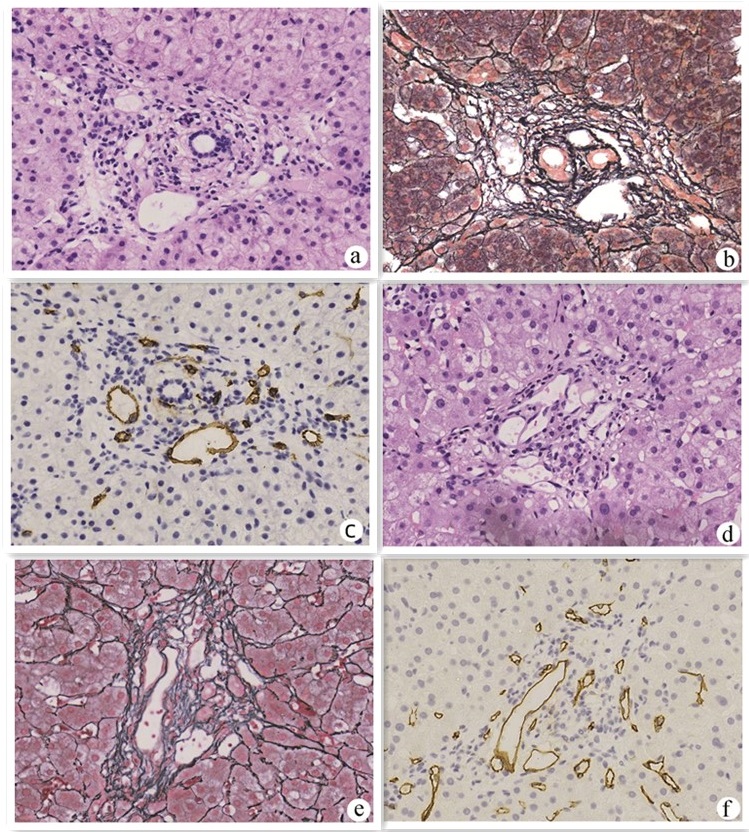
肝门静脉窦性血管病合并非门静脉高压性腹水的临床病理特点及治疗初探
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.029
伦理学声明:本报告已获得患者知情同意。
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:张玉姣、郑英参与了研究数据的获取分析解释过程并起草文章;王秀红、马安林参与修改文章关键内容。
Clinicopathological features and treatment of hepatic porto-sinusoidal vascular disease with non-portal hypertensive ascites: A preliminary study
-
-
Key words:
- Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disease /
- Ascites /
- Hypertension, Portal /
- Therapeutics
-
表 1 患者的腹水特点
Table 1. Characteristics of ascites
病例 SAAG (g/L) 比重 黎氏试验 细胞总数 有核细胞数(mm3) 单核比例(%) 糖(mmol/L) 氯(mmol/L) 乳酸脱氢酶(U/L) 血清白蛋白(g/L) 1 8 1.025 + 1070 70 98 6.59 106 84 33.1 2 7 1.021 ± 1200 150 95 12.35 111 210 30.7 注:SAAG,血清腹水白蛋白梯度。 -
[1] KMEID M, LIU X, BALLENTINE S, et al. Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension and porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: review of current data[J]. Gastroenterology Res, 2021, 14(2): 49-65. DOI: 10.14740/gr1376. [2] de GOTTARDI A, RAUTOU PE, SCHOUTEN J, et al. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: proposal and description of a novel entity[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(5): 399-411. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30047-0. [3] WÖRAN K, SEMMLER G, JACHS M, et al. Clinical course of porto-sinusoidal vascular disease is distinct from idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20(2): e251-e266. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.11.039. [4] HERNÁNDEZ-GEA V, BAIGES A, TURON F, et al. Idiopathic portal hypertension[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(6): 2413-2423. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30132. [5] HERNÁNDEZ-GEA V, CAMPRECIÓS G, BETANCOURT F, et al. Co-expression gene network analysis reveals novel regulatory pathways involved in porto-sinusoidal vascular disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(4): 924-934. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.014. [6] CARNEVALE R, RAPARELLI V, NOCELLA C, et al. Gut-derived endotoxin stimulates factor VⅢ secretion from endothelial cells. Implications for hypercoagulability in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(5): 950-956. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.002. [7] LEONARDI F, MARIA N, VILLA E. Anticoagulation in cirrhosis: a new paradigm?[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2017, 23(1): 13-21. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2016.0110. [8] CERINI F, GONZALEZ JM, TORRES F, et al. Impact of anticoagulation on upper-gastrointestinal bleeding in cirrhosis. A retrospective multicenter study[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62(2): 575-583. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27783. [9] GAO Y, LIU H, TANG F, et al. Efficacy and safety of anticoagulants in liver cirrhosis patients with portal vein thrombosis: A meta-analysis[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2021, 45(2): 101649. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101649. [10] HIDE D, WARREN A, FERNÁNDEZ-IGLESIAS A, et al. Ischemia/reperfusion injury in the aged liver: the importance of the sinusoidal endothelium in developing therapeutic strategies for the elderly[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2020, 75(2): 268-277. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glz012. [11] POSE E, TREBICKA J, MOOKERJEE RP, et al. Statins: Old drugs as new therapy for liver diseases?[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(1): 194-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.07.019. [12] BUNCHORNTAVAKUL C, REDDY KR. Pharmacologic management of portal hypertension[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2019, 23(4): 713-736. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2019.06.004. [13] HAN Y, CHEN J, QIU M, et al. Predicting long-term ischemic events using routine clinical parameters in patients with coronary artery disease: The OPT-CAD risk score[J]. Cardiovasc Ther, 2018, 36(5): e12441. DOI: 10.1111/1755-5922.12441. [14] KUMAR S, GRACE ND, QAMAR AA. Statin use in patients with cirrhosis: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(8): 1958-1965. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-014-3179-2. [15] MUÑOZ AE, POLLARSKY FD, MARINO M, et al. Addition of statins to the standard treatment in patients with cirrhosis: Safety and efficacy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(28): 4639-4652. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4639. [16] GIOIA S, NARDELLI S, RIDOLA L, et al. Causes and management of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension?[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2020, 22(12): 56. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-020-00792-0. -



 PDF下载 ( 3074 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3074 KB)

 下载:
下载:


