肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦对乙型肝炎肝硬化患者门静脉血栓发生的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.015
Effect of Ganshuang granule combined with entecavir on portal vein thrombosis in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis
-
摘要:
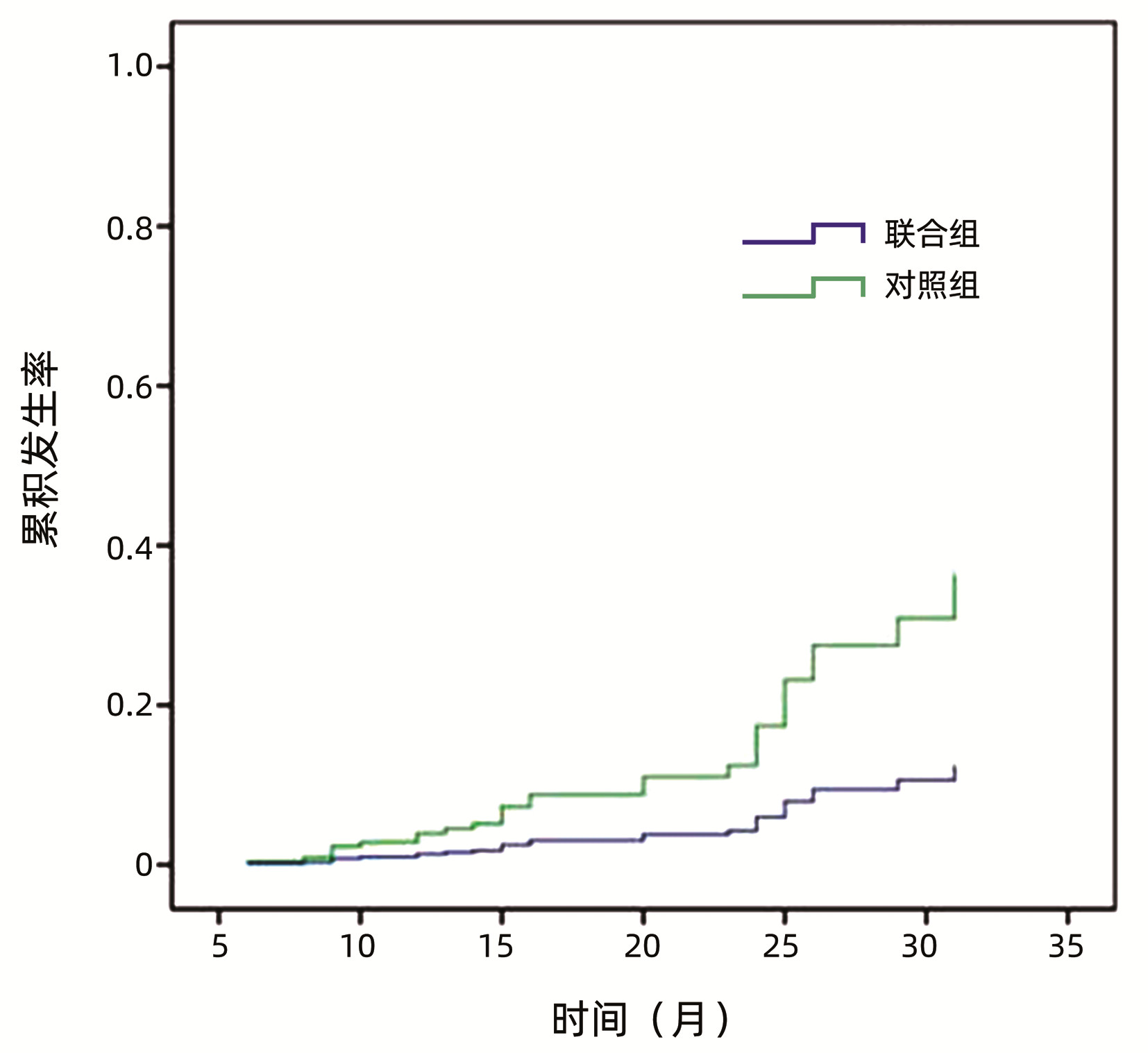
目的 探讨肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦对乙型肝炎肝硬化患者门静脉血栓(PVT)发生的影响。 方法 选取2018年1月1日— 2020年12月31日于昆明市第三人民医院就诊及住院的乙型肝炎肝硬化患者356例。将纳入患者随机分为联合组(n=191)和对照组(n=165),其中联合组应用肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦治疗,对照组单独应用恩替卡韦治疗。疗程至少24周。计量资料两组间比较采用t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验。应用Kaplan-Meier法绘制两组患者PVT的累积发生率,并以log-rank检验进行比较。采用单因素和多因素Cox比例风险回归模型分析乙型肝炎肝硬化患者PVT的影响因素。 结果 联合组191例患者共随访296.25人年,人均随访时间(1.55±0.65)年,PVT发生率为4.19%(8例),发病密度1.41/万人年。对照组165例患者共随访253.25人年,人均随访时间(1.53±0.67)年,PVT发生率为12.12%(20例),发病密度4.79/万人年。两组PVT发生率比较,差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.687,P=0.006)。Kaplan-Meier法绘制两组PVT累积发生率,结果显示联合组PVT的累积发生率明显低于对照组(χ2=7.226,P=0.007),相对危险度为3.155(95%CI:1.351~7.370)。单因素Cox分析结果显示:合并高血压、TBil、ALT、AST、Alb、ChE、eGFR、AFP、D-D、Child-Pugh、肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦治疗是PVT的影响因素(P值均<0.05);多因素Cox分析结果显示:AST(HR=1.002,95%CI:1.000~1.004,P=0.025)、D-D(HR=1.907,95%CI:1.554~2.338,P<0.001)是乙型肝炎肝硬化患者发生PVT的独立危险因素,Alb(HR=0.844,95%CI:0.755~0.944,P=0.003)、肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦治疗(HR=0.350,95%CI:0.144~0.851,P=0.021)是乙型肝炎肝硬化患者发生PVT的独立保护因素。 结论 肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦治疗可显著降低乙型肝炎肝硬化患者PVT的发生率,对PVT的形成有一定的预防作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of Ganshuang granule combined with entecavir on portal vein thrombosis (PVT) in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis. Methods A total of 356 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis who attended and were hospitalized in The Third People's Hospital of Kunming from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2020 were enrolled and randomly divided into combination group with 191 patients and control group with 165 patients. The patients in the combination group received Ganshuang granule combined with entecavir, and those in the control group received entecavir alone. The course of treatment was at least 24 weeks. The t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test or the Fisher's exact test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze the cumulative incidence rate of PVT in both groups, and the log-rank test was used for comparison between two groups. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional-hazards regression model analyses were used to investigate the influencing factors for PVT in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis. Results The 191 patients in the combination group were followed up for 296.25 person-years in total, with a mean follow-up time of 1.55±0.65 years, and there were 8 patients with PVT, with an incidence rate of 4.19% and an incidence density of 1.41 per ten-thousand person-years. The 165 patients in the control group were followed up for 253.25 person-years in total, with a mean follow-up time of 1.53±0.67 years, and there were 20 patients with PVT, with an incidence rate of 12.12% and an incidence density of 4.79 per ten-thousand person-years. There was a significant difference in the incidence rate of PVT between the two groups (χ2=7.687, P=0.006). The cumulative incidence rate of PVT plotted by the Kaplan-Meier method showed that the combination group had a significantly lower cumulative incidence rate of PVT than the control group (χ2=7.226, P=0.007), with a relative risk of 3.155 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.351-7.370). The univariate Cox analysis showed that hypertension, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), albumin (Alb), cholinesterase, estimated glomerular filtration rate, alpha-fetoprotein, D-dimer (D-D), Child-Pugh class, and Ganshuang granule combined with entecavir were influencing factors for PVT (all P < 0.05); the multivariate Cox analysis showed that AST (hazard ratio [HR]=1.002, 95% CI: 1.000-1.004, P=0.025), and D-D (HR=1.907, 95%CI: 1.554-2.338, P < 0.001) were independent risk factors for PVT in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis, while Alb (HR=0.844, 95%CI: 0.755-0.944, P=0.003) and Ganshuang granule combined with entecavir (HR=0.350, 95%CI: 0.144-0.851, P=0.021) were independent protective factors against PVT in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis. Conclusion Ganshuang granule combined with entecavir can significantly reduce the incidence rate of PVT in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis, thereby exerting a certain preventive effect against PVT. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Portal Vein Thrombosis /
- Entecavir /
- Ganshuang Granule
-
表 1 两组患者的基线特征
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the two groups of patients
项目 联合组(n=191) 对照组(n=165) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 133/58 118/47 χ2=0.151 0.698 年龄(岁) 48.29±9.89 49.45±10.48 t=-1.062 0.289 BMI(kg/m2) 24.76±5.74 24.75±4.79 t=0.024 0.981 高血压(例) 22 17 χ2=0.134 0.714 糖尿病(例) 18 18 χ2=0.215 0.643 饮酒(例) 22 18 χ2=0.033 0.856 WBC(×109/L) 2.78(2.06~3.65) 2.64(1.92~3.52) Z=-1.095 0.273 PLT(×109/L) 77(41~119) 81(42~162) Z=-0.549 0.583 TBil(μmol/L) 84.2(41.9~150.7) 90.6(41.9~161.6) Z=-0.984 0.325 ALT(U/L) 127(62~221) 124(53~234) Z=-0.649 0.517 AST(U/L) 178(90~303) 192(100~361) Z=-1.664 0.096 GGT(U/L) 78.0(51.1~114.1) 81.8(56.4~115.7) Z=-0.997 0.319 TBA(μmol/L) 33.3(20.2~51.1) 34.7(19.2~58.8) Z=-0.667 0.505 Alb(g/L) 31.79±4.84 30.94±6.02 t=1.475 0.141 ChE(U/L) 2424(1761~3114) 2393(1720~3083) Z=-0.701 0.483 GLU(mmol/L) 4.59±1.60 4.86±1.69 t=-1.554 0.121 BUN(mmol/L) 5.95(3.89~7.94) 5.99(4.43~8.57) Z=-0.981 0.327 Cr(μmol/L) 81.36±19.22 80.62±16.92 t=0.382 0.703 eGFR(mL/min) 103.56±26.45 100.21±26.70 t=1.189 0.234 AFP(ng/mL) 68.6(50.8~91.4) 71.4(48.8~92.2) Z=-0.203 0.839 PT(s) 24.93±4.39 25.25±4.80 t=-0.650 0.516 INR 1.61±0.44 1.67±0.46 t=-1.353 0.177 D-D(mg/L) 3.44±1.33 3.59±1.29 t=-1.063 0.289 HBV DNA(IU/mL) 5.41±1.61 5.66±1.47 t=-0.658 0.501 Child-Pugh B/C(例) 99/92 78/87 χ2=0.736 0.391 肝硬化并发症(例) χ2=0.340 0.987 自发性细菌性腹膜炎 10 8 腹水 17 12 肝性脑病 2 1 肝肾综合征 6 5 上消化道出血 4 4 LSM(kPa) 30.83±8.78 30.79±8.34 t=0.041 0.967 表 2 单因素和多因素Cox比例风险分析乙型肝炎肝硬化患者PVT的影响因素
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis of the influencing factors of portal vein thrombosis in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis
项目 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR 95%CI P值 HR 95%CI P值 性别 0.634 0.257~1.564 0.323 年龄 0.971 0.938~1.005 0.092 BMI 1.055 0.983~1.133 0.140 高血压 2.775 1.276~6.035 0.010 糖尿病 4.033 0.547~29.724 0.171 高血压 1.142 0.344~3.796 0.828 WBC 1.141 0.852~1.529 0.377 PLT 0.992 0.984~1.001 0.080 TBil 1.006 1.003~1.009 <0.001 ALT 1.003 1.001~1.006 0.012 AST 1.002 1.001~1.004 0.002 1.002 1.000~1.004 0.025 GGT 1.000 0.992~1.009 0.906 TBA 1.007 0.992~1.022 0.361 Alb 0.842 0.770~0.921 <0.001 0.844 0.755~0.944 0.003 ChE 1.000 0.999~1.000 0.027 GLU 1.182 0.961~1.455 0.113 BUN 1.100 0.989~1.223 0.078 Cr 1.019 0.997~1.041 0.096 eGFR 0.986 0.978~0.995 0.001 AFP 1.013 1.000~1.026 0.046 PT 0.997 0.917~1.084 0.952 INR 1.547 0.667~3.590 0.310 D-D 1.908 1.606~2.268 <0.001 1.907 1.554~2.338 <0.001 HBV DNA 1.071 0.840~1.366 0.579 Child-Pugh分级 0.218 0.083~0.574 0.002 LSM 1.039 0.999~1.081 0.058 肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦治疗 0.344 0.151~0.780 0.011 0.350 0.144~0.851 0.021 表 3 两组患者并发症发生情况比较
Table 3. Comparison of complications between the two groups
并发症 联合组(n=191) 对照组(n=165) χ2值 P值 腹水[例(%)] 10(5.24) 19(11.52) 4.514 0.034 自发性细菌性腹膜炎[例(%)] 3(1.57) 10(6.06) 5.072 0.024 上消化道出血[例(%)] 3(1.57) 9(5.45) 4.100 0.043 肝性脑病[例(%)] 2(1.05) 6(3.64) 0.100 肝肾综合征[例(%)] 2(1.05) 8(4.85) 0.030 肝癌[例(%)] 2(1.05) 3(1.82) 0.538 -
[1] BAKI JA, TAPPER EB. Contemporary epidemiology of cirrhosis[J]. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol, 2019, 17(2): 244-253. DOI: 10.1007/s11938-019-00228-3. [2] TAPPER EB, PARIKH ND. Mortality due to cirrhosis and liver cancer in the United States, 1999-2016: observational study[J]. BMJ, 2018, 362: k2817. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.k2817. [3] FU GS, SHEN EH, WANG ML, et al. Effect comparison of Entecavir and Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and liver cirrhosis[J]. China Med Herald, 2021, 18(35): 121-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202135029.htm付广双, 申恩华, 王茉莉, 等. 恩替卡韦、富马酸替诺福韦二吡夫酯片治疗慢性乙型肝炎及其肝硬化的效果比较[J]. 中国医药导报, 2021, 18(35): 121-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202135029.htm [4] LISMAN T, CALDWELL SH, BURROUGHS AK, et al. Hemostasis and thrombosis in patients with liver disease: the ups and downs[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 53(2): 362-371. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.01.042. [5] NG KJ, LEE YK, HUANG MY, et al. Risks of venous thromboembolism in patients with liver cirrhosis: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2015, 13(2): 206-213. DOI: 10.1111/jth.12805. [6] ZOCCO MA, DI STASIO E, de CRISTOFARO R, et al. Thrombotic risk factors in patients with liver cirrhosis: correlation with MELD scoring system and portal vein thrombosis development[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 51(4): 682-689. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.013. [7] ABDEL-RAZIK A, MOUSA N, ELHELALY R, et al. De-novo portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: risk factors and correlation with the Model for End-stage Liver Disease scoring system[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 27(5): 585-592. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000325. [8] STINE JG, WANG J, SHAH PM, et al. Decreased portal vein velocity is predictive of the development of portal vein thrombosis: A matched case-control study[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38(1): 94-101. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13500. [9] TSOCHATZIS EA, BOSCH J, BURROUGHS AK. Liver cirrhosis[J]. Lancet, 2014, 383(9930): 1749-1761. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60121-5. [10] XU X, GUO X, DE STEFANO V, et al. Nonselective beta-blockers and development of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13(4): 468-481. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09951-6. [11] QI X, HAN G, YE C, et al. Splenectomy causes 10-fold increased risk of portal venous system thrombosis in liver cirrhosis patients[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22: 2528-2550. DOI: 10.12659/msm.898866. [12] CARNEVALE R, RAPARELLI V, NOCELLA C, et al. Gut-derived endotoxin stimulates factor VⅢ secretion from endothelial cells. Implications for hypercoagulability in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(5): 950-956. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.002. [13] RAPARELLI V, BASILI S, CARNEVALE R, et al. Low-grade endotoxemia and platelet activation in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(2): 571-581. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28853. [14] HUANG X, FAN X, ZHANG R, et al. Systemic inflammation and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with gastroesophageal varices[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 32(3): 401-405. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001526. [15] PALARETI G, COSMI B, LEGNANI C, et al. D-dimer to guide the duration of anticoagulation in patients with venous thromboembolism: a management study[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(2): 196-203. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-548065. [16] Group of Portal Hypertension, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric varices bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension (2015 edition)[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2016, 31(2): 167-170. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2016.02.032.中华外科学分会门静脉高压症学组. 肝硬化门静脉高压症食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血的诊治共识(2015版)[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2016, 31(2): 167-170. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2016.02.032. [17] TSOCHATZIS EA, SENZOLO M, GERMANI G, et al. Systematic review: portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 31(3): 366-374. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04182.x. [18] CHEN H, TRILOK G, WANG F, et al. A single hospital study on portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients-clinical characteristics & risk factors[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2014, 139(2): 260-266. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=d328645d4470b7dfdf71e73a06cddfb9 [19] STINE JG, SHAH PM, CORNELLA SL, et al. Portal vein thrombosis, mortality and hepatic decompensation in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015, 7(27): 2774-2780. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i27.2774. [20] QI X, SU C, REN W, et al. Association between portal vein thrombosis and risk of bleeding in liver cirrhosis: A systematic review of the literature[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2015, 39(6): 683-691. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.02.012. [21] ZUO HW, SHA QM, SUN J, et al. Risk factors of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(1): 63-67. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.013.左怀文, 沙启梅, 孙姣, 等. 肝硬化食管静脉曲张患者门静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(1): 63-67. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.013. [22] INTAGLIATA NM, ARGO CK, STINE JG, et al. Concepts and controversies in haemostasis and thrombosis associated with liver disease: Proceedings of the 7th International Coagulation in Liver Disease Conference[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2018, 118(8): 1491-1506. DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1666861. [23] de FRANCHIS R; Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 743-752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. [24] XU X, ZHANG C, SHI C, et al. Antiviral therapy effectively improves liver hemodynamics as evidenced by serum biomarker and contrast-enhanced ultrasound examinations in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. PeerJ, 2018, 6: e5484. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.5484. [25] PAYANCÉ A, RAUTOU PE. Cirrhosis regression: extrahepatic angiogenesis and liver hyperarterialization persist[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2018, 132(12): 1341-1343. DOI: 10.1042/CS20180129. [26] HSIEH YH, HUANG HC, CHANG CC, et al. Nucleos(t)ide analogs do not independently influence hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension beyond viral suppression in CBDL-induced cirrhotic rat[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2018, 367(2): 260-266. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.118.250431. [27] HE Y, HU ZF, LI P, et al. Experimental study of saikosaponin-d (SSd) on lipid peroxidation of hepatic fibrosis on rat[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2008, 33(8): 915-919. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.2008.08.013.何燕, 胡志峰, 李平, 等. 柴胡皂苷d抗肝纤维化大鼠脂质过氧化作用的研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2008, 33(8): 915-919. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.2008.08.013. [28] ZHU HL, ZHANG GB, ZHANG C. Effect and mechanism of Bupleuri injection on multiple organ injury in endotoxin-inducing disseminated inravascular coagulation rat[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2012, 32(23): 5196-5199. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2012.23.043.朱海龙, 张根葆, 张翠. 柴胡注射液对内毒素大鼠弥散性血管内凝血多器官损伤的影响及作用机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2012, 32(23): 5196-5199. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2012.23.043. [29] DAS D, BISWAL S, BARHWAL KK, et al. Methanolic root extract of Codonopsis clematidea prevents hypoxia induced procoagulant state by inhibition of GPIb receptor regulated Lyn kinase activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 59: 152903. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152903. [30] LIU M. Study about the brain protective effect and its mechanism of CPPS on cycloheximide induced memory consolidation disorder in mice[D]. Zhangjiakou: Hebei North University, 2020.刘梅. 党参多糖对环已酰亚胺所致记忆巩固障碍小鼠脑保护作用及其机制研究[D]. 张家口: 河北北方学院, 2020. [31] CHENG Y, ZHANG YY, HUANG T, et al. Effect of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide on fatigue in exhausted mice[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(16): 3498-3501. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.16.031.程艺, 张彦昀, 黄婷, 等. 党参多糖对运动力竭小鼠疲劳的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(16): 3498-3501. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.16.031. [32] FU XF, LIU XH. Research progress of pharmacological actions and clinical applications of Danshen[J]. China Pharm, 2006, 15(1): 76-77. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2006.01.060.付辛芳, 刘晓红. 丹参的药理作用与临床应用研究进展[J]. 中国药业, 2006, 15(1): 76-77. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2006.01.060. [33] SUN C, SU S, ZHU Y, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza stem-leaf active components of salvianolic acids and flavonoids improved the hemorheological disorder and vascular endothelial function on microcirculation dysfunction rats[J]. Phytother Res, 2020, 34(7): 1704-1720. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.6652. [34] CAO H, ZHANG L, SUN ZB, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza prevents deep vein thrombosis via antioxidative effects in endothelial cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 11(5): 3593-3600. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3153. [35] ZHOU Q, ZHANG ZH, ZHANG XL, et al. Spectrum-effect correlation-based study on anticoagulant activity enhancement induced by ingredients of wine-processed Salvia miltiorrhiza[J]. Chin Tradit Patent Med, 2021, 43(4): 954-958. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.04.023.周巧, 张智慧, 张学兰, 等. 基于谱效相关法探究酒炙丹参增强抗凝血活性的物质基础[J]. 中成药, 2021, 43(4): 954-958. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.04.023. [36] LIN XR, LIU X, LU CY. Effects of tanshinol and tanshinone ⅡA on diffuse intravascular coagulation in rats[J]. Chin Tradit Patent Med, 2016, 38(12): 2673-2676. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2016.12.030.林小茹, 刘湘, 鲁澄宇. 丹参素和丹参酮ⅡA对大鼠弥漫性血管内凝血的影响[J]. 中成药, 2016, 38(12): 2673-2676. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2016.12.030. [37] WANG Q, JIANG LL, XIAO TS, et al. Study on the active parts of Salvia miltiorrhiza inhibiting coagulation factors Xa and ⅡA[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2013, 24(5): 1153-1154. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2013.05.055.王琼, 蒋骊龙, 肖同书, 等. 丹参抑制凝血因子Ⅹa和Ⅱa的活性部位研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2013, 24(5): 1153-1154. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2013.05.055. [38] SHI H, SHI H, REN F, et al. Naringin in Ganshuang Granule suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells for anti-fibrosis effect by inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2017, 21(3): 500-509. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12994. [39] LU F, GENG JB, ZHANG JW, et al. Effect of entecavir plus Ganshuang granule on fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 41(4): 624-629. DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2021.03.015. [40] LIU YM, SHI HB, LIU YR, et al. Protective effect of Ganshuang Granules on liver cirrhosis by suppressing regulatory T cells in mouse model[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 25(1): 51-58. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-015-2430-9. [41] LIU L, LI JY, LIU CY, et al. Effect of Tenofovir combined with Ganshuang granule on hemodynamics of portal vein system in hepatitis B liver cirrhosis[J]. J Kunming Med Univ, 2021, 42(11): 134-139. DOI: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211125.刘立, 李俊义, 刘春云, 等. 富马酸替诺福韦酯联合肝爽颗粒对乙型肝炎肝硬化门静脉系统血流动力学的影响[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2021, 42(11): 134-139. DOI: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211125. -



 PDF下载 ( 2185 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2185 KB)

 下载:
下载:


