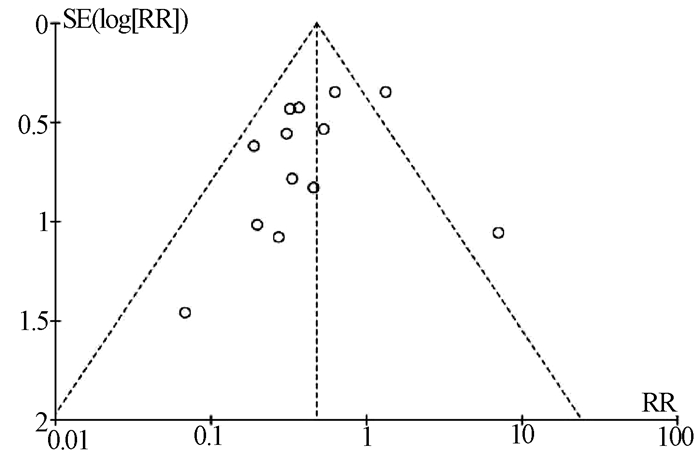
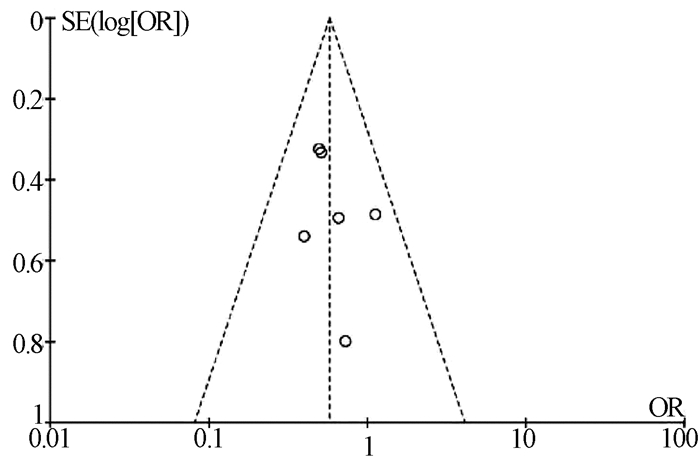
| [1] |
DEVER JB, SHEIKH MY. Review article: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis-bacteriology, diagnosis, treatment, risk factors and prevention[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2015, 41(11): 1116-1131. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13172 |
| [2] |
FERNANDEZ J, NAVASA M, PLANAS R, et al. Primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis delays hepatorenal syndrome and improves survival in cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2007, 133(3): 818-824. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.065 |
| [3] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 53(3): 397-417. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.004 |
| [4] |
TANDON P, DELISLE A, TOPAL JE, et al. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections among patients with cirrhosis at a US liver center[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 10(11): 1291-1298. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.08.017 |
| [5] |
GOEL A, RAHIM U, NGUYEN LH, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Rifaximin for the prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 46(11): 1029-1036.
|
| [6] |
MARCIANO S, DIRCHWOLF M, DIAZ JM, et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis recurrence in patients with cirrhosis receiving secondary prophylaxis with norfloxacin[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31(4): 540-546. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001331 |
| [7] |
OLIVER A, WONG M, SANCHEZ C. Role of rifaximin in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis prevention[J]. South Med J, 2018, 111(11): 660-665. DOI: 10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000887 |
| [8] |
ELFERT A, ABO ALIL, SOLIMAN S, et al. Randomized-controlled trial of rifaximin versus norfloxacin for secondary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 28(12): 1450-1454. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000724 |
| [9] |
ASSEM M, ELSABAAWY M, ABDELRASHED M, et al. Efficacy and safety of alternating norfloxacin and rifaximin as primary prophylaxis for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic ascites: A prospective randomized open-label comparative multicenter study[J]. Hepatol Int, 2016, 10(2): 377-385. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-015-9688-z |
| [10] |
MOSTAFA T, BADRA G, ABDALLAH M. The efficacy and the immunomodulatory effect of rifaximin in prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic Egyptian patients[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2015, 26(2): 163-169. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2015.7782 |
| [11] |
PRAHARAJ D, TANEJA S, DUSEJA A, et al. Randomized control trial of rifaximin and norfloxacin in primary and secondary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) in cirrhotic patients[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2017, 7(S2): s71.
|
| [12] |
SHAMSEYA MM, MADKOUR MA. Rifaximin: A reasonable alternative for norfloxacin in the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with HCV-related liver cirrhosis[J]. Alex J Med, 2015, 52(3): 219-226.
|
| [13] |
KUMAR A, SHAIKH BA, SHAIKH ZA, et al. Effectiveness of rifaximin versus norfloxacin in prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients[J]. Med Forum, 2019, 30(8): 90-94.
|
| [14] |
FLAMM SL, MULLEN KD, HEIMANSON Z, et al. Rifaximin has the potential to prevent complications of cirrhosis[J]. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 2018, 11: 1-10.
|
| [15] |
HANOUNEH MA, HANOUNEH IA, HASHASH JG, et al. The role of rifaximin in the primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2012, 46(8): 709-715. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182506dbb |
| [16] |
LUTZ P, PARCINA M, BEKEREDJIAN-DING I, et al. Impact of rifaximin on the frequency and characteristics of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e93909. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093909 |
| [17] |
VLACHOGIANNAKOS J, VIAZIS N, VASIANOPOULOU P, et al. Long-term administration of rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28(3): 450-455. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12070 |
| [18] |
SHOKOOHI S, ZIVONY A, LE D, et al. Rifaximin is associated with decreased incidence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotics with ascites[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(s1): 858a.
|
| [19] |
DONG T, ARONSOHN A, REDDY KG, et al. Rifaximin decreases the incidence and severity of acute kidney injury and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2016, 61(12): 3621-3626. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-016-4313-0 |
| [20] |
DANULESCU RM, CIOBICA A, STANCIU C, et al. The role of rifaximine in the prevention of the spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi, 2013, 117(2): 315-320.
|
| [21] |
MENSHAHAWY A, MATTAR O, BARSSOUM K, et al. Safety and efficacy of rifaximin in prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2019, 20(4): 380-387. DOI: 10.2174/1389450119666180924145156 |
| [22] |
SIDHU GS, GO A, ATTAR BM, et al. Rifaximin versus norfloxacin for prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A systematic review[J]. BMJ Open Gastroenterol, 2017, 4(1): e000154. DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000154 |
| [23] |
FIORE M, MARAOLO AE, GENTILE I, et al. Current concepts and future strategies in the antimicrobial therapy of emerging Gram-positive spontaneous bacterial peritonitis[J]. World J Hepatol, 2017, 9(30): 1166-1175. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i30.1166 |
| [24] |
SALEHI S, TRANAH TH, LIM S, et al. Rifaximin reduces the incidence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal bleeding and all-cause admissions in patients on the liver transplant waiting list[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(4): 435-441. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15326 |
| [25] |
KAMAL F, KHAN MA, KHAN Z, et al. Rifaximin for the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 29(10): 1109-1117. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000940 |
| [26] |
NAVASA M, FOLLO A, FILELLA X, et al. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: Relationship with the development of renal impairment and mortality[J]. Hepatology, 1998, 27(5): 1227-1232. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510270507 |
| [27] |
BAJAJ JS. Review article: Potential mechanisms of action of rifaximin in the management of hepatic encephalopathy and other complications of cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43(S1): 11-26.
|
| [28] |
KIMER N, KRAG A, MOLLER S, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The effects of rifaximin in hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 40(2): 123-132. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12803 |
| [29] |
LYU XY, LI L. ClinicaI effect of rifaximin in treatment of complications associated with Iiver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(7): 1551-1554.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.07.040 |



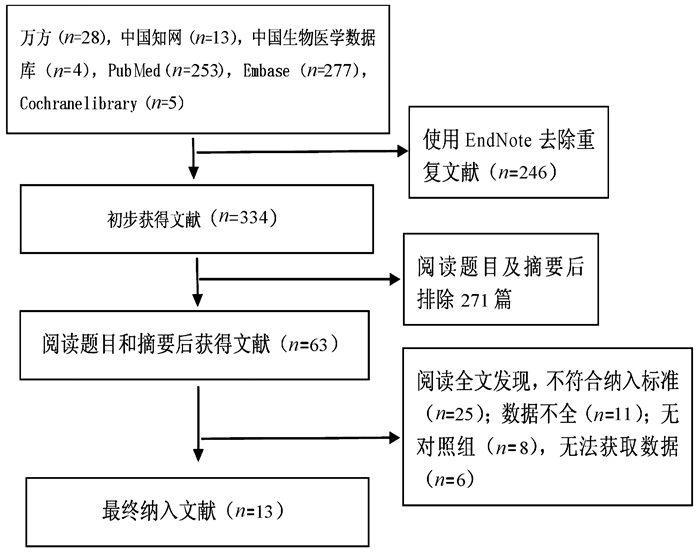




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: