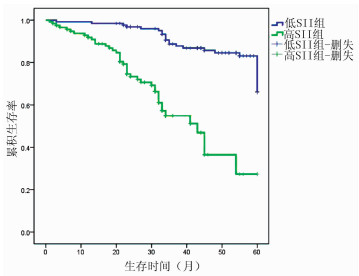
| [1] |
WANG WT, YANG C, YAN LN. New concept and strategy of surgical radical treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Natl Med J China, 2018, 98(38): 3049-3051. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.38.001 |
| [2] |
GERAMIZADEH B, BAGHERNEZHAD M. Hepatic alveolar hydatid cyst: A brief review of published cases from Iran in the last 20 years[J]. Hepat Mon, 2016, 16(10): e38920. DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.38920 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
LIU R, HE J, WANG H, et al. Accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus contrast-enhanced computed tomography in measuring hepatic alveolar echinococcosis lesions: A comparative study[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2019, 47(7): 750-751. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGZ201907037.htm |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
LI YF, SHAO J, WANG ZX, et al. Effects of hydatid cyst fluid on the expression of TGF-β1, IL-6 and TNF-α in rat hepatic stellate cells[J]. Chin J Bases Clin Gen Surg, 2016, 23(12): 1500-1502. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7507/1007-9424.20160378 |
| [7] |
TURGUN TS, SHAN JY, LI T, et al. Effect of Th17 cells and Treg cells on immune evasion in patients with hepatic hydatid disease[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2010, 9(4): 283-286. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2010.04.015 |
| [8] |
LABELLE M, BEGUM S, HYNES RO. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2011, 20(5): 576-590. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.09.009 |
| [9] |
GAO Y, GUO W, CAI S, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(14): 3188-3196. DOI: 10.7150/jca.30281 |
| [10] |
WANG P, YUE W, LI W, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index and ultrasonographic classification of breast imaging-reporting and data system predict outcomes of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 813-819. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S185890 |
| [11] |
HU B, YANG XR, XU Y, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(23): 6212-6222. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442 |
| [12] |
AZIZ MH, SIDERAS K, AZIZ NA, et al. The systemic-immune-inflammation index independently predicts survival and recurrence in resectable pancreatic cancer and its prognostic value depends on bilirubin levels: A retrospective multicenter cohort study[J]. Ann Surg, 2019, 270(1): 139-146. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002660 |
| [13] |
BEAL EW, WEI L, ETHUN CG, et al. Elevated NLR in gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma - making bad cancers even worse: Results from the US extrahepatic biliary malignancy consortium[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2016, 18(11): 950-957. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2016.08.006 |
| [14] |
PINATO DJ, NORTH BV, SHARMA R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2012, 106(8): 1439-1445. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.92 |
| [15] |
LI C, TIAN W, ZHAO F, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index, SII, for prognosis of elderly patients with newly diagnosed tumors[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(82): 35293-35299. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24293 |
| [16] |
YANG R, CHANG Q, MENG X, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(18): 3295-3302. DOI: 10.7150/jca.25691 |
| [17] |
WANG K, DIAO F, YE Z, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with gastric cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2017, 36(1): 75. DOI: 10.1186/s40880-017-0243-2 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
YIN SH. The preliminary study of TGF-β inhibiting the natural killer cells functions in the immune escape of Echinococcus granulosus[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2014. (in Chinese)
印双红. TGF-β抑制自然杀伤细胞在细粒棘球蚴免疫逃逸作用中的初步探讨[D].石河子: 石河子大学, 2014.
|
| [21] |
ZHANG F, PANG N, ZHU Y, et al. CCR7(lo)PD-1(hi) CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells are positively correlated with levels of IL-21 in active and transitional cystic echinococcosis patients[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2015, 15: 457. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-015-1156-9 |



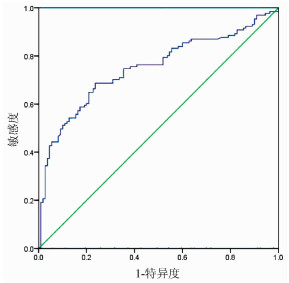




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: