEM S. Pancreatitis: The neglected duct[J]. Gut, 2008, 57( 8): 1037- 1039. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2008.150961. |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
MALÉTH J, BALÁZS A, PALLAGI P, et al. Alcohol disrupts levels and function of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to promote development of pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148( 2): 427- 439.e16. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.002. |
| [30] |
LARUSCH J, JUNG J, GENERAL IJ, et al. Mechanisms of CFTR functional variants that impair regulated bicarbonate permeation and increase risk for pancreatitis but not for cystic fibrosis[J]. PLoS Genet, 2014, 10( 7): e1004376. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004376. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: